Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C.
FORM 10/AMENDMENT 3
GENERAL FORM FOR REGISTRATION OF SECURITIES
Pursuant to Section 12(b) or (g) of the Securities
Exchange Act of 1934
|
ASIARIM CORP.
AKA UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD.
|
|
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
|
Nevada
|
|
83-0500896
|
|
(State of other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization)
|
|
(IRS Employer
Identification No.)
|
5689 Condor Place
Mississauga ON
L5V 2J4 Canada
Westagate Mall
(Address of Principal
Executive Offices) (Zip Code)
1-905-962-0823
(Registrant’s
telephone number, including area code)
Securities to be
Registered Under Section 12(b) of the Act:
None
Securities to be
Registered Under Section 12(g) of the Act:
Common Stock, Par
Value $0.001
(Title of Class)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant
is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company.
See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and
“emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer
|
☐
|
Accelerated filer
|
☐
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
|
☒
|
Smaller reporting company
|
☒
|
|
|
|
Emerging growth company
|
☐
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by
check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting
standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
ASIARIM CORP.
INDEX TO FORM 10
Cautionary Note Regarding
Forward-Looking Statements
This registration statement
on Form 10 contains “forward-looking statements” concerning our future results, future performance, intentions, objectives,
plans, and expectations, including, without limitation, statements regarding the plans and objectives of management for future operations,
any statements concerning our proposed services, any statements regarding future economic conditions or performance, and any statements
of assumptions underlying any of the foregoing. All forward-looking statements included in this document are made as of the date hereof
and are based on information available to us as of such date. We assume no obligation to update any forward-looking statements. In some
cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of terminology such as “may,” “will,” “expects,”
“plans,” “anticipates,” “intends,” “believes,” “estimates,” “potential,”
or “continue,” or the negative thereof or other comparable terminology. Although we believe that the expectations reflected
in the forward-looking statements contained herein are reasonable, there can be no assurance that such expectations or any of the forward-looking
statements will prove to be correct, and actual results could differ materially from those projected or assumed in the forward-looking
statements. Future financial condition and results of operations, as well as any forward-looking statements are subject to inherent risks
and uncertainties, including those discussed under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Form 10.
Introductory Comment
We are filing this General
Form for Registration of Securities on Form 10 to register our common stock pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act. Once this
registration statement is deemed effective, we will be subject to the requirements of Section 13(a) under the Exchange Act, which will
require us to file annual reports on Form 10-K (or any successor form), quarterly reports on Form 10-Q (or any successor form), and current
reports on Form 8-K, and we will be required to comply with all other obligations of the Exchange Act applicable to issuers filing registration
statements pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act.
Throughout this Form 10,
unless the context otherwise requires, the terms “we,” “us,” “our,” the “Company,” “ARMC"
and “our Company” refer to Asiarim Corp., a Nevada corporation. Asiarim Corp. is a Blank Check Company under Rule 419 of the
Securities Act of 1933.
The term ‘blank
check company” means that we are a development stage company and have no specific business plan or purpose or has indicated that
is business plan is to engage in a merger or acquisition with an unidentified company, or other entity or person. A blank check company:
(i) Is a development stage company
that has no specific business plan or purpose or has indicated that its business plan is to engage in a merger or acquisition with an
unidentified company or companies, or other entity or person; and
(ii) Is issuing “penny stock,”
as defined in Rule 3a51-1 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Our
officers and directors reside outside the United States, investors may have limited legal recourse against them including
difficulties in enforcing judgments made against them by U.S. courts. Our officers and directors reside in Canada. There is a
reciprocal arrangement between Canada and the United States regarding recognition or enforcement of civil judgments. However, the
investor will incur additional costs to pursue a judgment in Canada and the Canadian courts may deny enforcement of the
judgment.
The following disclosures are based on
operations being located in China. As of this time, the Company has not committed to any China operations. Our officers and
directors reside in Canada and may decide that operations will be located in their place of residence.
Our operations, may or may not,
be in China. If we decide to base our operations in China, legal claims, including federal securities law claims, against China-based
Issuers may be difficult or impossible for investors to pursue in U.S. courts. Even if an investor obtains a judgment in a U.S. court,
the investor may be unable to enforce such judgment, particularly in the case of a China-based Issuer, where the related assets or persons
are typically located outside of the United States and in jurisdictions that may not recognize or enforce U.S. judgments. If an investor
is unable to bring a U.S. claim or collect on a U.S. judgment, the investor may have to rely on legal claims and remedies available in
China or other overseas jurisdictions where the China-based Issuer may maintain assets. The claims and remedies available in these jurisdictions
are often significantly different from those available in the United States and difficult to pursue.
Recent statements and regulatory actions by China’s government,
such as those related to the use of variable interest entities and data security or anti-monopoly concerns, may impact the company’s
ability to conduct its business, accept foreign investments, or list on an U.S. or other foreign exchange.
These risks are highlighted below and in Item 1A. Risk Factors.
The Company does not have a variable interest entity at this time and
may, or may not, decide to base their operations in China.
The Company is currently organized under the operating structure of
the public entity, Asiarim Corp., incorporated in the state of Nevada. ARMC may conduct operations in China and may acquire Chinese companies
as subsidiaries to carry out its plan of operation.
The Company is not currently organized under a variable interest entity
(VIE) creating a question of whether China’s Foreign Investment Law (FIL) prevents foreign ownership in our company. We will continue
to monitor the changes in FIL, and the Company may consider migrating to a VIE structure to continue receiving participation from foreign
investors.
The VIE structure consists of at least three core entities: a Chinese
company with legitimate operations (referred to as the VIE); a wholly foreign-owned enterprise established as an intermediary in China;
and an offshore shell company that lists on a U.S. or other foreign exchange.
The VIE structure enables a Chinese company to list on an overseas
stock exchange, such as OTC Markets, because direct ownership in the shares of the Chinese company is restricted by China’s laws.
To expand upon this, a Chinese company sets up an offshore shell company for overseas listing purposes that allows foreign investors to
buy into the stock. The shell company is not the Chinese operating company and does not hold the assets of the operating company.
The Chinese government could rule that the structure is against public
policy and this ruling would likely result in a material change in our contemplated operations. Furthermore, the value of our common stock
may decline or become worthless, and the shareholder could lose their entire investment.
Any failure by our VIEs or their shareholders
to perform their obligations under our contractual arrangements with them would have a material and adverse effect on our business. If
our VIEs or their shareholders fail to perform their respective obligations under the contractual arrangements, we may have to incur substantial
costs and expend additional resources to enforce such arrangements. We may also have to rely on legal remedies under PRC law, including
seeking specific performance or injunctive relief, and contractual remedies, which we cannot assure you will be sufficient or effective
under PRC law.
In addition, if any third parties claim any
interest in such shareholders' equity interests in our VIEs, our ability to exercise shareholders' rights or foreclose the share pledge
according to the contractual arrangements may be impaired. If these or other disputes between the shareholders of our VIEs and third parties
were to impair our control over our VIEs, our ability to consolidate the financial results of our VIEs would be affected, which would
in turn result in a material adverse effect on our business, operations and financial condition.
We may lose the ability to use and enjoy assets
held by our VIEs that are critical to the operation of our business if our VIEs declare bankruptcy or become subject to a dissolution
or liquidation proceeding. Our VIEs will hold certain assets that may be critical to the operation of our business. If the shareholders
of our VIEs breach the contractual arrangements and voluntarily liquidate our VIEs, or if our VIEs declare bankruptcy and all or part
of its assets become subject to liens or rights of third-party creditors or are otherwise disposed of without our consent, we may be unable
to continue some or all of our business activities. This could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results
of operations. In addition, if any of our VIEs undergoes an involuntary liquidation proceeding, third-party creditors may claim rights
to some or all of its assets, thereby hindering our ability to operate our business, which could materially or adversely affect our business,
financial condition and results of operations.
The Chinese government could rule in the future, that the structure
is against public policy and this ruling would likely result in a material change in our contemplated operations. Furthermore, the value
of our common stock may decline or become worthless, and the shareholder could lose their entire investment.
The Chinese government may intervene or influence our operations
at any time, or may exert more control over offerings conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers, which could
result in a material change in our operations and/or the value of our common stock.
We will continue to monitor the changes in
FIL, and ARMC may consider migrating to a VIE structure to continue receiving participation from foreign investors.
If and when, the majority of our contemplated operations are to be
in China, the Chinese government could rule that the structure is against public policy and this ruling would likely result in a material
change in our contemplated operations. Furthermore, the value of our common stock may decline or become worthless, and the shareholder
could lose their entire investment.
China may be subject to considerable
degrees of economic, political and social instability. Investments in securities of Chinese issuers involve risks that are specific to
China, including regulatory, liquidity and enforcement risks.
Regulatory cycles are not uncommon
in China. Policy and regulatory scrutiny should be seen as ongoing risks when it comes to investing in China. The revised Chinese regulations
have not ruled on for our industry. We are not currently engaged in a VIE structure, however that could change moving forward.
We are subject to differing and sometimes
conflicting laws and regulations in the various China jurisdictions where we provide our services. Considerable uncertainties still exist
with respect to the interpretation and implementation of existing laws and regulations governing our contemplated business activities.
As we implement our business plan and expand into new cities or countries or as we add new products and services to our platform, we may
become subject to additional laws and regulations that we are not subject to now. Existing or new laws and regulations could expose us
to substantial liability, including significant expenses necessary to comply with such laws and regulations, and could dampen our growth,
which could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
China’s legal system is substantially different from the legal
system in the United States and may raise risks and uncertainties concerning the intent, effect, and enforcement of its laws, rules, and
regulations, including those that restrict the inflow and outflow of foreign capital or provide the Chinese government with significant
authority to exert influence on a China-based Issuer’s ability to conduct business or raise capital. This lack of certainty may
result in the inconsistent and unpredictable interpretation and enforcement of laws, rules, and regulations, which may change quickly.
China-based Issuers face risks related to evolving laws and regulations, which could impede their ability to obtain or maintain permits
or licenses required to conduct business in China. In the absence of required permits or licenses, governmental authorities may impose
material sanctions or penalties on the company. Such actions could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue
to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
A more detailed discussion on
the risks of investing in Chinese companies can be found in Item A. Risk Factors
If and when, our contemplated operations are to be in China, we
may be governed by the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), Cyber Administration of China (CAC) and The Ministry of Education
of the People’s Republic of China.
CAC oversees data security and recently
revised its laws to include operators that possess personal information for over one million individuals would be subject to cybersecurity
review when listing of foreign exchanges. Personal information is defined in Article76(5) of Cybersecurity Law as various information
which is recorded in electronic or any other form and used alone or in combination with other information to recognize the identity of
a natural person, including but not limited to name, date of birth, ID number, personal biological identification information, address
and telephone number of natural persons.
As we have not implemented our business
plan, ARMC does not meet the criteria to trigger the CAC revised rule. However, we may, upon executing our business model, be subject
to CAC rules and regulations. Our operations could be suspended if the CAC finds we are in violation of data security laws.
The CRSC oversees China's nationwide
centralized securities supervisory system, with the power to regulate and supervise securities issuers, as well as to investigate, and
impose penalties for illegal activities related to securities and futures.
ARMC will be subject to CRSC
rules and regulations. As such, we will be required to submit information about our business to CRSC for approval and will be subject
to continued compliance. At this time, we have not submitted applications for permission to conduct our business, however we will submit
all requested information to CRSC once our business plan has been implemented.
The CRSC oversees China's
nationwide centralized securities supervisory system, with the power to regulate and supervise securities issuers, as well as to investigate,
and impose penalties for illegal activities related to securities and futures.
ARMC will be subject to CRSC
rules and regulations and has not received approval at this time. As such, we will be required to submit information about our business
to CRSC for approval and will be subject to continued compliance. In addition, if we decide to implement a VIE structure, the CRSC could
deny us permission as an issuer to foreign investors if it is ruled that VIE’s are illegal.
The value of our stock could
decline or become worthless. The CRSC and SEC are working together to ensure compliance and protection of foreign investor rules. ARMC
could be delisted as a result of not complying with these rules.
If, in the future, we become
noncompliant with CRSC rules, our business operations could be suspended and our stock could be worthless. In addition, the CRSC
could deny us permission as an issuer to foreign investors if it is ruled that VIE’s are illegal.
The Ministry of Education of
People’s Republic of China (“MEPRC”) is the agency of the State Council that oversee education throughout the country.
ARMC will be subject to MEPRC regulation.
Laws in China regulating the
system of education include the Regulation on Academic Degrees, the Compulsory Education Law, the Teachers Law, the Education Law, the
Law on Vocational Education, and the Law on Higher Education. MEPRC will also continue to review the VIE structure and may rule that this
structure is illegal in the future.
Our curriculum, teachers, and
facilities will be subject to inspection and require approval by MEPRC to operate. If, in the future, we become noncompliant with MEPRC
rules, our business operations could be suspended.
The CRSC, CAC and MEPRC are working
to ensure compliance and protection of foreign investors. ARMC could be delisted as a result of not complying with any one of these regulatory
agencies and could completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such
securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
If and when, our contemplated operations are to be in China, ARMC
may be required to comply with CRSC, CAC and MERPC rules and regulations. Our operations may be required to receive permission from these
entities to conduct business. As of this time, we have not received the requisite permissions from CAC, CSRC and the MEPRC.
ARMC may conduct operations
in China and may acquire Chinese companies as subsidiaries to carry out its plan of operation. Daily operations in PRC include curriculum
training, selling our program, hiring labor forces, and R&D. Cash associated with these activities will circulate in PRC in the form
of local currency. Activities such as raising capital to support PRC operations, hiring employees, paying for working capital, and paying
out dividends will involve cross-border payments. As of this date, we have not made transfers, dividends, or distributions and have not
implemented a cross border payment a cross border payment system.
If we acquire a Chinese business,
we will be subject to cross-border payments must comply with the relevant regulation of the China State Administration of Foreign Exchange
(SAFE).
Companies based in China
have utilized SWIFT and the Clearing House Interbank Payments System, which has widely been used to transfer cash between entities, across
borders, and to for from US investors
At this time, we do not have a plan in place for cross border payments
as we have not acquired a company based in China. If we acquire a Chinese business, we will be
subject to cross-border payments must comply with the relevant regulation of the China State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE).
If we acquire a company based
in China our ability to transfer cash between entities, across borders, and to US investors may be restricted or prohibited if SAFE determines
our business does not meet its criteria.
PRC adopts a partial foreign
exchange administration. As such, foreign currency is forbidden to circulate within the territory. It allows exchange and payment
on current accounts such as trading while implementing certain controls on capital accounts such as investment. We may face obstacles
even if transactions are legal and reasonable after proper registration. So far, ARMC has not yet to establish a VIE nor has determined
the structure.
If we adopt a VIE structure,
ARMC will comply with US laws, PRC laws and regulations. ARMC will also work out financial plans to establish cash flow to parent company,
subsidiaries level and VIE level regarding daily operation and dividends pay out. However, there is no guarantee that cash will be distributed
from businesses, including subsidiaries and/or consolidated VIEs, to the parent company. There is also no guarantee we will have
the ability to settle amounts owed under the VIE agreements. If this occurs our business would be greatly affected and our stock could
decline or become worthless. In addition, the investor could lose all of their investment.
Trading in our securities may be prohibited under the Holding Foreign
Companies Accountable Act if the PCAOB determines that it cannot inspect or fully investigate the auditor of a company that we may target
for a business combination, as a result an exchange may determine to delist our securities.
(a) Business Development
The Company was organized under the laws of the State of Nevada on
June 15, 2007, under its current name. The Company was a development stage company with the goal
of acquire private corporations that are involved in education and management services offering private, distinguished, specialized,
and internationalized education to international students in schools.
Prior to 2012, the Company engaged
in the computer electronics business as it completed the acquisition of Commodore.
Business operations for Asiarim Corp. and its subsidiaries were abandoned
by former management and a custodianship action, as described in the subsequent paragraph, was commenced in 2016. The Company filed its
last 10Q in 2011, this financial report included liabilities and debts. As of the date of this filing, these liabilities and debts have
been addressed and the legal opinion for debt write off is attached as an Exhibit.
On May 5, 2016, the Eighth District
Court of Clark County, Nevada granted the Application for Appointment of Custodian as a result of the absence of a functioning board of
directors and the revocation of the Company’s charter. The order appointed Bryan Glass (“Mr. Glass”, the “Custodian”)
custodian with the right to appoint officers and directors, negotiate and compromise debt, execute contracts, issue stock, and authorize
new classes of stock.
The court awarded custodianship to Mr. Glass based on the absence of
a functioning board of directors, revocation of the company’s charter, and abandonment of the business. At this time, Ms. Glass
was appointed sole officer and director.
The Company was severely delinquent in filing annual reports for the
Company’s charter. The last annual report was filed on September 30, 2010 in on Form 10-K. In addition, the company was subject
to Exchange Act reporting requirements including filing 10Q’s and 10Ks. The Company filed its last 10Q for quarter ending June 30,
2011, and was out of compliance with Exchange Act reporting. Mr. Glass attempted to contact the Company’s officers and directors
through letters, emails, and phone calls, with no success.
Mr. Glass was a shareholder in the Company and applied to the Court
for an Order appointing Brian Glass as the Custodian. This application was for the purpose of reinstating ARMC’s corporate charter
to do business and restoring value to the Company for the benefit of the stockholders.
Mr. Glass performed the following actions in its capacity as custodian:
|
|
•
|
Funded any expenses of the company including paying off outstanding liabilities
|
|
|
•
|
Brought the Company back into compliance with the Nevada Secretary of State, resident agent, transfer agent
|
|
|
•
|
Appointed officers and directors and held a shareholders meeting
|
The Custodian paid the following expenses
on behalf of the company:
Nevada Secretary of State for reinstatement of the Company, $3,925
Transfer agent, Island Stock Transfer, $9,100
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation for the Company, $175.
Upon appointment as the Custodian of ARMC
and under its duties stipulated by the Nevada court, Mr. Glass took initiative to organize the business of the issuer. As Custodian, the
duties were to conduct daily business, hold shareholder meetings, appoint officers and directors, reinstate the company with the Nevada
Secretary of State. Mr. Glass also had authority to enter into contracts and find a suitable merger candidate. Mr. Glass was compensated
for its role as custodian in the amount of 40,000,000 shares of Restricted Common Stock. SCC did not receive any additional compensation,
in the form of cash or stock, for custodian services. The custodianship was discharged on November 9, 2016.
On January 30, 2019, Mr. Glass entered into
a Stock Purchase Agreement with Asia Gateway Capital Ltd.*, whereby Asia Gateway Capital Ltd. purchased 40,000,000 shares of Restricted
Common Stock. These shares represent the controlling block of stock. Mr. Glass resigned his position of sole officer and director and
appointed Ci Zhang as as CEO, Treasurer, Secretary, and Director of the Company. Mr. Glass also appointed ChangJun Xue and Bing Qing
Xie as Directors.
*Asia Gateway Capital Ltd. is controlled
by Jamie Liu.
We are currently a shell company, as defined
in Rule 405 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and Rule 12b-2.
(b) Business of Issuer
Asiarim Corp. is a developmental stage company,
incorporated under the laws of the State of Nevada on June 15, 2007. Our plan of business has not been implemented but will incorporate
the acquisition of private corporations involved in education and management services offering private, distinguished, specialized, and
internationalized education to international students in schools.
The Company changed its name in Nevada, the
state of domicile, to Un Monde International Ltd.
At present financial revenue has not yet been realized. The Company
hopes to raise capital in order to fund the acquisitions.
All statements involving our business plan are forward looking statements
and have not been implemented as of this filing.
The
Company is moving in a new direction, statements made relating to our business plan are forward looking statements and we have no history
of performance. Current management does not have any experience in acquisition of international educational companies but is actively
looking for a suitable person to incorporate into the management team.
We feel that our business plan addresses the
need for additional development in the education industry.
We are in the business of acquiring private
corporations in the business of educating international students, so they have the tools to contribute and thrive in an interdependent
world. Our vision incorporates the spirit of social responsibility, not only on a local community basis but also on a global scale. We
will achieve this through multilingual education and critical thinking so the student may integrate into any cultural situation.
The impact of social distancing requirements
due to Covid-19 has accelerated already robust global growth in online education, a trend many expect to continue even after Covid-19
restrictions are lifted.
As governments in China attempt to reduce
the cost of studying abroad, providing such opportunities in a cost-effective way has become the focus for leading educational institutions.
In a post-Covid world, online education is far and away now the ideal solution.
International education is generally
taken to include
|
|
·
|
Traditional curriculum (math, sciences, languages)
|
|
|
·
|
Knowledge of other world regions & cultures;
|
|
|
·
|
Familiarity with international and global issues;
|
|
|
·
|
Skills in working effectively within global or cross-cultural environments, and using information from different sources around the
world;
|
|
|
·
|
Ability to communicate in multiple languages; and
|
|
|
·
|
Dispositions towards respect and concern for other cultures and peoples.
|
The Company intends to implement its business
plan upon raising capital. Subject to available capital, the Company intends to invest in:
Development
|
|
·
|
Formal and informal education curriculum
|
|
|
o
|
Training, exchange programs, cross-cultural communication
|
Implementation
|
|
·
|
Promoting international understanding/international-mindedness and/or global awareness/understanding
|
|
|
·
|
Being active in global engagement/global or world citizenship
|
|
|
·
|
Increasing intercultural understanding and respect for difference
|
|
|
·
|
Encouraging tolerance and commitment to peace
|
The analysis will be undertaken by or under
the supervision of our management. As of the date of this filing, we have not entered into definitive agreements. In our continued efforts
to analyze potential business plan, we intend to consider the following factors:
|
|
·
|
Potential for growth, indicated by anticipated market expansion or new technology;
|
|
|
·
|
Competitive position as compared to other schools of similar size and experience within the education segment as well as within the
industry as a whole;
|
|
|
·
|
Strength and diversity of management, and the accessibility of required management expertise, personnel, services, professional assistance
and other required items;
|
|
|
·
|
Capital
requirements and anticipated availability of required funds, to be provided by the Company or from operations, through the sale of additional
securities or convertible debt, through joint ventures or similar arrangements or from other sources;
|
|
|
·
|
The extent to which the business opportunity can be advanced in the marketplace; and
|
|
|
·
|
Other relevant factors
|
In applying the foregoing criteria, management
will attempt to analyze all factors and circumstances and make a determination based upon reasonable investigative measures and available
data. Due to our limited capital available for investigation, we may not discover or adequately evaluate adverse facts about the opportunity
to be acquired. Additionally, we will be competing against other entities that may have greater financial, technical, and managerial capabilities
for identifying and completing our business plan.
We are unable to predict when we will, if
ever, identify and implement our business plan. We anticipate that proposed business plan would be made available to us through personal
contacts of our directors, officers and principal stockholders, professional advisors, broker-dealers, venture capitalists, members of
the financial community and others who may present unsolicited proposals. In certain cases, we may agree to pay a finder’s fee or
to otherwise compensate the persons who introduce the Company to business opportunities in which we participate.
As of the time of this filing, the Company
has not implemented its business plan.
We expect that our due diligence will encompass,
among other things, meetings with incumbent management of the target business and inspection of its facilities, as necessary, as well
as a review of financial and other information, which is made available to the Company. This due diligence review will be conducted either
by our management or by third parties we may engage. We anticipate that we may rely on the issuance of our common stock in lieu of cash
payments for services or expenses related to any analysis.
We may incur time and costs required to select
and evaluate our business structure and complete our business plan, which cannot presently be determined with any degree of certainty.
Any costs incurred with respect to the indemnification and evaluation of a prospective international education program that is not ultimately
completed may result in a loss to the Company. These fees may include legal costs, accounting costs, finder’s fees, consultant’s
fees and other related expenses. We have no present arrangements for any of these types of fees.
We anticipate that the investigation of specific
business opportunities and the negotiation, drafting and execution of relevant agreements, disclosure documents and other instruments
will require substantial management time and attention and substantial cost for accountants, attorneys, consultants, and others. Costs
may be incurred in the investigation process, which may not be recoverable. Furthermore, even if an agreement is reached for the participation
in a specific business opportunity, the failure to consummate that transaction may result in a loss to the Company of the related costs
incurred.
Competition
Our
company expects to compete with many countries in the international education industry. In addition, there are several competitors that
are larger and more profitable than ARMC. We expect that the quantity and composition of our competitive environment will continue to
evolve as the industry matures. Additionally, increased competition is possible to the extent that new geographies enter the marketplace
as a result of continued enactment of regulatory and legislative changes. We believe that diligently establishing and expanding our funding
sources will establish us in an already established industry. Additionally, we expect that establishing our product offerings on new platforms
are factors that mitigate the risk associated with operating in a developing competitive environment. Additionally, the contemporaneous
growth of the industry as a whole will result in new students entering the international education marketplace, thereby further mitigating
the impact of competition on our future operations and results.
Compliance with education standards
and guidelines will increase development costs and the cost of operating our business. In turn, we may not be able to meet the competitive
price point for our education curriculum dictated by the market and our competitors.
Again,
these are forward looking statements and not an indication of past performance. There is no guarantee that we will be able to implement
our business plan and have no merger candidates as of the time of this filing.
Effect of Existing or Probable Governmental
Regulations on the Business
Upon effectiveness of this Form 10, we will
be subject to the Exchange Act and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Under the Exchange Act, we will be required to file with the SEC annual
reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act creates a strong and independent
accounting oversight board to oversee the conduct of auditors of public companies and to strengthen auditor independence. It also (1)
requires steps be taken to enhance the direct responsibility of senior members of management for financial reporting and for the quality
of financial disclosures made by public companies; (2) establishes clear statutory rules to limit, and to expose to public view, possible
conflicts of interest affecting securities analysts; (3) creates guidelines for audit committee members’ appointment, and compensation
and oversight of the work of public companies’ auditors; (4) prohibits certain insider trading during pension fund blackout periods;
and (5) establishes a federal crime of securities fraud, among other provisions.
We will also be subject to Section 14(a) of
the Exchange Act, which requires all companies with securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act to comply with
the rules and regulations of the SEC regarding proxy solicitations, as outlined in Regulation 14A. Matters submitted to our stockholders
at a special or annual meeting thereof or pursuant to a written consent will require us to provide our stockholders with the information
outlined in Schedules 14A or 14C of Regulation 14A. Preliminary copies of this information must be submitted to the SEC at least 10 days
prior to the date that definitive copies of this information are provided to our stockholders.
Employees
As of March 31, 2021, we had one officer,
three directors and no employees. We anticipate that we will begin to fill out our management team as and when we raise capital to begin
implementing our business plan. In the interim, we will utilize independent consultants to assist with accounting and administrative matters.
We currently have no employment agreements and believe our consulting relationships are satisfactory. We plan to continue to hire independent
consultants from time to time on an as-needed basis.
Risks Relating to Our Business
Our
business plan involves a number of very significant risks. Our future business, operating results and financial condition could be seriously
harmed as a result of the occurrence of any of the following risks. You could lose all or part of your investment due to any of these
risks. You should invest in our common stock only if you can afford to lose your entire investment.
Our officers and directors reside
outside the United States, investors may have limited legal recourse against them including difficulties in enforcing judgments made
against them by U.S. courts. Our officers and directors reside in Canada. There is a reciprocal arrangement between Canada and the United
States regarding recognition or enforcement of civil judgments. However, the investor will incur additional costs to pursue a judgment
in Canada and the Canadian courts may deny enforcement of the judgment.
The following disclosures are based
on operations being located in China. As of this time, the Company has not committed to China operations. Our officers and directors
reside in Canada and may decide that operations will be located in their place of residence.
ARMC may implement a VIE structure in the future if our operations
are located in China. If the PRC government determines that the contractual arrangements constituting part of our VIE structure does
not comply with PRC regulations, or if these regulations change or are interpreted differently in the future, our shares may decline
in value or be worthless if we are unable to assert our contractual control rights over the assets of our PRC subsidiaries that may conduct
all or substantially all of our operations.
Our Auditor is U.S based and registered with the PCAOB so
Our Company is Subject to PCAOB Inspections
The Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act (“HFCAA”)
became law in December 2020 and prohibits foreign companies from listing their securities on U.S.
exchanges if the company has been unavailable for PCAOB inspection or investigation for three consecutive years.
The HFCAA requires the SEC to identify registrants that have retained
a registered public accounting firm to issue an audit report where that registered public accounting firm has a branch
or office that:
|
|
·
|
Is located in a foreign jurisdiction; and
|
|
|
·
|
The PCAOB has determined that it is unable to inspect or investigate completely because of a position taken by an authority
in the foreign jurisdiction
|
|
|
·
|
As reflected on the PCAOB's website, the PCAOB is currently unable to inspect or investigate accounting firms due to a position
of the local authority in two jurisdictions: China and Hong Kong
|
If our
PCAOB auditor is unable to inspect the issuer's public accounting firm for three consecutive years,
the issuer's securities are banned from trade on a national exchange or through other methods. The United States Senate passed
the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act, which, if enacted, would decrease the number of non-inspection years from
three years to two years. As a result, our securities could be delisted rendering our stock worthless.
Merger & Acquisition Approval
is Required
Under the PRC Anti-monopoly Law, merger & acquisitions that
meet certain turnover thresholds must notify the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) for merger control clearance and may
not be implemented without SAMR’s approval.
ARMC may merge with, or acquire, a target company to commence its
business operations. If our target business meets the threshold for review by SAMR, we will be required to submit an application for
approval.
The SAMR utilizes a substantive test for
merger review. The substantive test takes into consideration the:
|
|
•
|
Market
shares and market control power of the business operators concerned
|
|
|
•
|
Concentration levels of relevant
markets
|
|
|
•
|
Impact
of the concentration on market entry, technological development, consumers and other relevant
operators
|
|
|
•
|
Impact
of the concentration on national economic development
|
|
|
•
|
Foreign investment
|
If the merger or acquisition does not meet the SAMR criteria, our
application will be denied.
Such action could significantly limit or completely hinder our
ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Our business is subject to numerous
legal and regulatory risks that could have an adverse impact on our contemplated business.
We are subject to differing and sometimes
conflicting laws and regulations in the various China jurisdictions where we provide our services. As the carbon neutrality and air purification
is still at a relatively early stage of development, new laws and regulations may be adopted from time to time to address new issues
that come to the authorities' attention. In addition, considerable uncertainties still exist with respect to the interpretation and implementation
of existing laws and regulations governing our contemplated business activities. A large number of proposals are before various national,
regional, and local legislative bodies and regulatory entities regarding issues related to our industry or our business model. As we
implement our business plan and expand into new cities or countries or as we add new products and services to our platform, we may become
subject to additional laws and regulations that we are not subject to now. Existing or new laws and regulations could expose us to substantial
liability, including significant expenses necessary to comply with such laws and regulations, and could dampen our growth, which could
adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Risks Related to Access to Information
and Regulatory Oversight
PRC Securities Law state that no overseas securities regulator
can directly conduct investigations or evidence collection activities within the PRC and no entity or individual in China may provide
documents and information relating to securities business activities to overseas regulators without Chinese government approval. The
SEC, U.S. Department of Justice, and other U.S. authorities face substantial challenges in bringing and enforcing actions against China-based
Issuers and their officers and directors. As a result, investors in China-based Issuers may not benefit from a regulatory environment
that fosters effective enforcement of U.S. federal securities laws.
The Chinese government’s significant oversight and discretion
over the conduct of the business of any China-based company that we may target, could hinder, or influence our operations at any time.
If the Chinese government were to intervene in the target of a potential business combination it could result in a material change in
our operations. If it were determined that the target is not compliant with Chinese law, we would be prevented from moving forward with
our business plan. Such actions could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to
investors and cause the value our securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Risks Related to the Regulatory Environment
China’s legal system is substantially different from the
legal system in the United States and may raise risks and uncertainties concerning the intent, effect, and enforcement of its laws, rules,
and regulations, including those that restrict the inflow and outflow of foreign capital or provide the Chinese government with significant
authority to exert influence on a China-based Issuer’s ability to conduct business or raise capital.
Regarding China based issuers, the Chinese government has made
recent statements indicating the intent to exert more oversight and control over offerings that are conducted overseas and relating to
foreign investment.
This lack of certainty may
result in the inconsistent and unpredictable interpretation and enforcement of laws, rules, and regulations, which may change quickly.
China-based Issuers face risks related to evolving laws and regulations, which could impede their ability to obtain or maintain permits
or licenses required to conduct business in China. In the absence of required permits or licenses, governmental authorities may impose
material sanctions or penalties on the company. Such actions could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or
continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Limitations on Shareholder Rights and
Recourse
Legal claims, including federal securities
law claims, against China-based Issuers may be difficult or impossible for investors to pursue in U.S. courts. Even if an investor obtains
a judgment in a U.S. court, the investor may be unable to enforce such judgment, particularly in the case of a China-based Issuer, where
the related assets or persons are typically located outside of the United States and in jurisdictions that may not recognize or enforce
U.S. judgments. If an investor is unable to bring a U.S. claim or collect on a U.S. judgment, the investor may have to rely on legal
claims and remedies available in China or other overseas jurisdictions where the China-based Issuer may maintain assets. The claims and
remedies available in these jurisdictions are often significantly different from those available in the United States and difficult to
pursue.
We are not currently required to comply with regulations and policies
of the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) because we have not commenced our business in China.
CAC regulates the collection of personal information, which is
recorded electronically, or in any other form, to recognize the identity of a natural person. In light of greater oversight regarding
the collection of personal information we will be subject to cybersecurity review upon execution of our contemplated business plan.
Our potential business combination, international education and
management services, will have operations in China and will be subject to cybersecurity review. We face uncertainties as to whether such
clearance can be timely obtained, or at all, and we may incur additional time delays to complete any anticipated acquisitions.
In light of greater oversight by CAC for companies seeking to list
on a foreign exchange, target business combinations could be impacted. If CAC determines our target business does not meet its requirements,
our ability to implement our business plan will be greatly affected.
If CAC determines that we have violated any portion of PRC laws and
regulation, our ability to obtain or maintain permits or licenses required to conduct business in China may be affected. In the absence
of required permits or licenses, governmental authorities may impose material sanctions or penalties on the company. Such actions could
significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of our
securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
If CAC determines that we have violated any portion of PRC laws
and regulation, our ability to obtain or maintain permits or licenses required to conduct business in China may be affected. In the absence
of required permits or licenses, governmental authorities may impose material sanctions or penalties on the company. Such actions could
significantly limit or completely hinder your ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such
securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Resale limitations of Rule 144(i) on your shares
According to the Rule 144(i), Rule 144 is not available for the resale
of securities initially issued by either a reporting or non-reporting shell company. Moreover, Rule 144(i)(1)(ii) states that Rule 144
is not available to securities initially issued by an issuer that has been “at any time previously” a reporting or non-reporting
shell company. Rule 144(i)(1)(ii) prohibits shareholders from utilizing Rule 144 to sell their shares in a company that at any time in
its existence was a shell company. However, according to Rule 144(i)(2), an issuer can “cure” its shell status.
To “cure” a company’s current or former shell company
status, the conditions of Rule 144(i)(2) must be satisfied regardless of the time that has elapsed since the public company ceased to
be a shell company and regardless of when the shares were issued. The availability of Rule 144 for resales of shares issued while the
company is a shell company or thereafter may be restricted even after the expiration of the one-year period since it filed its Form 10
information if the company is not current on all of its periodic reports required to be filed within the SEC during the 12 months before
the date of the shareholder’s sale. Thus, the company must file all 10-Qs and 10-K for the preceding 12 months and since the filing
of the Form 10, or Rule 144 is not available for the resale of securities.
We have extremely limited assets, have
incurred operating losses, and have no current source of revenue
We have had minimal assets. We do not expect
to generate revenues until we begin to implement our business plan. However, we can provide no assurance that we will produce any material
revenues for our stockholders, or that our business will operate on a profitable basis.
We will, likely, sustain operating expenses
without corresponding revenues, at least until the consummation of our business plan. This may result in our incurring a net operating
loss that will increase unless we consummate a business plan with a profitable business or internally develop our business. We cannot
assure you that we can identify a suitable business combination or successfully internally develop our business, or that any such business
will be profitable at the time of its acquisition by the Company or ever.
Our capital resources may not be sufficient
to meet our capital requirements, and in the absence of additional resources we may have to curtail or cease business operations
We have historically generated negative cash
flow and losses from operations and could experience negative cash flow and losses from operations in the future. Our independent auditors
have included an explanatory paragraph in their report on our financial statements for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020, and
2019 expressing doubt regarding our ability to continue as a going concern. We currently only have a minimal amount of cash available,
which will not be sufficient to fund our anticipated future operating needs. The Company will need to raise substantial sums to implement
its business plan. There can be no assurance that the Company will be successful in raising funds. To the extent that the Company is
unable to raise funds, we will be required to reduce our planned operations or cease any operations.
We may encounter substantial competition
in our business and our failure to compete effectively may adversely affect our ability to generate revenue
International education is an emerging industry.
We believe that existing and new competitors will continue to improve in cost control and performance of their curriculum. We have global
competitors and we will be required to continue to invest in product development and productivity improvements to compete effectively
in our markets. Our competitors could develop a more efficient product or undertake more aggressive and costly marketing campaigns than
ours, which may adversely affect our marketing strategies and could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations
and financial condition.
Our major competitors may be better able than
we to successfully endure downturns in our industrial sector. In periods of reduced demand for our product, we can either choose to maintain
market share by reducing our selling prices to meet competition or maintain selling prices, which would likely sacrifice market share.
Sales and overall profitability would be reduced in either case. In addition, we cannot assure you that additional competitors will not
enter our existing markets, or that we will be able to compete successfully against existing or new competition.
Effect
of Environmental Laws
We
believe we are in compliance with all applicable environmental laws, in all material respects. We do not expect future compliance with
environmental laws to have a material adverse effect on our business.
We may not be able to obtain regulatory
approvals for our product
Our business is subject to laws and regulations governing development
of curriculum, accreditation, and other matters. The Company believes acquisition of already accredited private corporations will mitigate
this risk.
All operating plans have been made in consideration of existing scholastic
regulations. Regulations that most affect operations are related to curriculums of the private corporations we acquire.
We face a number of risks associated
with our business plan, including the possibility that we may incur substantial debt or convertible debt, which could adversely affect
our financial condition
We intend to use reasonable efforts to complete
our business plan. The risks commonly encountered in implementing our business plan is insufficient revenues to offset increased expenses
associated with finding a merger candidate. Failure to raise sufficient capital to carry out our business plan. Additionally, we have
no operations at this time so our expenses are likely to increase and it is possible that we may incur substantial debt or convertible
debt in order to complete our business plan, which can adversely affect our financial condition. Incurring a substantial amount of debt
or convertible debt may require us to use a significant portion of our cash flow to pay principal and interest on the debt, which will
reduce the amount available to fund working capital, capital expenditures, and other general purposes. Our indebtedness may negatively
impact our ability to operate our business and limit our ability to borrow additional funds by increasing our borrowing costs, and impact
the terms, conditions, and restrictions contained in possible future debt agreements, including the addition of more restrictive covenants;
impact our flexibility in planning for and reacting to changes in our business as covenants and restrictions contained in possible future
debt arrangements may require that we meet certain financial tests and place restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness
and place us at a disadvantage compared to similar companies in our industry that have less debt.
Our future success is highly dependent
on the ability of management to locate and attract suitable business opportunities and our stockholders will not know what business we
will enter into until we consummate a transaction with the approval of our then existing directors and officers
At this time, we have no operations and future
implementation of our business plan is highly speculative, there is a consequent risk of loss of an investment in the Company. The success
of our plan of operations will depend to a great extent on the operations, financial condition and management of future business and internal
development. While management intends to seek businesses opportunities with entities having established operating histories, we cannot
provide any assurance that we will be successful in locating opportunities meeting that criterion. In the event we complete a business
plan, the success of our operations will be dependent upon management, its financial position and numerous other factors beyond our control.
There can be no assurance that we will
successfully consummate a business plan or internally develop a successful business
We are a blank check company and can give
no assurance that we will successfully identify and evaluate suitable business opportunities or that we will successfully implement our
business plan. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to negotiate contracts on favorable terms. No assurances can be given that we
will successfully identify and evaluate suitable business opportunities, that we will conclude a business plan or that we will be able
to develop a successful business. Our management and affiliates will play an integral role in establishing the terms for any future business.
We will incur increased costs as a result
of becoming a reporting company, and given our limited capital resources, such additional costs may have an adverse impact on our profitability.
Following the effectiveness of this Form 10,
we will be an SEC reporting company. The Company currently has no business and no revenue. However, the rules and regulations under the
Exchange Act require a public company to provide periodic reports with interactive data files which will require the Company to engage
legal, accounting and auditing services, and XBRL and EDGAR service providers. The engagement of such services can be costly, and the
Company is likely to incur losses, which may adversely affect the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. In addition,
the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as well as a variety of related rules implemented by the SEC, have required changes in corporate governance
practices and generally increased the disclosure requirements of public companies. For example, as a result of becoming a reporting company,
we will be required to file periodic and current reports and other information with the SEC and we must adopt policies regarding disclosure
controls and procedures and regularly evaluate those controls and process.
The additional costs we will incur in connection
with becoming a reporting company will serve to further stretch our limited capital resources. The expenses incurred for filing periodic
reports and implementing disclosure controls and procedures may be as high as $70,000 USD annually. In other words, due to our limited
resources, we may have to allocate resources away from other productive uses in order to pay any expenses we incur in order to comply
with our obligations as an SEC reporting company. Further, there is no guarantee that we will have sufficient resources to meet our reporting
and filing obligations with the SEC as they come due.
The time and cost of preparing a private
company to become a public reporting company may preclude us from entering into an acquisition or merger with the most attractive private
companies and others
From time to time the Company may come across
target merger companies. These companies may fail to comply with SEC reporting requirements may delay or preclude acquisitions. Sections
13 and 15(d) of the Exchange Act require reporting companies to provide certain information about significant acquisitions, including
certified financial statements for the company acquired, covering one or two years, depending on the relative size of the acquisition.
The time and additional costs that may be incurred by some target entities to prepare these statements may significantly delay or essentially
preclude consummation of an acquisition. Otherwise, suitable acquisition prospects that do not have or are unable to obtain the required
audited statements may be inappropriate for acquisition so long as the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act are applicable.
A Business may result in a change of
control and a change of management.
In conjunction with completion of a business
acquisition, it is anticipated that we may issue an amount of our authorized but unissued common or preferred stock which represents the
majority of the voting power and equity of our capital stock, which would result in stockholders of a target company obtaining a controlling
interest in us. As a condition of the business combination agreement, our current stockholders may agree to sell or transfer all or a
portion of our common stock as to provide the target company with all or majority control. The resulting change in control may result
in removal of our present officers and directors and a corresponding reduction in or elimination of their participation in any future
affairs.
We depend on our officers and the loss of their services would
have an adverse effect on our business
We have officers and directors of the Company that are critical to
our chances for business success. We are dependent on their services to operate our business and the loss of these persons, or any of
them would have an adverse impact on our future operations until such time as he or she could be replaced, if he could be replaced. We
do not have employment contracts or employment agreements with our officers, and we do not carry key man life insurance on their lives.
Because we are significantly smaller than the some of our competitors,
we may lack the resources needed to capture market share
The international education industry is highly competitive, and our
business plan has not been implemented and we are smaller in size than some of our competitors. We are at a disadvantage as a blank check
company, we do not have an established business. Many of our competitors have an already established their business, more established
market presence, and substantially greater financial, marketing, and other resources than do we. New competitors may emerge and may develop
new or innovative products that compete with our anticipated future production. No assurance can be given that we will be able to compete
successfully within the international education industry.
Our ability to use our net operating loss carry-forwards and
certain other tax attributes may be limited
We have incurred losses during our history. To the extent that we
continue to generate taxable losses, unused losses will carry forward to offset future taxable income, if any, until such unused losses
expire. Under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change,”
generally defined as a greater than 50% change (by value) in its equity ownership over a three-year period, the corporation’s ability
to use its pre-change net operating loss carry-forwards, or NOLs, and other pre-change tax attributes (such as research tax credits)
to offset its post-change income may be limited. We may experience ownership changes in the future because of subsequent shifts in our
stock ownership. As a result, if we earn net taxable income, our ability to use our pre-change net operating loss carryforwards to offset
U.S. federal taxable income may be subject to limitations, which could potentially result in increased future tax liability to us. In
addition, at the state level, there may be periods during which the use of NOLs is suspended or otherwise limited, which could accelerate
or permanently increase state taxes owed.
Our ability to hire and retain key personnel
will be an important factor in the success of our business and a failure to hire and retain key personnel may result in our inability
to manage and implement our business plan
Our management has limited experience in the
educational industry and we may not be able to attract and retain the necessary qualified personnel. If we are unable to retain or to
hire qualified personnel as required, we may not be able to adequately manage and implement our business plan.
Legal disputes could have an impact on our Company
We plan to engage in business matters that are common to the business
world that can result in disputations of a legal nature. In the event the Company is ever sued or finds it necessary to bring suit
against others, there is the potential that the results of any such litigation could have an adverse impact on the Company.
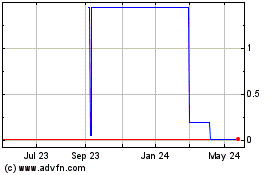
Our common stock is quoted on the OTC MARKETS. An investment
in our common stock is risky and there can be no assurance that the price for our stock will not decrease substantially in the future
Our common stock is quoted on the OTC Markets. The market for our stock
has been volatile and has been characterized by large swings in the trading price that do not appear to be directly related to our business
or financial condition. As a result, an investment in our common stock is risky and there can be no assurance that the price for our stock
will not decrease substantially in the future.
Our stock trades below $5.00 per share and is subject to special
sales practice requirements that could have an adverse impact on any trading market that may develop for our stock
If our stock trades below $5.00 per share and is subject to special
sales practice requirements applicable to "penny stocks" which are imposed on broker-dealers who sell low-priced securities
of this type. These rules may be anticipated to affect the ability of broker-dealers to sell our stock, which may in turn be anticipated
to have an adverse impact on the market price for our stock if and when an active trading market should develop.
Our officers, directors and principal stockholders own a large
percentage of our issued and outstanding shares and other stockholders have little or no ability to elect directors or influence corporate
matters
As of July 6, 2021, our officers, directors, and principal stockholders
were deemed to be the beneficial owners of approximately of our 52.6% issued and outstanding shares of common stock. As a result, such
persons can determine the outcome of any actions taken by us that require stockholder approval. For example, they will be able to elect
all of our directors and control the policies and practices of the Company.
Risks Related to Our Shareholders and Shares
of Common Stock
There is presently no public market
for our securities
Our common stock is not currently trading
on any market, and a robust and active trading market may never develop. Because of our current status as a “shell company,”
Rule 144 is not currently available. Future sales of our common stock by existing stockholders pursuant to an effective registration
statement or upon the availability of Rule 144 could adversely affect the market price of our common stock. A shareholder who decides
to sell some, or all, of their shares in a private transaction may be unable to locate persons who are willing to purchase the shares,
given the restrictions. Also, because of the various risk factors described above, the price of the publicly traded common stock may
be highly volatile and not provide the true market price of our common stock.
Our stock is not traded, so you may
be unable to sell your shares at or near the quoted bid prices if you need to sell a significant number of your shares
Even if our stock becomes trading, it is likely
that our common stock will be thinly traded, meaning that the number of persons interested in purchasing our common shares at or near
bid prices at any given time may be relatively small or non-existent. This situation is attributable to a number of factors, including
the fact that we are a small company which is relatively unknown to stock analysts, stock brokers, institutional investors and others
in the investment community that generate or influence sales volume, and that even if we came to the attention of such persons, they tend
to be risk-averse and would be reluctant to follow an unproven company such as ours or purchase or recommend the purchase of our shares
until such time as we became more seasoned and viable. Consequently, there may be periods of several days or more when trading activity
in our shares is minimal or non-existent, as compared to a seasoned issuer which has a large and steady volume of trading activity that
will generally support continuous sales without an adverse effect on share price. We cannot give you any assurance that a broader or more
active public trading market for our common shares will develop or be sustained, or that current trading levels will be sustained. Due
to these conditions, we can give you no assurance that you will be able to sell your shares at or near bid prices or at all if you need
money or otherwise desire to liquidate your shares.
Our common stock is be considered a
“penny stock,” and thereby be subject to additional sale and trading regulations that may make it more difficult to sell
A common stock is a “penny stock”
if it meets one or more of the following conditions (i) the stock trades at a price less than $5.00 per share; (ii) it is not traded on
a “recognized” national exchange; (iii) it is not quoted on the Nasdaq Capital Market, or even if so, has a price less than
$5.00 per share; or (iv) is issued by a company that has been in business less than three years with net tangible assets less than $5
million.
The principal result or effect of being designated
a “penny stock” is that securities broker-dealers participating in sales of our common stock will be subject to the “penny
stock” regulations set forth in Rules 15g-2 through 15g-9 promulgated under the Exchange Act. For example, Rule 15g-2 requires broker-dealers
dealing in penny stocks to provide potential investors with a document disclosing the risks of penny stocks and to obtain a manually signed
and dated written receipt of the document at least two business days before effecting any transaction in a penny stock for the investor’s
account. Moreover, Rule 15g-9 requires broker-dealers in penny stocks to approve the account of any investor for transactions in such
stocks before selling any penny stock to that investor. This procedure requires the broker-dealer to (i) obtain from the investor information
concerning his or her financial situation, investment experience and investment objectives; (ii) reasonably determine, based on that information,
that transactions in penny stocks are suitable for the investor and that the investor has sufficient knowledge and experience as to be
reasonably capable of evaluating the risks of penny stock transactions; (iii) provide the investor with a written statement setting forth
the basis on which the broker-dealer made the determination in (ii) above; and (iv) receive a signed and dated copy of such statement
from the investor, confirming that it accurately reflects the investor’s financial situation, investment experience and investment
objectives. Compliance with these requirements may make it more difficult and time consuming for holders of our common stock to resell
their shares to third parties or to otherwise dispose of them in the market or otherwise.
We may issue more shares in an acquisition
or merger, which will result in substantial dilution
Our Articles of Incorporation, as amended, authorize the Company to
issue an aggregate of 90,000,000 shares of common stock of which 77,698,333 shares are currently
outstanding and 10,000,000 shares of Preferred Stock are authorized, of which 0 shares are outstanding. Any acquisition or merger effected
by the Company may result in the issuance of additional securities without stockholder approval and may result in substantial dilution
in the percentage of our common stock held by our then existing stockholders. Moreover, shares of our common stock issued in any such
merger or acquisition transaction may be valued on an arbitrary or non-arm’s-length basis by our management, resulting in an additional
reduction in the percentage of common stock held by our then existing stockholders. In an acquisition type transaction, our Board of
Directors has the power to issue any, or all, of such authorized but unissued shares without stockholder approval. To the extent that
additional shares of common stock are issued in connection with a business combination or otherwise, dilution to the interests of our
stockholders will occur and the rights of the holders of common stock might be materially adversely affected.
Obtaining additional capital though
the sale of common stock will result in dilution of stockholder interests
We may raise additional funds in the future
by issuing additional shares of common stock or other securities, which may include securities such as convertible debentures, warrants
or preferred stock that are convertible into common stock. Any such sale of common stock or other securities will lead to further dilution
of the equity ownership of existing holders of our common stock. Additionally, the existing conversion rights may hinder future equity
offerings, and the exercise of those conversion rights may have an adverse effect on the value of our stock. If any such conversion rights
are exercised at a price below the then current market price of our shares, then the market price of our stock could decrease upon the
sale of such additional securities. Further, if any such conversion rights are exercised at a price below the price at which any stockholder
purchased shares, then that particular stockholder will experience dilution in his or her investment.
Our directors have the authority to
authorize the issuance of preferred stock
Our Articles of Incorporation, as amended,
authorize the Company to issue an aggregate of 10,000,000 shares of Preferred Stock. Our directors, without further action by our stockholders,
have the authority to issue shares to be determined by our board of directors of Preferred Stock with the relative rights, conversion
rights, voting rights, preferences, special rights, and qualifications as determined by the board without approval by the shareholders.
Any issuance of Preferred Stock could adversely affect the rights of holders of common stock. Additionally, any future issuance of preferred
stock may have the effect of delaying, deferring, or preventing a change in control of the Company without further action by the shareholders
and may adversely affect the voting and other rights of the holders of common stock. Our Board does not intend to seek shareholder approval
prior to any issuance of currently authorized stock, unless otherwise required by law or stock exchange rules.
We have never paid dividends on our
common stock, nor are we likely to pay dividends in the foreseeable future. Therefore, you may not derive any income solely from ownership
of our stock
We have never declared or paid dividends on
our common stock and do not presently intend to pay any dividends in the foreseeable future. We anticipate that any funds available for
payment of dividends will be re-invested into the Company to further our business strategy. This means that your potential for economic
gain from ownership of our stock depends on appreciation of our stock price and will only be realized by a sale of the stock at a price
higher than your purchase price.
|
|
Item 2.
|
Financial Information
|
Management’s Discussion and Analysis
or Plan of Operation
Upon effectiveness of this Registration Statement,
we will file with the SEC annual and quarterly information and other reports that are specified in the Securities Exchange Act of 1934,
as amended (the “Exchange Act”), and SEC regulations. Thus, we will need to ensure that we will have the ability to prepare,
on a timely basis, financial statements that comply with SEC reporting requirements following the effectiveness of this registration statement.
We will also become subject to other reporting and corporate governance requirements, including the listing standards of any securities
exchange upon which we may list our Common Stock, and the provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act”),
and the regulations promulgated hereunder, which impose significant compliance obligations upon us. As a public company, we will be required,
among other things, to:
|
|
·
|
Prepare and distribute reports and other stockholder communications in compliance with our obligations under the federal securities laws and the applicable national securities exchange listing rules;
|
|
|
·
|
Define and expand the roles and the duties of our Board of Directors and its committees;
|
|
|
·
|
Institute more comprehensive compliance, investor relations and internal audit functions;
|
|
|
·
|
Involve and retain outside legal counsel and accountants in connection with the activities listed above.
|
Management for each year commencing with the
year ending December 31, 2021 must assess the adequacy of our internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control over financial
reporting will be required to meet the standards required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. We will incur additional costs in
order to improve our internal control over financial reporting and comply with Section 404, including increased auditing and legal fees
and costs associated with hiring additional accounting and administrative staff. Ultimately, our efforts may not be adequate to comply
with the requirements of Section 404. If we are unable to implement and maintain adequate internal control over financial reporting or
otherwise to comply with Section 404, we may be unable to report financial information on a timely basis, may suffer adverse regulatory
consequences, may have violations of the applicable national securities exchange listing rules, and may breach covenants under our credit
facilities.
The significant obligations related to being
a public company will continue to require a significant commitment of additional resources and management oversight that will increase
our costs and might place a strain on our systems and resources. As a result, our management’s attention might be diverted from
other business concerns. In addition, we might not be successful in implementing and maintaining controls and procedures that comply with
these requirements. If we fail to maintain an effective internal control environment or to comply with the numerous legal and regulatory
requirements imposed on public companies, we could make material errors in, and be required to restate, our financial statements. Any
such restatement could result in a loss of public confidence in the reliability of our financial statements and sanctions imposed on us
by the SEC.
Asiarim Corporation is a blank check company
and has no operations. Our business plan includes international education. In summary, ARMC is focused
on raising capital for te educational platform. As of this filing, we have not raised any capital and our business is not yet operational.
Results of Operations for Asiarim Corporation
—Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2019 and 2020
Revenue
We had no revenues from operations during
either 2019 or 2020.
General and Administrative Expense
General and Administrative Expenses were
5,629 for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to $2,037 for the year ended December 31, 2019, an increase of $3,592. The expenses
consist primarily of transfer agent fees and annual state filing fees.
Stock compensation expense
During the year ended December 31, 2020,
we incurred Nil on non-cash stock compensation expense from the issuance of common stock for services. There was no stock issued for
services in the prior year.
Net Loss
We had a net loss of $5,629 for the year ended
December 31, 2020 compared to $2,037 for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2020, we had $0 of cash,
$7,666 of liabilities and an accumulated deficit of $2,331,376. The Company has working capital deficit of $7,666.
We used nil of cash in operations for the
year ended December 31, 2020 and used net cash of $2,037 for the year ended December 31, 2019.
We received net advances from related party
of $2,037.
The financial statements accompanying this
Report have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities and commitments
in the normal course of our business. As reflected in the accompanying financial statements, we have not yet generated any revenue, had
a net loss of $5,629 and have accumulated stockholders’ deficit of $7,666 as of December 31, 2020. These factors raise substantial
doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent on our ability to raise
additional funds and implement our business plan. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might be necessary if
we are unable to continue as a going concern.
We do not own any property and do not pay
for office space.
|
|
Item 4.
|
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management
|
(a) Security ownership of certain beneficial
owners.
The following table sets
forth, as of July 6, 2021, the number of shares of common stock owned of record and beneficially by our executive officer, director and
persons who beneficially own more than 5% of the outstanding shares of our common stock.
Amount and Nature
of Beneficial Ownership Percentage of Class
|
Name and Address of Beneficial Owner
|
|
Amount and Nature of Beneficial
Ownership
|
|
Percentage of Class
|
|
Mitex Group Ltd
|
|
5,591,533
|
|
7.19%
|
|
271 Lockhart Rd, Ste 1601
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jie Yang Bldg.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wanchai Hong Kong
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reunite Investments Inc.
|
|
7,173,334
|
|
9.23%
|
|
24338 El Toro Rd, Unit e
|
|
|
|
|
|
Laguan Woods, CA 92637
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Di Pan
|
|
11,400,000
|
|
14.6%
|
|
1005-33 Sheppard Ave
|
|
|
|
|
|
North York, Ontario
|
|
|
|
|
|
M2K 3E5 Canada
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bingqiang Xie
|
|
11,400,000
|
|
14.6%
|
|
1309-8081 Birchmount Rd
|
|
|
|
|
|
Markham, Ontario
|
|
|
|
|
|
L6G 0G5 Canada
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ci Zhang
|
|
15,200,000
|
|
19.56%
|
|
5689 Condor Pl
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mississauga, ON
|
|
|
|
|
|
L5V 2J4 Canada
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5.
|
Directors and Executive Officers
|
A. Identification of Directors and Executive Officers.
Our Officers and directors and additional information concerning them
are as follows:
|
Name
|
|
Age
|
|
|
Position
|
|
Dr. Ci Zhang
|
|
|
39
|
|
|
CEO, President, Secretary, Treasurer, Director
|
|
Bingqiang Xie
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
Director
|
|
Changjun Xue
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
CFO
|
Officer Bios
Ci Zhang, Chief Executive Officer (age 39)
Ci Zhang has more than 15 years of experience in the education and
technology sectors. As a Cisco Certified Network (CCN) Professional, he combines extensive experience in network design and management
with strong business management as well as student management, counselling and instructional skills.
Un Monde International Ltd., CEO, he has led the development
of the schools unique technology platform that integrates all school functions in a single cloud based system that leverages the power
of Artificial Intelligence and big data.
Prior to One World, Mr. Zhang held multiple management positions at
Multi-Tech Computer Systems In Hamilton, ON leading the design and implementation of computer and local area networks. Before Multi-tech,
he served as an instructor teaching students Cisco Network CCN certification courses at Xincon College in Toronto, as well as an International
Student Counselor advising on admission and program requirements.
After technical training at Cisco Systems in Beijing, Mr. Zhang obtained
a Bachelor of Science form McMaster University in Hamilton, ON. He also holds certifications as a Cisco Certified Network Associate, Expert,
and Professional as well as a Microsoft Systems Engineer.
Bingqiang Xie, Director (Age 25)
Bingqiang Xie is an award-winning software engineer and mechatronics
engineer and a former international student at St. Lawrance College. Over the past eight years, Mr. Xie has participated in numerous
projects, including developing a heads up display for testing vehicles for General Motors, developing software for robotics and 3D-printing
projects, security systems, wireless locks, and an image decoder.
Changjun Xue, Chief Financial Officer (age 55)
Changiun Xue has more than 30 years of experience as an executive and
consultant in the securities industry and as a business lawyer. Prior to joining One World, Mr. Xue served as President and CEO of the
Harbin Grain Exchange for five years after having held the vice-president position for two years. Harbin owns and operates an online spot
grain-trading platform.
Before Harbin, he was a consultant to Aijian Securities, a securities
firm headquartered in Shanghai that offers brokerage services, investment consulting, asset management, and investment banking. Xue’s
work for Aijian followed 11 years as the Deputy General Manager of CITIC Securities, China's
largest full-service investment bank. Prior to CITI, he was a lawyer with Shenzhen Business Law.
Mr. Xue has a Bachelor of Law degree from Renmin University of China
in Beijing, and a Master of Business Administration degree from the China Europe International
Business School (CEIBS). CEIBS is a member of EFMD, the largest international network association in the field of management development.
|
|
Item 6.
|
Executive Compensation
|
For
the past two years, no sole officer or director has received any cash remuneration. No remuneration of any nature has been paid for on
account of services rendered by a director in such capacity to date. Our officer and director intend to devote all of his time to ARMC
and its subsidiaries.
The Company for the benefit
of its employees has adopted no retirement, pension, profit sharing, stock option or insurance programs or other similar programs.
|
|
Item 7.
|
Certain Relationship and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
|
Regulation S-K, Item 4, Section C require
disclosure of promoters and certain control persons for registrants that are filing a registration statement on Form 10 under the Exchange
Act and that had a promoter at any time during the past five fiscal years shall:
(i) State the names of the promoter(s), the
nature and amount of anything of value (including money, property, contracts, options or rights of any kind) received or to be received
by each promoter, directly or indirectly, from the registrant and the nature and amount of any assets, services or other consideration
therefore received or to be received by the registrant; and
(ii) As to any assets acquired or to be acquired
by the registrant from a promoter, state the amount at which the assets were acquired or are to be acquired and the principle followed
or to be followed in determining such amount, and identify the persons making the determination and their relationship, if any, with the
registrant or any promoter. If the assets were acquired by the promoter within two years prior to their transfer to the registrant, also
state the cost thereof to the promoter.
Bryan Glass is considered a promoter(s) under the meaning of Securities
Act Rule 405. Mr. Glass was appointed custodian of the Company and under its duties stipulated by the Nevada court. Mr. Glass took initiative
to organize the business of the issuer. As custodian, his duties were to conduct daily business, hold shareholder meetings, appoint officers
and directors, reinstate the company with the Nevada Secretary of State. The custodian also had authority to enter into contracts and
find a suitable merger candidate. In addition, Mr. Glass was compensated for his role as custodian and paid outstanding bills to creditors
on behalf of the company. The custodian has not, and will not, receive any additional compensation, in the form of cash or stock, for
custodian services. The custodianship was discharged on November 9, 2016.
Under Regulation S-K Item 404(c)(2) Registrants
shall provide the disclosure required by paragraphs (c)(1)(i) and (c)(1)(ii) of this Item as to any person who acquired control of a registrant
that is a shell company, or any person that is part of a group, consisting of two or more persons that agree to act together for the purpose
of acquiring, holding, voting or disposing of equity securities of a registrant, that acquired control of a registrant that is a shell
company.
As discussed in Item 1, the Company is deemed a shell company. As disclosed
in Item 4, there are several persons, Ci Zhang, Bingquiang Xie, and Di Pan are considered control persons and acquired control of the
Company. As discussed in Item 1, Asia Gateway Capital Ltd. purchased 40,000,000 million shares of the Company’s Restricted Common
Stock. These shares represent the controlling block of stock and were purchased from Bryan Glass for $120,000.
Ci
Zhang is our CEO and President. He is not deemed to be independent under applicable rules. We have not established any committees of the
Board of Directors.
Except
as set forth above, there have been no related party transactions, or any other transactions or relationships required to be disclosed.
|
|
Item 8.
|
Legal Proceedings
|
Presently,
there are not any material pending legal proceedings to which the Registrant is a party or as to which any of its property is subject,
and no such proceedings are known to the Registrant to be threatened or contemplated against it.
|
|
Item 9.
|
Market Price and Dividends on the Registrant’s Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters
|
(a) Market information.
Our
Common Stock is not trading on any stock exchange. However, it is currently quoted on OTC Markets under the symbol ARMC and there is no
established public trading market for the class of common equity.
(b) Holders.
As
of July 6, 2021, there are approximately 89 holders of an aggregate of 77,698,333 shares of our Common Stock issued and outstanding.
(c) Dividends.
We
have not paid any cash dividends to date and do not anticipate or contemplate paying dividends in the foreseeable future. It is the president
intention of management to utilize all available funds for the development of the Registrant’s business.
(d) Securities authorized for issuance under
equity compensation plans.
None.
|
|
Item 10.
|
Recent Sale of Unregistered Securities
|
On
January 30, 2019, Mr. Glass entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement with Asia Gateway Capital Ltd., whereby Asia Gateway Capital Ltd.
purchased 40,000,000 shares of Restricted Common Stock, the controlling block of stock, for the purchase price of $120,000.
The
restricted shares were sold in a private transaction pursuant to Rule 144(i) of the ’33 Securities Act. As of this date, the shares
have not been registered.
The
shares were issued to the following individuals:
|
Ci Zhang
|
15,200,000 shares
|
|
Di Pan
|
11,400,000 shares
|
|
Bingqiang Xie
|
11,400,000 shares
|
|
Chih Teh Liu
|
1,000,000 shares
|
|
PoayGuan Lee
|
700,000 shares
|
|
Catherine Miao
|
300,000 shares
|
On September 30, 2019,
the Company entered into a Private Placement Memorandum with Tai Yuet Loy Trading company Ltd. whereby Tai Yet Loy Trading Company Ltd.
purchased 500,000 shares of Restricted Common Stock for the purchase price of $50,000.
On September 30, 2019,
the Company entered into a Private Placement Memorandum with Fan Ming whereby Fan Ming purchased 1,500,000 shares of Restricted Common
Stock for the purchase price of $150,000.
On October 3, 2019, the
Company entered into a Private Placement Memorandum with Reagan Li whereby Reagan Li purchased 1,000,000 shares of Restricted Common
Stock for the purchase price of $100,000.
On October 9, 2019, the
Company entered into a Private Placement Memorandum with ILIC Food Corp whereby ILIC Food Corp. purchased 500,000 shares of Restricted
Common Stock for the purchase price of $50,000.
On October 9, 2019, the
Company entered into a Private Placement Memorandum with Shuk Wan Cheng whereby Shuk Wan Cheng purchased 1,000,000 shares of Restricted
Common Stock for the purchase price of $100,000.
|
|
Item 11.
|
Description of Registrant’s Securities to be Registered
|
(a) Common.
We are authorized by our Certificate of Incorporation to issue an
aggregate of 100,000,000 shares of capital stock, of which 90,000,000 are shares of common stock, Par Value $0.001 per share (the “Common
Stock”) and 10,000,000 are shares of preferred stock, Par Value $0.001 per share (the “Preferred Stock”). As of July
6, 2021, there are 77,698,333 shares of Common Stock.
Common Stock
All
outstanding shares of Common Stock are of the same class and have equal rights and attributes. The holders of Common Stock are entitled
to one vote per share on all matter submitted to a vote of stockholders of the Company. All stockholders are entitled to share equally
dividends, if any, as may be declared from time to time by the Board of Directors out of funds legally available. In the event of liquidation,
the holders of Common Stock are entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of all liabilities. The stockholders do
not have cumulative or preemptive rights.
Preferred Stock
Our
Certificate of Incorporation authorizes the issuances of up to 10,000,000 shares of Preferred Stock with designations, rights and preferences
determined from time to time by its Board of Directors. Accordingly, our Board of Directors is empowered, without stockholder approval,
to issue Preferred Stock with dividend, liquidation, conversion, voting, or other rights, which could adversely affect the voting power
or, other rights of the holders of the Common Stock. In the event of issuance, the Preferred Stock could be utilized, under certain circumstances,
as a method of discouraging, delaying or preventing a change in control of the Company.
At
this time there are 10,000,000 shares of Preferred Stock authorized and 0 issued and outstanding.
The description of certain
matters relating to the securities of the Company is a summary and is qualified in its entirely by the provisions of the Company’s
Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws copies of which have been filed as exhibits to this Form 10.
(b) Debt Securities.
None.
(c) Other Securities To Be Registered.
None.
|
|
Item 12.
|
Indemnification of Directors and Officers
|
Our
Officers and Directors are indemnified as provided by the Nevada corporate law and our Bylaws. We have agreed to indemnify all our directors
and certain officers against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933. Insofar as indemnification for
liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to our directors, officers and controlling persons pursuant to the
provisions described above, or otherwise, we have been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification
is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933 and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification
against such liabilities (other than our payment of expenses incurred or paid by our director, officer or controlling person in connection
with the securities being registered, we will, unless in the opinion of our counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent,
submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in
the Securities Act and will be governed by the adjudication of such issue.
We
have been advised that in the opinion of the Securities Exchange Commission indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities
Act against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act, and is, therefore, unenforceable. If a claim for indemnification against
such liabilities is asserted by one of our directors, officers, or controlling persons in connection with the securities being registered,
we will, unless in the opinion of our legal counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit question of whether such
indemnification is against public policy to a court of appropriate jurisdiction. We will then be governed by the court’s decision.
|
Item 13.
|
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
|
|
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD.
|
|
FORMERLY ASIARIM CORPORATION
|
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
(Audited)
|
|
Page
|
|
|
|
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
|
23
|
|
|
|
|
Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2019 and 2020
|
24
|
|
|
|
|
Statements of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2019 and 2020
|
25
|
|
|
|
|
Statement of Stockholders’ Deficit for the Years Ended December 31, 2019 and 2020
|
26
|
|
|
|
|
Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2019 and 2020
|
27
|
|
|
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
28
|
|
|
|
|
Balance Sheets as of March 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020 (Unaudited)
|
33
|
|
|
|
|
Statements of Operations for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2021 and March 31, 2020 (Unaudited)
|
34
|
|
|
|
|
Statement of Stockholders’ Deficit for the Period Ended March 31, 2021 (Unaudited) Restated
|
35
|
|
|
|
|
Statements of Cash Flows for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2021 and 2020 (Unaudited)
|
36
|
|
|
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
37
|
|
|
|
|
Balance Sheets as of June 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020 (Unaudited)
|
42
|
|
|
|
|
Statements of Operations for the Three Months and Six Months Ended June 30, 2021 and June 30, 2020 (Unaudited)
|
43
|
|
|
|
|
Statement of Stockholders’ Deficit for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2021 and June 30, 2020 (Unaudited)
|
44
|
|
|
|
|
Statements of Cash Flows for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2021 and June 30, 2020 (Unaudited)
|
45
|
|
|
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
46
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting
Firm
To the shareholders and the board of directors
of Un Monde International Ltd
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets
of Un Monde International Ltd as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, the related statements of operations, stockholders' equity (deficit),
and cash flows for the years then ended, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In
our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31,
2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States.
Substantial Doubt about the Company’s
Ability to Continue as a Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been
prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 3 to the financial statements, the Company has
suffered recurring losses from operations and has a significant accumulated deficit. In addition, the Company continues to experience
negative cash flows from operations. These factors raise substantial doubt about the Company's ability to continue as a going concern.
Management's plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 3. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that
might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility
of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audit. We
are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are
required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and
regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the
standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial
statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged
to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding
of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s
internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess
the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond
to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements.
Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating
the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/S/ BF Borgers CPA PC
BF Borgers CPA PC
We have served as the Company's auditor since
2021
Lakewood, CO
August 19, 2021
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD.
FORMERLY ASIARIM CORPORATION
BALANCE SHEETS
|
|
|
December 31
|
|
|
December 31
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Other assets
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total Assets
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued expenses
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Amount due to related party
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
Total Liabilities
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitment & contingencies
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 77,698,333 and 76,805,000 issued shares and outstanding, respectively
|
|
|
77,698
|
|
|
|
76,805
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
|
2,246,905
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
|
(2,325,747
|
)
|
|
Total Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
|
(7,666
|
)
|
|
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD.
FORMERLY ASIARIM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS
OF OPERATIONS
|
|
|
Years Ended
|
|
|
|
|
December 31
|
|
|
December 31
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Professional Fees
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
700
|
|
|
Other General & Administrative Expense
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
|
1,337
|
|
|
Total Operating Expenses
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss from operations
|
|
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Income (Expenses)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Expense
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total Other Income (Expenses)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) before Income Taxes
|
|
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income Tax Benefit
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss)
|
|
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Loss per Common Share - Basic and Diluted
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Weighted Average Number of Common Shares Outstanding - Basic and Diluted
|
|
|
64,654,066
|
|
|
|
60,657,941
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD.
FORMERLY ASIARIM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' DEFICIT
|
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Par Value
|
|
|
|
Additional Paid-in
|
|
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
|
|
Total Stockholders
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
|
$0.001
|
|
|
|
Capital
|
|
|
|
Deficit
|
|
|
|
Deficit
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2018
|
|
|
72,305,000
|
|
|
$
|
72,305
|
|
|
$
|
2,251,405
|
|
|
$
|
(2,323,710
|
)
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Issued 4,500,000 shares for proceeds
|
|
|
4,500,000
|
|
|
|
4,500
|
|
|
|
(4,500
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019
|
|
|
76,805,000
|
|
|
$
|
76,805
|
|
|
$
|
2,246,905
|
|
|
$
|
(2,325,747
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
Issued 893,330 shares for proceeds
|
|
|
893,333
|
|
|
|
893
|
|
|
|
(893
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2020
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
$
|
77,698
|
|
|
$
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
$
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
$
|
(7,666
|
)
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD.
FORMERLY ASIARIM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS
OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
|
Years Ended
|
|
|
|
|
December 31
|
|
|
December 31
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Loss
|
|
$
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
Adjustment to reconcile net loss from operations:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in Operating Assets and Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from related party
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Cash at Beginning of Period
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Cash at End of Period
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental Cash Flow Information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income Taxes Paid
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Interest Paid
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD
Formerly Asiarim
corporation
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019
NOTE 1 - ORGANIZATION AND OPERATIONS
Un Monde International Ltd formerly known as Asiarim Corporation (the
“Company”) is a corporation organized under the laws of the State of Nevada on June 15, 2007. The operations of Asiarim Corporation
and its subsidiaries were abandoned by former management and a custodianship action was commenced in 2016.
On May 5, 2016, the Eighth District Court of Clark County of Nevada
granted the Application for Appointment of Custodian as a result of the absence of a functioning board of directors and the revocation
of the Company’s charter. The order appointed a custodian to take any Corporation actions on behalf of the Company that would further
the interests of its shareholders.
On March 29, 2019, a change of control occurred with respect to the
Company to better reflect its new business direction.
The Company intends to acquire private corporations that are involved
in education and management services offering private, distinguished, specialized, and internationalized education to international students
in schools.
NOTE 2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of presentation
The Company’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The preparation of financial
statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the
date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ
from those estimates.
Management further acknowledges that it is solely responsible for adopting
sound accounting practices, establishing and maintaining a system of internal accounting control and preventing and detecting fraud. The
Company's system of internal accounting control is designed to assure, among other items, that 1) recorded transactions are valid; 2)
valid transactions are recorded; and 3) transactions are recorded in the proper period in a timely manner to produce financial statements
which present fairly the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the Company for the respective periods being presented.
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the
reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reported period.
The Company’s significant estimates include income taxes provision
and valuation allowance of deferred tax assets; the fair value of financial instruments; the carrying value and recoverability of long-lived
assets, including the values assigned to an estimated useful lives of computer equipment; and the assumption that the Company will continue
as a going concern. Those significant accounting estimates or assumptions bear the risk of change due to the fact that there are uncertainties
attached to those estimates or assumptions, and certain estimates or assumptions are difficult to measure or value. Management bases its
estimates on historical experience and on various assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results
of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other
sources.
Management regularly reviews its estimates utilizing currently available
information, changes in facts and circumstances, historical experience and reasonable assumptions. After such reviews, and if deemed appropriate,
those estimates are adjusted accordingly. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Carrying value, recoverability and impairment of long-lived assets
The Company has adopted paragraph 360-10-35-17 of the FASB Accounting
Standards Codification for its long-lived assets. The Company’s long-lived assets, which include computer equipment are reviewed
for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
The Company assesses the recoverability of its long-lived assets by
comparing the projected undiscounted net cash flows associated with the related long-lived asset or group of long-lived assets over their
remaining estimated useful lives against their respective carrying amounts. Impairment, if any, is based on the excess of the carrying
amount over the fair value of those assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash
flows or market value, if readily determinable. If long-lived assets are determined to be recoverable, but the newly determined remaining
estimated useful lives are shorter than originally estimated, the net book values of the long-lived assets are depreciated over the newly
determined remaining estimated useful lives.
The Company considers the following to be some examples of important
indicators that may trigger an impairment review: (i) significant under-performance or losses of assets relative to expected historical
or projected future operating results; (ii) significant changes in the manner or use of assets or in the Company’s overall strategy
with respect to the manner or use of the acquired assets or changes in the Company’s overall business strategy; (iii) significant
negative industry or economic trends; (iv) increased competitive pressures; (v) a significant decline in the Company’s stock price
for a sustained period of time; and (vi) regulatory changes. The Company evaluates acquired assets for potential impairment indicators
at least annually and more frequently upon the occurrence of such events.
The impairment charges, if any, is included in operating expenses in
the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity
of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Related parties
The Company follows subtopic 850-10 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to Section 850-10-20 the Related parties include a) affiliates
of the Company; b) Entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the election of the fair value
option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of Section 825–10–15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing
entity; c) trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and profit-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship
of management; d) principal owners of the Company; e) management of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one
party controls or can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting
parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g) Other parties that can significantly influence the management
or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and can significantly
influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests.
Commitments and contingencies
The Company follows subtopic 450-20 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification to report accounting for contingencies. Certain conditions may exist as of the date the consolidated financial statements
are issued, which may result in a loss to the Company but which will only be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to
occur. The Company assesses such contingent liabilities, and such assessment inherently involves an exercise of judgment. In assessing
loss contingencies related to legal proceedings that are pending against the Company or unasserted claims that may result in such proceedings,
the Company evaluates the perceived merits of any legal proceedings or unasserted claims as well as the perceived merits of the amount
of relief sought or expected to be sought therein.
If the assessment of a contingency indicates that it is probable that
a material loss has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be estimated, then the estimated liability would be accrued in the
Company’s consolidated financial statements. If the assessment indicates that a potential material loss contingency is not probable
but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, and an estimate of the
range of possible losses, if determinable and material, would be disclosed.
Loss contingencies considered remote are generally not disclosed unless
they involve guarantees, in which case the guarantees would be disclosed. Management does not believe, based upon information available
at this time, that these matters will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of
operations or cash flows. However, there is no assurance that such matters will not materially and adversely affect the Company’s
business, financial position, and results of operations or cash flows.
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted ASU 2014-09, Topic 606 on January 1, 2018, using
the modified retrospective method. ASC 606 requires the use of a new five-step model to recognize revenue from customer contracts. The
five-step model requires that the Company (i) identify the contract with the customer, (ii) identify the performance obligations in the
contract, (iii) determine the transaction price, including variable consideration to the extent that it is probable that a significant
future reversal will not occur, (iv) allocate the transaction price to the respective performance obligations in the contract, and (v)
recognize revenue when (or as) the Company satisfies the performance obligation.
The adoption of Topic 606 has no impact on revenue amounts recorded
on the Company’s financial statements as the Company has not generate any revenues.
Income Tax Provisions
The Company follows Section 740-10-30 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification, which requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that
have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are based on the
differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the fiscal year
in which the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance to the extent management concludes
it is more likely than not that the assets will not be realized. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates
expected to apply to taxable income in the fiscal years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled.
The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in the Statements of Income and Comprehensive
Income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company adopted section 740-10-25 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification (“Section 740-10-25”) with regards to uncertainty income taxes. Section 740-10-25 addresses the determination
of whether tax benefits claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the financial statements. Under Section
740-10-25, the Company may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position
will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized
in the financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than fifty percent
(50%) likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Section 740-10-25 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification,
interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and requires increased disclosures.
Net income (loss) per common share
Net income (loss) per common share is computed pursuant to section
260-10-45 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification. Basic net income (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net income (loss)
by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted net income (loss) per common share is
computed by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of shares of common stock and potentially outstanding shares of
common stock during the period. The weighted average number of common shares outstanding and potentially outstanding common shares assumes
that the Company incorporated as of the beginning of the first period presented.
Cash flows reporting
The Company adopted paragraph 230-10-45-24 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification for cash flows reporting, classifies cash receipts and payments according to whether they stem from operating, investing,
or financing activities and provides definitions of each category, and uses the indirect or reconciliation method (“Indirect method”)
as defined by paragraph 230-10-45-25 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification to report net cash flow from operating activities by
adjusting net income to reconcile it to net cash flow from operating activities by removing the effects of (a) all deferrals of past operating
cash receipts and payments and all accruals of expected future operating cash receipts and payments and (b) all items that are included
in net income that do not affect operating cash receipts and payments. The Company reports the reporting currency equivalent of foreign
currency cash flows, using the current exchange rate at the time of the cash flows and the effect of exchange rate changes on cash held
in foreign currencies is reported as a separate item in the reconciliation of beginning and ending balances of cash and cash equivalents
and separately provides information about investing and financing activities not resulting in cash receipts or payments in the period
pursuant to paragraph 830-230-45-1 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification.
NOTE 3 – GOING CONCERN
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that
the Company will continue as a going concern, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets, and liquidation of liabilities
in the normal course of business.
As reflected in the accompanying financial statements, the Company
had an accumulated deficit at December 31 ,2020 of $2,331,376 without any revenues. These factors among others raise substantial doubt
about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
While the Company has not commenced operations and generate revenues,
the Company’s cash position may not be significant enough to support the Company’s daily operations. Management intends to
raise additional funds by way of a public or private offering. Management believes that the actions presently being taken to further implement
its business plan and generate revenues provide the opportunity for the Company to continue as a going concern. While the Company believes
in the viability of its strategy to generate revenues and in its ability to raise additional funds, there can be no assurances to that
effect. The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern is dependent upon the Company’s ability to further implement its
business plan and generate revenues.
The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might
be necessary if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
NOTE 4 – STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Common Stock
The Company is authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of common stock.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company issued 893,330 shares
at $0.30 per share for proceeds of $267,999. The proceeds were provided to the sole director’s and officer’s company as working
capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued 4,500,000
shares at $0.10 per share for proceeds of $450,000. The proceeds were provided to the sole director’s and officer’s company
as working capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital.
On October 3, 2016, certain shareholders have entered into an Assignment
of Rights agreement with the Company to return 12,764,867 shares of common stock to the Company as treasury stock. However, such shares
have not been returned by the shareholders to date and are presented as issued and outstanding.
As of December 31 ,2020, the Company has 77,698,333 shares issued and
outstanding.
NOTE 5 – INCOME TAX
On December 22, 2017, the President of the United States signed into
law the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“Tax Reform Act”). The legislation significantly changes U.S. tax law by, among other things,
lowering corporate income tax rates, implementing a territorial tax system and imposing a transition tax on deemed repatriated earnings
of foreign subsidiaries. The Tax Reform Act permanently reduces the U.S. corporate income tax rate from a maximum of 34% to a flat 21%
rate, effective January 1, 2018. As a result of the reduction in the U.S. corporate income tax rate from 34% to 21% under the Tax Reform
Act, the Company revalued its ending net deferred tax assets.
The Company has accumulated approximately $2,331,376 of net operating
losses (“NOL”) carried forward to offset future taxable income. In assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, management
considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will be realized. The ultimate realization
of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences
become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning
strategies in making this assessment. Based on the assessment, management has established a full valuation allowance against all of the
deferred tax asset relating to NOLs for every period because it is more likely than not that all of the deferred tax asset will not be
realized.
NOTE 6 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTION
Zhang Ci, majority shareholder, director and officer of the Company,
have paid certain expenses on behalf of the Company. Such amounts are due on demand and non-interest bearing. The outstanding amount due
to related parties was $2,037 and $2,037 as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
The proceeds from the share issuance were provided to the sole director’s
and officer’s company as working capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital (Refer to Note 4).
NOTE 7 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On October 3, 2016, the Company has entered into an agreement with
Mitex Group Limited (“Mitex”) and Reunite Investment Inc. (“Reunite”). Pursuant to the agreement, Mitex and Reunite
have agreed to return the outstanding common stock held by them. The outstanding common stock are 5,591,533 and 7,173,334, respectively.
Both Mitex and Reunite have represented to the Company that they have lost the certificates and cannot return the stock certificates to
the Company for cancellation. Therefore, the cancellation was not completed until July 12, 2021.
The Company has evaluated subsequent
events to the date the financial statements were issued and has determined that there are no items to disclose or require adjustments.
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim Corp.
BALANCE SHEETS
Unaudited
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total Assets
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
Due to related party
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
Total Liabilities
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitment & contingencies
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 780,000,000 shares authorized; 77,698,333 issued shares and outstanding, respectively.
|
|
|
77,698
|
|
|
|
77,698
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
Total Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
|
(7,666
|
)
|
|
|
(7,666
|
)
|
|
Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim Corp.
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Unaudited
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
|
|
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other general & administrative expense
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Loss from operations
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Income (Expenses)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest income (expense)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total Other Income (Expenses)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) before income taxes
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Income tax expense
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net income (loss)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to common stockholders
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (Loss) per Share - Basic and Diluted
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Weighted Average Shares Outstanding - Basic and Diluted
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
76,939,176
|
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
76,939,176
|
|
|
Earnings (Loss) per Share - Basic
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Weighted Average Shares Outstanding - Basic
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
76,939,176
|
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
76,939,176
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim
Corp.
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' DEFICIT
For the Three Months Ended March 31, 2021 and 2020
Unaudited
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Par Value,
$0.001
|
|
|
Additional
Paid-in Capital
|
|
|
Accumulated
Deficit
|
|
|
Total
Stockholders'
Deficit
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019
|
|
|
76,805,000
|
|
|
$
|
76,805
|
|
|
$
|
2,246,905
|
|
|
$
|
(2,325,747
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
330,000 shares issuance
|
|
|
330,000
|
|
|
|
330
|
|
|
|
98,670
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
99,000
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Balance, March 31, 2020
|
|
|
77,135,000
|
|
|
$
|
77,135
|
|
|
$
|
2,345,575
|
|
|
$
|
(2,325,747
|
)
|
|
$
|
96,963
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2020
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
$
|
77,698
|
|
|
$
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
$
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
$
|
(7,666
|
)
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Balance, March 31, 2021
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
$
|
77,698
|
|
|
$
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
$
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
$
|
(7,666
|
)
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim Corp.
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Unaudited
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
|
|
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Loss
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Adjustment to reconcile net loss from operations:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation & Amortization expense
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
|
|
|
(5,629
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Investing Activities
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from (Repayment of) related party payables
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Cash at Beginning of Period
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Cash at End of Period
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental Cash Flow Information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income Taxes Paid
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Interest Paid
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends accrued on convertible preferred stock
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Common stock issued for payment of related party debt
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Common stock issued
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
99,000
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD
Formerly Asiarim
corporation
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the three months ended March 31, 2021 and
2020
(Unaudited)
NOTE 1 - ORGANIZATION AND OPERATIONS
Un Monde International Ltd formerly known as Asiarim Corporation (the
“Company”) is a corporation organized under the laws of the State of Nevada on June 15, 2007. The operations of Asiarim Corporation
and its subsidiaries were abandoned by former management and a custodianship action was commenced in 2016.
On May 5, 2016, the Eighth District Court of Clark County of Nevada
granted the Application for Appointment of Custodian as a result of the absence of a functioning board of directors and the revocation
of the Company’s charter. The order appointed a custodian to take any Corporation actions on behalf of the Company that would further
the interests of its shareholders.
On March 29, 2019, a change of control occurred with respect to the
Company to better reflect its new business direction.
The Company intends to acquire private corporations that are involved
in education and management services offering private, distinguished, specialized, and internationalized education to international students
in schools.
NOTE 2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of presentation
The Company’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The preparation of financial
statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the
date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ
from those estimates.
Management further acknowledges that it is solely responsible for adopting
sound accounting practices, establishing and maintaining a system of internal accounting control and preventing and detecting fraud. The
Company's system of internal accounting control is designed to assure, among other items, that 1) recorded transactions are valid; 2)
valid transactions are recorded; and 3) transactions are recorded in the proper period in a timely manner to produce financial statements
which present fairly the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the Company for the respective periods being presented.
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the
reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reported period.
The Company’s significant estimates include income taxes provision
and valuation allowance of deferred tax assets; the fair value of financial instruments; the carrying value and recoverability of long-lived
assets, including the values assigned to an estimated useful lives of computer equipment; and the assumption that the Company will continue
as a going concern. Those significant accounting estimates or assumptions bear the risk of change due to the fact that there are uncertainties
attached to those estimates or assumptions, and certain estimates or assumptions are difficult to measure or value. Management bases its
estimates on historical experience and on various assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results
of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other
sources.
Management regularly reviews its estimates utilizing currently available
information, changes in facts and circumstances, historical experience and reasonable assumptions. After such reviews, and if deemed appropriate,
those estimates are adjusted accordingly. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Carrying value, recoverability and impairment of long-lived assets
The Company has adopted paragraph 360-10-35-17 of the FASB Accounting
Standards Codification for its long-lived assets. The Company’s long-lived assets, which include computer equipment are reviewed
for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
The Company assesses the recoverability of its long-lived assets by
comparing the projected undiscounted net cash flows associated with the related long-lived asset or group of long-lived assets over their
remaining estimated useful lives against their respective carrying amounts. Impairment, if any, is based on the excess of the carrying
amount over the fair value of those assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash
flows or market value, if readily determinable. If long-lived assets are determined to be recoverable, but the newly determined remaining
estimated useful lives are shorter than originally estimated, the net book values of the long-lived assets are depreciated over the newly
determined remaining estimated useful lives.
The Company considers the following to be some examples of important
indicators that may trigger an impairment review: (i) significant under-performance or losses of assets relative to expected historical
or projected future operating results; (ii) significant changes in the manner or use of assets or in the Company’s overall strategy
with respect to the manner or use of the acquired assets or changes in the Company’s overall business strategy; (iii) significant
negative industry or economic trends; (iv) increased competitive pressures; (v) a significant decline in the Company’s stock price
for a sustained period of time; and (vi) regulatory changes. The Company evaluates acquired assets for potential impairment indicators
at least annually and more frequently upon the occurrence of such events.
The impairment charges, if any, is included in operating expenses in
the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity
of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Related parties
The Company follows subtopic 850-10 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to Section 850-10-20 the Related parties include a) affiliates
of the Company; b) Entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the election of the fair value
option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of Section 825–10–15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing
entity; c) trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and profit-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship
of management; d) principal owners of the Company; e) management of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one
party controls or can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting
parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g) Other parties that can significantly influence the management
or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and can significantly
influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests.
Commitments and contingencies
The Company follows subtopic 450-20 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification to report accounting for contingencies. Certain conditions may exist as of the date the consolidated financial statements
are issued, which may result in a loss to the Company but which will only be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to
occur. The Company assesses such contingent liabilities, and such assessment inherently involves an exercise of judgment. In assessing
loss contingencies related to legal proceedings that are pending against the Company or unasserted claims that may result in such proceedings,
the Company evaluates the perceived merits of any legal proceedings or unasserted claims as well as the perceived merits of the amount
of relief sought or expected to be sought therein.
If the assessment of a contingency indicates that it is probable that
a material loss has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be estimated, then the estimated liability would be accrued in the
Company’s consolidated financial statements. If the assessment indicates that a potential material loss contingency is not probable
but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, and an estimate of the
range of possible losses, if determinable and material, would be disclosed.
Loss contingencies considered remote are generally not disclosed unless
they involve guarantees, in which case the guarantees would be disclosed. Management does not believe, based upon information available
at this time, that these matters will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of
operations or cash flows. However, there is no assurance that such matters will not materially and adversely affect the Company’s
business, financial position, and results of operations or cash flows.
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted ASU 2014-09, Topic 606 on January 1, 2018, using
the modified retrospective method. ASC 606 requires the use of a new five-step model to recognize revenue from customer contracts. The
five-step model requires that the Company (i) identify the contract with the customer, (ii) identify the performance obligations in the
contract, (iii) determine the transaction price, including variable consideration to the extent that it is probable that a significant
future reversal will not occur, (iv) allocate the transaction price to the respective performance obligations in the contract, and (v)
recognize revenue when (or as) the Company satisfies the performance obligation.
The adoption of Topic 606 has no impact on revenue amounts recorded
on the Company’s financial statements as the Company has not generate any revenues.
Income Tax Provisions
The Company follows Section 740-10-30 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification, which requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that
have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are based on the
differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the fiscal year
in which the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance to the extent management concludes
it is more likely than not that the assets will not be realized. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates
expected to apply to taxable income in the fiscal years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled.
The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in the Statements of Income and Comprehensive
Income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company adopted section 740-10-25 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification (“Section 740-10-25”) with regards to uncertainty income taxes. Section 740-10-25 addresses the determination
of whether tax benefits claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the financial statements. Under Section
740-10-25, the Company may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position
will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized
in the financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than fifty percent
(50%) likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Section 740-10-25 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification,
interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and requires increased disclosures.
Net income (loss) per common share
Net income (loss) per common share is computed pursuant to section
260-10-45 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification. Basic net income (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net income (loss)
by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted net income (loss) per common share is
computed by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of shares of common stock and potentially outstanding shares of
common stock during the period. The weighted average number of common shares outstanding and potentially outstanding common shares assumes
that the Company incorporated as of the beginning of the first period presented.
Cash flows reporting
The Company adopted paragraph 230-10-45-24 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification for cash flows reporting, classifies cash receipts and payments according to whether they stem from operating, investing,
or financing activities and provides definitions of each category, and uses the indirect or reconciliation method (“Indirect method”)
as defined by paragraph 230-10-45-25 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification to report net cash flow from operating activities by
adjusting net income to reconcile it to net cash flow from operating activities by removing the effects of (a) all deferrals of past operating
cash receipts and payments and all accruals of expected future operating cash receipts and payments and (b) all items that are included
in net income that do not affect operating cash receipts and payments. The Company reports the reporting currency equivalent of foreign
currency cash flows, using the current exchange rate at the time of the cash flows and the effect of exchange rate changes on cash held
in foreign currencies is reported as a separate item in the reconciliation of beginning and ending balances of cash and cash equivalents
and separately provides information about investing and financing activities not resulting in cash receipts or payments in the period
pursuant to paragraph 830-230-45-1 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification.
NOTE 3 – GOING CONCERN
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that
the Company will continue as a going concern, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets, and liquidation of liabilities
in the normal course of business.
As reflected in the accompanying financial statements, the Company
had an accumulated deficit at March 31 ,2021 of $2,331,376 without any revenues. These factors among others raise substantial doubt about
the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
While the Company has not commenced operations and generate revenues,
the Company’s cash position may not be significant enough to support the Company’s daily operations. Management intends to
raise additional funds by way of a public or private offering. Management believes that the actions presently being taken to further implement
its business plan and generate revenues provide the opportunity for the Company to continue as a going concern. While the Company believes
in the viability of its strategy to generate revenues and in its ability to raise additional funds, there can be no assurances to that
effect. The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern is dependent upon the Company’s ability to further implement its
business plan and generate revenues.
The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might
be necessary if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
NOTE 4 – STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Common Stock
The Company is authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of common stock.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company issued 893,333 shares
at $0.30 per share for proceeds of $267,999. The proceeds were provided to the sole director’s and officer’s company as working
capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued 4,500,000
shares at $0.10 per share for proceeds of $450,000. The proceeds were provided to the sole director’s and officer’s company
as working capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital.
On October 3, 2016, certain shareholders have entered into an Assignment
of Rights agreement with the Company to return 12,764,867 shares of common stock to the Company as treasury stock. However, such shares
have not been returned by the shareholders to date.
As of March 31 ,2021, the Company has 77,698,333 shares issued and
outstanding.
NOTE 5 – INCOME TAX
On December 22, 2017, the President of the United States signed into
law the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“Tax Reform Act”). The legislation significantly changes U.S. tax law by, among other things,
lowering corporate income tax rates, implementing a territorial tax system and imposing a transition tax on deemed repatriated earnings
of foreign subsidiaries. The Tax Reform Act permanently reduces the U.S. corporate income tax rate from a maximum of 34% to a flat 21%
rate, effective January 1, 2018. As a result of the reduction in the U.S. corporate income tax rate from 34% to 21% under the Tax Reform
Act, the Company revalued its ending net deferred tax assets.
The Company has accumulated approximately $2,331,376 of net operating
losses (“NOL”) carried forward to offset future taxable income. In assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, management
considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will be realized. The ultimate realization
of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences
become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning
strategies in making this assessment. Based on the assessment, management has established a full valuation allowance against all of the
deferred tax asset relating to NOLs for every period because it is more likely than not that all of the deferred tax asset will not be
realized.
NOTE 6 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTION
Zhang Ci, majority shareholder, director and officer of the Company,
have paid certain expenses on behalf of the Company. Such amounts are due on demand and non-interest bearing. The outstanding amount due
to related parties was $7,666 and $2,037 as of March 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively.
The proceeds from the share issuance were provided to the sole director’s
and officer’s company as working capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital (Refer to Note 4).
NOTE 7 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On October 3, 2016, the Company has entered into an agreement with
Mitex Group Limited (“Mitex”) and Reunite Investment Inc. (“Reunite”). Pursuant to the agreement, Mitex and Reunite
have agreed to return the outstanding common stock held by them. The outstanding common stock are 5,591,533 and 7,173,334, respectively.
Both Mitex and Reunite have represented to the Company that they have lost the certificates and cannot return the stock certificates to
the Company for cancellation. Therefore, the cancellation was not completed until July 12, 2021.
The Company has evaluated subsequent events to the date the financial
statements were issued and has determined that there are no items to disclose or require adjustments.
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim Corp.
BALANCE SHEETS
Unaudited
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total Assets
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
14,840
|
|
|
|
5,629
|
|
|
Due to related party
|
|
|
30,923
|
|
|
|
2,037
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
|
45,763
|
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
Total Liabilities
|
|
|
45,763
|
|
|
|
7,666
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitment & contingencies
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 90,000,000 shares authorized; 77,698,333 issued shares and outstanding, respectively.
|
|
|
77,698
|
|
|
|
77,698
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(2,369,473
|
)
|
|
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
Total Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
|
(45,763
|
)
|
|
|
(7,666
|
)
|
|
Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Deficit
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim Corp.
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Unaudited
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
|
|
|
Six Months Ended
|
|
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other professional fees
|
|
|
11,475
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
11,475
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Other general & administrative expense
|
|
|
26,622
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
26,622
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
38,097
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
38,097
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Loss from operations
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Income (Expenses)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest income (expense)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Total Other Income (Expenses)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) before income taxes
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Income tax expense
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net income (loss)
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to common stockholders
|
|
$
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (Loss) per Share - Basic and Diluted
|
|
$
|
(0.000
|
)
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
(0.000
|
)
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Weighted Average Shares Outstanding - Basic and Diluted
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
77,135,000
|
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
77,135,000
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim
Corp.
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' DEFICIT
For the Six Months Ended June 30, 2021 and 2020
Unaudited
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Par Value,
$0.001
|
|
|
Additional
Paid-in Capital
|
|
|
Accumulated
Deficit
|
|
|
Total
Stockholders'
Deficit
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019
|
|
|
76,805,000
|
|
|
$
|
76,805
|
|
|
$
|
2,246,905
|
|
|
$
|
(2,325,747
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,037
|
)
|
|
Issued 330,000 shares of common stock
|
|
|
330,000
|
|
|
|
330
|
|
|
|
98,670
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
99,000
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Balance, March 31, 2020
|
|
|
77,135,000
|
|
|
|
77,135
|
|
|
|
2,345,575
|
|
|
|
(2,325,747
|
)
|
|
|
96,963
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Balance, June 30, 2020
|
|
|
77,135,000
|
|
|
|
77,135
|
|
|
|
2,345,575
|
|
|
|
(2,325,747
|
)
|
|
|
96,963
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2020
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
$
|
77,698
|
|
|
$
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
$
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
$
|
(7,666
|
)
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Balance March 31, 2021
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
77,698
|
|
|
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
|
(2,331,376
|
)
|
|
|
(7,666
|
)
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
Balance June 30, 2021
|
|
|
77,698,333
|
|
|
|
77,698
|
|
|
|
2,246,012
|
|
|
|
(2,369,473
|
)
|
|
|
(45,763
|
)
|
See
accompanying notes to financial statements
Un Monde International Ltd
FORMERLY Asiarim Corp.
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Unaudited
|
|
|
Six Months Ended
|
|
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Loss
|
|
$
|
(38,097
|
)
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Adjustment to reconcile net loss from operations:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation & Amortization expense
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
9,211
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
|
|
|
(28,886
|
)
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Investing Activities
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from (Repayment of) related party payables
|
|
|
28,886
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
28,886
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Cash at Beginning of Period
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
|
–
|
|
|
Cash at End of Period
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental Cash Flow Information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income Taxes Paid
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Interest Paid
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends accrued on convertible preferred stock
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Common stock issued for payment of related party debt
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
Common stock issued
|
|
$
|
–
|
|
|
$
|
99,000
|
|
See
accompanying notes to financial statements
UN MONDE INTERNATIONAL LTD
Formerly Asiarim
corporation
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the six months ended June 30, 2021 and 2020
(Unaudited)
NOTE 1 - ORGANIZATION AND OPERATIONS
Un Monde International Ltd formerly known as Asiarim Corporation (the
“Company”) is a corporation organized under the laws of the State of Nevada on June 15, 2007. The operations of Asiarim Corporation
and its subsidiaries were abandoned by former management and a custodianship action was commenced in 2016.
On May 5, 2016, the Eighth District Court of Clark County of Nevada
granted the Application for Appointment of Custodian as a result of the absence of a functioning board of directors and the revocation
of the Company’s charter. The order appointed a custodian to take any Corporation actions on behalf of the Company that would further
the interests of its shareholders.
On March 29, 2019, a change of control occurred with respect to the
Company to better reflect its new business direction.
The Company intends to acquire private corporations that are involved
in education and management services offering private, distinguished, specialized, and internationalized education to international students
in schools.
NOTE 2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of presentation
The Company’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The preparation of financial
statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the
date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ
from those estimates.
Management further acknowledges that it is solely responsible for adopting
sound accounting practices, establishing and maintaining a system of internal accounting control and preventing and detecting fraud. The
Company's system of internal accounting control is designed to assure, among other items, that 1) recorded transactions are valid; 2)
valid transactions are recorded; and 3) transactions are recorded in the proper period in a timely manner to produce financial statements
which present fairly the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the Company for the respective periods being presented.
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the
reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reported period.
The Company’s significant estimates include income taxes provision
and valuation allowance of deferred tax assets; the fair value of financial instruments; the carrying value and recoverability of long-lived
assets, including the values assigned to an estimated useful lives of computer equipment; and the assumption that the Company will continue
as a going concern. Those significant accounting estimates or assumptions bear the risk of change due to the fact that there are uncertainties
attached to those estimates or assumptions, and certain estimates or assumptions are difficult to measure or value. Management bases its
estimates on historical experience and on various assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results
of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other
sources.
Management regularly reviews its estimates utilizing currently available
information, changes in facts and circumstances, historical experience and reasonable assumptions. After such reviews, and if deemed appropriate,
those estimates are adjusted accordingly. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Carrying value, recoverability and impairment of long-lived assets
The Company has adopted paragraph 360-10-35-17 of the FASB Accounting
Standards Codification for its long-lived assets. The Company’s long-lived assets, which include computer equipment are reviewed
for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
The Company assesses the recoverability of its long-lived assets by
comparing the projected undiscounted net cash flows associated with the related long-lived asset or group of long-lived assets over their
remaining estimated useful lives against their respective carrying amounts. Impairment, if any, is based on the excess of the carrying
amount over the fair value of those assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash
flows or market value, if readily determinable. If long-lived assets are determined to be recoverable, but the newly determined remaining
estimated useful lives are shorter than originally estimated, the net book values of the long-lived assets are depreciated over the newly
determined remaining estimated useful lives.
The Company considers the following to be some examples of important
indicators that may trigger an impairment review: (i) significant under-performance or losses of assets relative to expected historical
or projected future operating results; (ii) significant changes in the manner or use of assets or in the Company’s overall strategy
with respect to the manner or use of the acquired assets or changes in the Company’s overall business strategy; (iii) significant
negative industry or economic trends; (iv) increased competitive pressures; (v) a significant decline in the Company’s stock price
for a sustained period of time; and (vi) regulatory changes. The Company evaluates acquired assets for potential impairment indicators
at least annually and more frequently upon the occurrence of such events.
The impairment charges, if any, is included in operating expenses in
the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity
of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Related parties
The Company follows subtopic 850-10 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to Section 850-10-20 the Related parties include a) affiliates
of the Company; b) Entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the election of the fair value
option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of Section 825–10–15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing
entity; c) trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and profit-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship
of management; d) principal owners of the Company; e) management of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one
party controls or can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting
parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g) Other parties that can significantly influence the management
or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and can significantly
influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests.
Commitments and contingencies
The Company follows subtopic 450-20 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification to report accounting for contingencies. Certain conditions may exist as of the date the consolidated financial statements
are issued, which may result in a loss to the Company but which will only be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to
occur. The Company assesses such contingent liabilities, and such assessment inherently involves an exercise of judgment. In assessing
loss contingencies related to legal proceedings that are pending against the Company or unasserted claims that may result in such proceedings,
the Company evaluates the perceived merits of any legal proceedings or unasserted claims as well as the perceived merits of the amount
of relief sought or expected to be sought therein.
If the assessment of a contingency indicates that it is probable that
a material loss has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be estimated, then the estimated liability would be accrued in the
Company’s consolidated financial statements. If the assessment indicates that a potential material loss contingency is not probable
but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, and an estimate of the
range of possible losses, if determinable and material, would be disclosed.
Loss contingencies considered remote are generally not disclosed unless
they involve guarantees, in which case the guarantees would be disclosed. Management does not believe, based upon information available
at this time, that these matters will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of
operations or cash flows. However, there is no assurance that such matters will not materially and adversely affect the Company’s
business, financial position, and results of operations or cash flows.
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted ASU 2014-09, Topic 606 on January 1, 2018, using
the modified retrospective method. ASC 606 requires the use of a new five-step model to recognize revenue from customer contracts. The
five-step model requires that the Company (i) identify the contract with the customer, (ii) identify the performance obligations in the
contract, (iii) determine the transaction price, including variable consideration to the extent that it is probable that a significant
future reversal will not occur, (iv) allocate the transaction price to the respective performance obligations in the contract, and (v)
recognize revenue when (or as) the Company satisfies the performance obligation.
The adoption of Topic 606 has no impact on revenue amounts recorded
on the Company’s financial statements as the Company has not generate any revenues.
Income Tax Provisions
The Company follows Section 740-10-30 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification, which requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that
have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are based on the
differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the fiscal year
in which the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance to the extent management concludes
it is more likely than not that the assets will not be realized. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates
expected to apply to taxable income in the fiscal years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled.
The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in the Statements of Income and Comprehensive
Income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company adopted section 740-10-25 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification (“Section 740-10-25”) with regards to uncertainty income taxes. Section 740-10-25 addresses the determination
of whether tax benefits claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the financial statements. Under Section
740-10-25, the Company may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position
will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized
in the financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than fifty percent
(50%) likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Section 740-10-25 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification,
interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and requires increased disclosures.
Net income (loss) per common share
Net income (loss) per common share is computed pursuant to section
260-10-45 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification. Basic net income (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net income (loss)
by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted net income (loss) per common share is
computed by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of shares of common stock and potentially outstanding shares of
common stock during the period. The weighted average number of common shares outstanding and potentially outstanding common shares assumes
that the Company incorporated as of the beginning of the first period presented.
Cash flows reporting
The Company adopted paragraph 230-10-45-24 of the FASB Accounting Standards
Codification for cash flows reporting, classifies cash receipts and payments according to whether they stem from operating, investing,
or financing activities and provides definitions of each category, and uses the indirect or reconciliation method (“Indirect method”)
as defined by paragraph 230-10-45-25 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification to report net cash flow from operating activities by
adjusting net income to reconcile it to net cash flow from operating activities by removing the effects of (a) all deferrals of past operating
cash receipts and payments and all accruals of expected future operating cash receipts and payments and (b) all items that are included
in net income that do not affect operating cash receipts and payments. The Company reports the reporting currency equivalent of foreign
currency cash flows, using the current exchange rate at the time of the cash flows and the effect of exchange rate changes on cash held
in foreign currencies is reported as a separate item in the reconciliation of beginning and ending balances of cash and cash equivalents
and separately provides information about investing and financing activities not resulting in cash receipts or payments in the period
pursuant to paragraph 830-230-45-1 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification.
NOTE 3 – GOING CONCERN
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that
the Company will continue as a going concern, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets, and liquidation of liabilities
in the normal course of business.
As reflected in the accompanying financial statements, the Company
had an accumulated deficit at June 30, 2021 of $2,369,473 without any revenues. These factors among others raise substantial doubt about
the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
While the Company has not commenced operations and generate revenues,
the Company’s cash position may not be significant enough to support the Company’s daily operations. Management intends to
raise additional funds by way of a public or private offering. Management believes that the actions presently being taken to further implement
its business plan and generate revenues provide the opportunity for the Company to continue as a going concern. While the Company believes
in the viability of its strategy to generate revenues and in its ability to raise additional funds, there can be no assurances to that
effect. The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern is dependent upon the Company’s ability to further implement its
business plan and generate revenues.
The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might
be necessary if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
NOTE 4 – STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Common Stock
The Company is authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of common stock.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company issued 893,333 shares
at $0.30 per share for proceeds of $267,999. The proceeds were provided to the sole director’s and officer’s company as working
capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued 4,500,000
shares at $0.10 per share for proceeds of $450,000. The proceeds were provided to the sole director’s and officer’s company
as working capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital.
On October 3, 2016, certain shareholders have entered into an Assignment
of Rights agreement with the Company to return 12,764,867 shares of common stock to the Company as treasury stock. However, such shares
have not been returned by the shareholders to date.
As of June 30, 2021, the Company has 77,698,333 shares issued and outstanding.
NOTE 5 – INCOME TAX
On December 22, 2017, the President of the United States signed into
law the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“Tax Reform Act”). The legislation significantly changes U.S. tax law by, among other things,
lowering corporate income tax rates, implementing a territorial tax system and imposing a transition tax on deemed repatriated earnings
of foreign subsidiaries. The Tax Reform Act permanently reduces the U.S. corporate income tax rate from a maximum of 34% to a flat 21%
rate, effective January 1, 2018. As a result of the reduction in the U.S. corporate income tax rate from 34% to 21% under the Tax Reform
Act, the Company revalued its ending net deferred tax assets.
The Company has accumulated approximately $2,369,473 of net operating
losses (“NOL”) carried forward to offset future taxable income. In assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, management
considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will be realized. The ultimate realization
of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences
become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning
strategies in making this assessment. Based on the assessment, management has established a full valuation allowance against all of the
deferred tax asset relating to NOLs for every period because it is more likely than not that all of the deferred tax asset will not be
realized.
NOTE 6 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTION
Zhang Ci, majority shareholder, director and officer of the Company,
have paid certain expenses on behalf of the Company. Such amounts are due on demand and non-interest bearing. The outstanding amount due
to related parties was $30,923 and $2,037 as of June 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively.
The proceeds from the share issuance were provided to the sole director’s
and officer’s company as working capital and were recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital (Refer to Note 4).
NOTE 7 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On July 12, 2021, the Company cancelled 5,591,533 and 7,173,334 shares
of common stock pursuant to an agreement dated October 3, 2016. Pursuant to the agreement, Mitex Group Limited (“Mitex”) and
Reunite Investment Inc. (“Reunite”) have agreed to return the outstanding common stock held by them. Both Mitex and Reunite
have represented to the Company that they have lost the certificates and cannot return the stock certificates to the Company for cancellation.
Therefore, the cancellation was not completed until then.
|
Item 14.
|
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
|
None.
|
Item 15.
|
Financial Statements and Exhibits
|
|
Exhibit Number and Description
|
|
Location Reference
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.1
|
Certificate of Incorporation
|
|
Filed with the
Company’s Form 10 Amendment No. 1 on September 7, 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.2
|
By-Laws
|
|
Filed with the
Company’s Form 10 Amendment No. 1 on September 7, 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.1
|
Stock Purchase Agreement
|
|
Filed with the
Company’s Form 10 Amendment No. 1 on September 7, 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.2
|
Court Custodial Order
|
|
Filed with the
Company’s Form 10 Amendment No. 1 on September 7, 2021
|
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 12 of the
Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned,
thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
Asiarim Corp.
AKA Un Monde International Ltd.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: December 16, 2021
|
By:
|
/s/ Ci Zhang_
|
|
|
|
Name:
|
Dr. Ci Zhang
|
|
|
|
Title:
|
CEO
|
|
Asiarim (PK) (USOTC:ARMC)
Historical Stock Chart
From Jan 2025 to Feb 2025
Asiarim (PK) (USOTC:ARMC)
Historical Stock Chart
From Feb 2024 to Feb 2025