TheRealReal, Inc.00015732212024FYfalsehttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#AccountingStandardsUpdate202006Member0.05626350.0314465iso4217:USDxbrli:sharesiso4217:USDxbrli:sharesreal:segmentxbrli:pureutr:Yutr:Dreal:tranchereal:plaintiff00015732212024-01-012024-12-3100015732212024-06-2800015732212025-02-1400015732212024-10-012024-12-3100015732212024-12-3100015732212023-12-310001573221us-gaap:ServiceMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ServiceMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:ServiceMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:ProductMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ProductMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:ProductMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMember2022-01-012022-12-3100015732212023-01-012023-12-3100015732212022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310001573221us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310001573221us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-3100015732212021-12-3100015732212021-01-012021-12-310001573221srt:CumulativeEffectPeriodOfAdoptionAdjustmentMemberus-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310001573221srt:CumulativeEffectPeriodOfAdoptionAdjustmentMemberus-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310001573221srt:CumulativeEffectPeriodOfAdoptionAdjustmentMember2021-12-310001573221us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-12-310001573221us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-12-310001573221us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-3100015732212022-12-310001573221us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:CommonStockMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:CommonStockMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2024-12-310001573221real:OtherAccruedAndCurrentLiabilitiesMember2024-12-310001573221real:OtherAccruedAndCurrentLiabilitiesMember2023-12-310001573221srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2024-12-310001573221srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:VehiclesMember2024-12-310001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221real:RestrictedCashMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:CashMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:CashMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2029ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2029ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2029ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberreal:A2029ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221real:A2029ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-3100015732212024-02-290001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputSharePriceMember2024-02-290001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputSharePriceMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMember2024-02-290001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMember2024-02-290001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMember2024-02-290001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedDividendRateMember2024-02-290001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedDividendRateMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2024-02-290001573221us-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2024-12-310001573221real:ProprietarySoftwareMember2024-12-310001573221real:ProprietarySoftwareMember2023-12-310001573221real:FurnitureAndEquipmentMember2024-12-310001573221real:FurnitureAndEquipmentMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:AutomobilesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:AutomobilesMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-12-310001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2024-02-290001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-02-290001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-02-290001573221us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2024-02-292024-02-2900015732212024-02-292024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMember2024-02-292024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMember2024-02-292024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMember2024-02-292024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMember2024-02-292024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFiveMember2024-02-292024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFiveMember2024-02-290001573221real:A2029SeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2020-06-300001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2020-06-012020-06-300001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-03-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-03-012021-03-310001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:ConversionOptionOneMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:ConversionOptionTwoMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221real:CappedCallTransactionsMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2020-06-012020-06-300001573221real:CappedCallTransactionsMemberreal:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-03-012021-03-310001573221real:CappedCallTransactionsMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221real:CappedCallTransactionsMemberreal:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-12-310001573221real:CappedCallTransactionsMemberreal:A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2020-06-100001573221real:CappedCallTransactionsMemberreal:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-03-030001573221real:CappedCallTransactionsMember2024-02-292024-02-290001573221real:OptionsIssuedAndOutstandingMember2024-12-310001573221real:OptionsIssuedAndOutstandingMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-12-310001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2024-12-310001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2023-12-310001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2024-12-310001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2023-12-310001573221real:WarrantsToPurchaseCommonStockMember2024-12-310001573221real:WarrantsToPurchaseCommonStockMember2023-12-310001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2019-12-310001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2021-05-050001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2022-02-230001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2023-02-130001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2024-02-200001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MinimumMember2022-02-012022-02-280001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MaximumMember2022-02-012022-02-280001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2022-02-012022-02-280001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberreal:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMemberus-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-03-310001573221us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberreal:TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMemberus-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-03-012023-03-310001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-10-012024-10-310001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-03-012024-03-310001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-10-012024-10-310001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-03-012024-03-310001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2024-10-012024-10-310001573221us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2024-03-012024-03-310001573221us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberreal:InducementGrantsMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberreal:InducementGrantsMemberus-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberreal:InducementGrantsMemberus-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberreal:InducementGrantsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2021-05-050001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2022-02-230001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2023-02-130001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2024-02-200001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2022-12-310001573221srt:MinimumMember2019-01-012019-12-310001573221srt:MaximumMember2019-01-012019-12-3100015732212019-01-012019-12-310001573221real:RestrictedStockUnitsAndPerformanceShareUnitsMember2024-12-310001573221real:RestrictedStockUnitsAndPerformanceShareUnitsMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2024-12-310001573221real:MarketingMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:MarketingMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:MarketingMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221real:OperationsAndTechnologyMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:OperationsAndTechnologyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:OperationsAndTechnologyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221srt:ChiefExecutiveOfficerMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221srt:MinimumMember2024-12-310001573221srt:MaximumMember2024-12-310001573221real:AustinTXAtlantaGAAndMiamiFLMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:FireAtSecaucusNewJerseyAuthenticationCenterMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:FireAtSecaucusNewJerseyAuthenticationCenterMember2024-12-310001573221real:ClassActionsComplaintFiledInSanMateoCountyCaliforniaMember2022-07-282022-07-280001573221real:ClassActionsComplaintFiledInSanMateoCountyCaliforniaMember2021-01-012021-12-310001573221real:ClassActionsComplaintFiledInSanMateoCountyCaliforniaMember2022-10-312022-10-310001573221us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2024-12-310001573221us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2023-12-310001573221us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2019-01-012019-12-310001573221us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2019-01-012019-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221real:ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:WarrantMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:WarrantMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:WarrantMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221srt:MaximumMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221real:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221real:ReportableSegmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:ServiceMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ServiceMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:ServiceMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:ProductMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ProductMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:ProductMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310001573221us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMemberreal:ReportableSegmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001573221real:A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:ConvertibleDebtMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2025-02-100001573221real:A2031ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:ConvertibleDebtMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2025-02-10
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
___________________________________
FORM 10-K
___________________________________
(Mark One)
| | | | | |
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(ad) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024
OR
| | | | | |
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For The Transition Period From To
Commission File Number 001-38953
______________________________________
The RealReal, Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its Charter)
_______________________________________
| | | | | |
| Delaware | 45-1234222 |
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) |
55 Francisco Street Suite 150 San Francisco, CA | 94133 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (855) 435-5893
_______________________________________
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | | Trading
Symbol(s) | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common stock, $0.00001 par value | | REAL | | The Nasdaq Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | o | Accelerated filer | x |
| Non-accelerated filer | o | Smaller reporting company | x |
| Emerging growth company | o | | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. x
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. o
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). o
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No x
The aggregate market value of the common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant was approximately $314,689,544 as of June 28, 2024, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, based on the closing price of the shares of common stock on The NASDAQ Stock Market reported for June 28, 2024. Excludes an aggregate of 9,846,945 shares of the registrant’s common stock held by officers, directors, affiliated stockholders as of June 28, 2024.
The number of shares of Registrant’s Common Stock outstanding as of February 14, 2025 was 111,246,608.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III incorporates information by reference from the definitive proxy statement for the registrant’s 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
Table of Contents
Unless the context suggests otherwise, references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K (the “Annual Report”) to “The RealReal,” the “Company,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to The RealReal, Inc.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws. All statements other than statements of historical fact contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including statements regarding our future results of operations and financial position, business strategy and plans, objectives of management for future operations, long term operating expenses, the opening of additional retail stores in the future, the development of our automation technology, expectations for capital requirements and the use of proceeds from our initial public offering, are forward-looking statements. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements.
In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “may,” “should,” “expects,” “plans,” “anticipates,” “could,” “intends,” “target,” “projects,” “contemplates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “predicts,” “potential” or “continue” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. The forward-looking statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are only predictions. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions described in the section titled “Risk Factors” included under Part I, Item 1A below and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Because forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified, you should not rely on these forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. The events and circumstances reflected in our forward-looking statements may not be achieved or occur and actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. Some of the key factors that could cause actual results to differ from our expectations include:
• our future financial performance, including our expectations regarding our revenue, cost of revenue, operating expenses, and our ability to achieve and maintain future profitability, in particular with respect to the impacts of macroeconomic uncertainty and geopolitical instability;
• our ability to return to historic levels of revenue growth and to effectively expand our operations;
• our ability to achieve anticipated savings in connection with our reduction in workforce and associated real estate reduction plan;
• our ability to successfully implement our growth strategies;
• our strategies, plans, objectives and goals;
• the market demand for authenticated, pre-owned luxury goods and new and pre-owned luxury goods in general and the online market for luxury goods;
• our ability to compete with existing and new competitors in existing and new markets and offerings;
• our ability to attract and retain consignors and buyers;
• our ability to increase the supply of luxury goods offered through our online marketplace;
• our ability to timely and effectively scale our operations;
• our ability to enter international markets;
• the accuracy and reliability of our authentication processes and methods;
• our ability to optimize, operate and manage our authentication centers;
• our ability to develop and protect our brand;
• our ability to comply with laws and regulations;
• our expectations regarding outstanding litigation;
• the reliable performance of our network infrastructure and content delivery process;
• our ability to detect and prevent data security breaches and fraud;
• our expectations and management of future growth;
• our expectations concerning relationships with third parties;
• economic and industry trends, projected growth or trend analysis;
• seasonal sales fluctuations;
• our ability to add capacity, capabilities and automation to our operations; and
• our ability to attract and retain key personnel.
In addition, statements such as “we believe” and similar statements reflect our beliefs and opinions on the relevant subject. These statements are based upon information available to us as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and, although we believe such information forms a reasonable basis for such statements, such information may be limited or incomplete, and our statements should not be read to indicate that we have conducted a thorough inquiry into, or review of, all potentially available relevant information. These statements are inherently uncertain and investors are cautioned not to unduly rely upon these statements. Furthermore, if our forward-looking statements prove to be inaccurate, the inaccuracy may be material. In light of the significant uncertainties in these forward-looking statements, you should not regard these statements as a representation or warranty by us or any other person that we will achieve our objectives and plans in any specified time frame, or at all. Except as required by applicable law, we do not plan to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, whether as a result of any new information, future events or otherwise.
PART I
Item 1. Business.
Overview
The RealReal is the world’s largest online marketplace for authenticated, resale luxury goods. We are revolutionizing luxury resale by providing an end-to-end service that unlocks supply and creates a trusted, curated online marketplace for buyers globally. Since our inception, we have cultivated a loyal and engaged consignor and buyer base through continuous investment in our technology platform, logistics infrastructure and people.
We offer a wide selection of authenticated, primarily pre-owned luxury goods on our online marketplace bearing the brands of thousands of luxury and premium designers. The top-selling luxury designers on our online marketplace include Cartier, Chanel, Christian Dior, Gucci, Hermès, Louis Vuitton, Prada, Rolex, Yves Saint Laurent, Tiffany & Co. and Van Cleef & Arpels. We offer products across multiple categories including women’s fashion, men’s fashion, jewelry and watches. We have built a vibrant online marketplace that we believe expands the overall luxury market, promotes the recirculation of luxury goods and contributes to a more sustainable world.

A strong network effect drives the growth of our online marketplace. As we bring more consignors onto our platform, we unlock more high-quality, luxury supply, which increases our merchandise assortment and attracts more buyers. This, in turn, increases sales velocity and commissions for our consignors. In addition, a meaningful share of our consignors are buyers and vice versa, which creates a differentiated flywheel that enhances the network effect of our online marketplace.
We operate neighborhood retail stores which are typically 1,800 to 3,500 square feet with items for sale reflecting a selection of the Company's online assortment. These smaller footprint neighborhood stores are located in areas we have identified as having a large amount of potential customers. In addition, we operate several larger footprint flagship stores in Los Angeles, California and New York, New York. Our flagship stores are typically 8,000 to 10,000 square feet with thousands of unique items for sale and are located in highly desirable, densely populated locations with strong foot traffic.
Our Market
The existing luxury resale market is outdated, fragmented, difficult to access and laden with counterfeit goods. Primarily due to these challenges, a vast quantity of consignable luxury goods languishes in homes, and buyers can be hesitant to purchase pre-owned luxury goods. We are transforming the luxury resale experience by addressing these challenges.
• We provide a seamless consignment experience enabled by our proprietary technology platform and data. We leverage our proprietary technology and data analytics to provide world-class service, making consignment easy, convenient, reliable and fast. As a result, we unlock luxury supply from first-time consignors, convert consignors who typically consign at local brick-and-mortar shops to our online marketplace and drive high repeat consignment rates. We leverage data from millions of transactions and current market data to optimize pricing and sales velocity for our consignors.
• We offer buyers a vast, yet curated supply of primarily pre-owned luxury goods and instill trust in the buying process. All consigned items are put through our authentication process and thoroughly inspected for quality and condition, which builds trust in our buyer base. This trust drives repeat purchases from our buyer base and instills confidence in first-time buyers to purchase pre-owned luxury goods.
• We also operate stores. Our retail stores are valuable to us in multiple ways as they help us reach higher value consignors and buyers, increase lifetime value, increase average order value, and lower return rates. We also benefit from increased brand awareness that accelerates overall market growth.
Our Competition
We compete with vendors of new and pre-owned luxury goods, including branded luxury goods stores, department stores, traditional brick-and-mortar consignment stores, pawn shops, auction houses, specialty retailers, discount chains, independent retail stores, the online offerings of traditional retail competitors, resale players focused on niche or single categories, as well as technology-enabled marketplaces that may offer the same or similar luxury goods and services that we offer. As the market evolves, new competitors may emerge, including traditional retail competitors who expand their offerings to include resale. We are able to compete for consignors based on our strong market positioning, diverse category and brand offerings, rich data and technology, and advanced authentication capabilities and expertise. Our full service, multi-channel approach provides consignors with convenient consignment options. For more information regarding risks of competitive factors impacting our business, see the information in “Item 1A: Risk Factors”.
Our Consignors
By making consignment easy, convenient, reliable and fast for our consignors, we aim to unlock a vast quantity of desirable, high-quality, primarily pre-owned luxury goods. Our sales professionals remove friction from the consignment process and build lasting relationships with our consignors. In 2024, over 80% of our gross merchandise value ("GMV") came from repeat consignors. Our unique service model incentivizes consumers to consign by making the process easy.
Our sales and service organization is responsible for obtaining exclusive supply for our online marketplace and retail stores. Our sales professionals generate a robust pipeline of new consignors and build lasting relationships, which cannot be easily replicated. They consult on the consignment process and leverage data to advise consignors on pricing, expected selling time and market trends.
• We deliver an end-to-end service experience. We remove friction from the consignment process by providing multiple consignment methods. We offer concierge at-home consultation and pickup, and virtual consultations with consignors. Consignors may also drop off items at our luxury consignment offices. Our retail stores provide an alternative location to drop off consigned items and an opportunity to interact with our authentication experts. Consignors may also utilize our complimentary shipping service to send items directly to our authentication centers.
• We do the work on behalf of consignors. All consigned items are authenticated, written up photographed, priced, sold and fulfilled on behalf of the individual consignor, making the consignment process seamless. Improvements in our automation of authentication, pricing, copywriting and photo retouching have improved the efficiency of our operations.
• We generate high commissions for consignors. Our scale and broad reach combined with our technology-driven online marketplace and proprietary data enable consignors to realize optimal value for their pre-owned luxury goods. In November 2022, we launched a pricing tool for our consignors that provides transparency and detail on commission rates for specific categories and other aspects of the take
rate structure. Our consignors can earn up to 90% of the proceeds from the sale of their consigned items in commissions and achieved an overall commission rate of approximately 62% in 2024.
• We offer a range of payment options for consignors and businesses. Our consignors are generally paid after an item has sold, however, we also offer trade-in terms and “Get Paid Now” options to both businesses we purchase items directly from and individuals who consign their items with us. “Get Paid Now” is a program whereby select items are evaluated, authenticated and priced and the business or consignor receives payment based on this process in advance of the sale of the item.
• We drive rapid monetization. Our online marketplace efficiently matches supply with demand finding optimal balance between sales velocity and consignor earnings. We sell approximately 50% of the products on our online marketplace within 30 days of being listed for sale. In addition, we measure the ratio of demand versus supply in a given period, which we refer to as our online marketplace sell-through ratio. Sell-through ratio is defined as GMV in the measurement period divided by the aggregate initial value of items added to our online marketplace in that period. Our online marketplace sell-through ratio in 2024 was approximately 85%.
Our Buyers
We make it easy for buyers to shop our vast, yet curated selection of authenticated, primarily pre-owned luxury goods. In 2024, we had approximately 1 million active buyers and approximately 88% of our GMV came from repeat buyers. As we continue to unlock exclusive luxury supply, we aim to attract new buyers and drive repeat purchases from our existing buyers.
•We offer a seamless buying experience. Buyers access our omni-channel online marketplace through our website, mobile app and retail stores, enabling them to purchase anytime, anywhere. Our retail stores also offer our buyers a sophisticated shopping experience, in a beautifully designed space, where they can shop our dynamic curation of authenticated pre-owned luxury goods across all of our categories.
•We build trust through our authentication process. We continue to invest and innovate in authentication, both in our people and our technology. We believe we have the most rigorous authentication process in the resale luxury goods marketplace. We have highly trained gemologists, horologists, and brand experts who collectively inspect thousands of items each day. All items pass through a rigorous brand-specific authentication process before they are accepted for consignment. This process includes, among other things, inspecting the item for attributes such as appropriate brand markings, date codes, serial tags and hologram stickers. We use proprietary artificial intelligence ("AI") microphotography to assist in authenticating multiple categories, including high-end handbags. Our gemologists and horologists inspect and authenticate fine jewelry and watches, and each piece we sell comes with an authentication certificate. We utilize state-of-the-art gemological devices, including proprietary gemstone technology, to assist these experts. Additionally, across all of our categories, our experts leverage proprietary item and consignor risk scoring algorithms to assist in authentication. For inventory sold through our drop-ship consignment service that does not pass through our authentication centers, our authentication process includes diligence of our partners and procedures for establishing provenance, as well as quality checks and audits. We have a zero-tolerance policy when it comes to counterfeit goods. Items that are deemed to be counterfeit are removed from our authentication centers.
•We provide access to unique, highly coveted and exclusive products. We provide buyers with access to a vast, yet curated selection of unique, authenticated, pre-owned luxury goods. In 2024, we sold goods bearing the brands of thousands of luxury and premium designers, including highly coveted items such as rare watches and handbags.
•We provide a gateway to luxury brands. We believe we are expanding the overall market for both new and pre-owned luxury goods, as the ability to experience and engage with luxury brands through our online marketplace results in an earlier appreciation for high-quality, well-crafted items, and inspires consumers to purchase new luxury items.
Our Technology
Technology powers all aspects of our business, including our complex, individual stock keeping unit (“single-SKU”) inventory management system. Our supply comes from thousands of individual consignors and businesses across the United States. Given the complexity of our inventory model, we developed AI enabled, specialized, proprietary
applications to optimize inbound processes. We increasingly use AI in our technology platform to automate item attribution, authentication, pricing, copywriting and photo retouching for goods sold through our online marketplace.
Our powerful AI and data analytics capabilities enable us to improve both consignor and buyer experiences. Our online marketplace generates and aggregates hundreds of millions of unique data points, including data from approximately 44.5 million item sales since our inception. Each consigned item also has up to 50 unique attributes. Informed by this data, we have developed proprietary machine learning technology and business processes to optimize our operations, including supply sourcing, merchandising, authentication, pricing and marketing.
Intellectual Property
Our intellectual property, including copyrights and trademarks, is an important component of our business. We rely on trademark, copyright, trade secrets, patents, patent applications, confidentiality agreements and other practices to protect our brands, proprietary information, technologies and processes. We primarily rely on copyright and trade secret laws to protect our proprietary technologies and processes, including the algorithms we use throughout our business. Our principal trademark assets include the registered trademark “The RealReal” and our logos and taglines. Our trademarks are valuable assets that support our brand and consumers’ perception of our services and merchandise. We also hold the rights to the “therealreal.com” Internet domain name and various related domain names, which are subject to Internet regulatory bodies and trademark and other related laws of each applicable jurisdiction. We continually review our development efforts to assess the existence and patentability of new intellectual property and intend to pursue patent protection to the extent we believe it would be beneficial and cost-effective.
We control access to and use of our intellectual property through confidentiality procedures, non-disclosure agreements with third parties and our employment and contractor agreements. We rely on contractual provisions to protect our proprietary technology, brands and creative assets with consignors and buyers.
Seasonality
Historically, we have observed trends in seasonality of supply and demand in our business. Specifically, our supply increases in the third and fourth quarters, and our demand increases in the fourth quarter. As a result of this seasonality, we typically see stronger average order value (“AOV”), and more rapid sell-through in the fourth quarter.
Environmental, Social and Governance
Our stakeholders are essential to our business—shareholders, consignors, buyers, employees and the communities in which we do business. We aspire to operate our business with positive social and environmental impact.
Our board of directors and its committees provide oversight on certain human capital matters. As noted in its charter, our Compensation, Diversity and Inclusion Committee is responsible for reviewing and recommending to our board of directors compensation plans, policies and programs intended to attract, retain and appropriately reward employees, as well as provide oversight of the Company’s policies, programs, and initiatives focusing on leadership and our workforce. Our Corporate Governance and Nominating Committee provides oversight of the Company’s policies, programs and initiatives focusing on social responsibility, including environmental, sustainability, social and human rights matters. Our Audit Committee works closely with our management to discuss current and emerging risks related to our workforce and what steps management is taking to manage and reduce the Company’s exposure to risk. The actions of these committees and the work of our board of directors and management seek to attract, retain and develop a diverse and inclusive workforce that is motivated to achieve the Company’s business objectives.
Our Sustainability Program
We are committed to extending the lifecycle of luxury goods by promoting their recirculation, rather than creating waste. In this way, sustainability is woven into the fabric of our business, and we hope to create a more sustainable future for fashion. Additionally, we believe a growing awareness of the reduced environmental impact of recirculating luxury goods compared to the production of new products significantly contributes to the appeal of consigning and purchasing on our online marketplace.
As we move forward, we strive to continuously review our sustainability commitments, strategies and priorities. Recent sustainability efforts include:
• Fair and As-is Condition Programs. These programs have enabled us to offer more secondhand, luxury items and have the effect of increasing the total number of consigned items in the circular economy. To
aid buyers in assessing the condition of items in our online marketplace, we assign each item a condition level. In the first quarter of 2022, we began accepting items in “fair” condition, which tend to be listed at more accessible price points given their level of wear. In 2023, with demand for items in fair condition remaining strong, we began accepting items in “as-is” condition. Items in “as-is” condition might show extensive signs of wear and may require repair. Even if an item requires repair, it is still likely to displace the purchase of a brand-new item and avoid unnecessary waste.
• Sustainability Task Force. In 2020, we formed a cross-functional Sustainability Task Force to identify projects throughout the organization that have the potential to reduce our environmental impact. The Sustainability Task Force prioritizes high impact projects and aims to embed a focus on sustainability across the organization. The Sustainability Task Force, through several individual working groups, has concentrated its efforts on specific, meaningful topics, including preferred materials, transportation optimization, employee travel, employee experience, reducing energy expenditures, limiting use of packaging materials, and waste. In 2024, the Sustainability Task Force was reorganized to expand its capabilities and increase its membership, and focused on projects related to packaging, employee engagement, and energy efficiency at our authentication centers.
Human Capital Resources
Our employees are guided by our mission to empower consignors and buyers to extend the life cycle of luxury goods. As of December 31, 2024, we had 3,011 full-time equivalent employees. Additionally, we rely on independent contractors and temporary personnel to supplement our workforce, primarily in our authentication centers. None of our employees is represented by a labor union or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We consider our relations with our employees to be positive.
Community
We work to inspire and empower our employees to think creatively and authentically, share their ideas, bring their whole selves to work, and strive for greatness every day. We are committed to providing an equal employment opportunity regardless of race, color, ancestry, religion, sex, national origin, sexual orientation, age, citizenship, marital status, disability, gender identity or expression, or veteran status.
Strategy. We believe that creating a more sustainable future by growing the circular economy requires us to bring different perspectives together. We believe that a more sustainable future is an equitable one, and that growing the circular economy requires us to unlock the power of differences and solve problems together in new and meaningful ways. We are committed to building a strong culture of trust, safety, collaboration, and belonging to fuel our purpose, people and performance.
Engagement. In 2024, we conducted our annual employee engagement survey to better understand employees’ sentiment across a range of topics and factors; management, teamwork, inclusion, and alignment, were among our top scoring factors. In 2024, our engagement efforts focused on well-being, leadership, communication, and inclusion. As part of our work to build a culture of trust, we encourage employees to share real-time feedback on culture, bias, discrimination and harassment, or behavior that does not reflect our values and policies through our company-wide employee reporting tool.
The RealReal, Inc. Foundation. The RealReal, Inc. Foundation was founded at the time of our initial public offering in 2019 with the aim of advancing equity in the communities in which we operate through access to education. Since its formation, the foundation has provided annual college scholarships and supported numerous community organizations, including the Success Bound Youth Leadership Academy, the Secaucus Youth Alliance, Enterprise for Youth, Friendly House, Education Forward Arizona and the Virgil Abloh™ "Post-Modern" Scholarship Fund, which aims to preserve his vision for a more diverse and equitable fashion industry.
Talent Development and Training
We believe that the training and development of our employees is critical to our long-term success. We offer a variety of employee training programs, including training specific to business functions, enabling us to provide our consignors and buyers with a consistent luxury experience. For example, we support our sales professionals by providing a three-week virtual onboarding sequence conducted through peer-to-peer, facilitated and self-learning sessions, followed by continuous professional development programs.
Our authentication teams receive training based on expertise level. Entry-level authenticators receive approximately 40 to 80 hours of training depending on their specialty in fashion or fine jewelry. Progression through the authentication training program is an additional minimum of 80 hours of training and at least three months per level. Training hours and tenure increase with expertise, with a Graduate Gemologist certification from GIA required in the highest levels of specialty in fine jewelry.
Each employee receives training appropriate to the scope and nature of their role. Our Fair Labor Standards Act-exempt employees receive an annual performance review and our people managers have quarterly meetings with their employees to address performance and development, as appropriate. As a part of our onboarding program, we have developed an engagement monitoring plan for our employees in the form of personal check-ins and questionnaires.
Health, Safety and Wellness
We are committed to ensuring the health and safety of all employees and require compliance with all applicable local laws and regulations governing working conditions, working hours, fair wages, and compensation.
We recognize that in addition to minimizing work-related injuries and illness, a safe and healthy work environment supports employee retention and morale and enhances the quality of products and services. We treat all applicable health and safety regulations as a minimum standard as we are committed to high standards for our working environments that protect the well-being of all employees. We encourage consultation and cooperation between management and employees in developing occupational health and safety mechanisms through ongoing dialogue. We expect senior management to integrate health and safety mechanisms in business activities and monitor the program’s effectiveness. In 2022, we implemented the REAL Respect program, which provides community guidelines for our employees, consignors and buyers aimed toward creating a positive and safe experience for all. In 2023, we launched TRR Secure, a smartphone security application that enables field employees to discreetly contact emergency services via multiple channels if they are in a situation that makes them feel uneasy, unsafe or uncomfortable.
We continued to focus on employees’ overall well-being in 2024 through a range of programs that support access to care, along with resources and tools to address the following pillars of wellness: physical, mental/emotional, financial, and community.
Corporate Information
We were incorporated in the state of Delaware in March 2011. Our principal executive offices are located at 55 Francisco Street, Suite 150, San Francisco, California 94133, and our telephone number is (855) 435-5893. You may access our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and other reports (and amendments and exhibits thereto) filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), as well as proxy statements filed by us, free of charge on our website at www.therealreal.com, as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. Information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website is not incorporated by reference into this or any other report we file with, or furnish to, the SEC, and you should not consider information on our website to be part of this or any other report we file with, or furnish to, the SEC. Such periodic reports, proxy statements and other information are also available at the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
The RealReal and other trademarks or service marks of The RealReal, Inc. appearing in this Annual Report are the property of The RealReal, Inc. This Annual Report contains additional trade names, trademarks and service marks of others, which are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, the trademarks, service marks, logos and trade names referred to in this Annual Report are without the ® and ™ symbols, but such references are not intended to indicate that we will not assert our rights in these trademarks, service marks and trade names.
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
Risk Factors Summary
The following is a summary of the principal risks and uncertainties described in more detail in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry
•We have a history of losses and we may not be able to achieve or maintain profitability in the future.
•The savings plan we implemented in February 2023 may not result in anticipated savings.
•We may not return to historic levels of revenue growth rate or effectively manage growth or new opportunities.
•We may not accurately forecast revenue and appropriately plan our expenses.
•We have experienced seasonal and quarterly variations in our revenue and operating results.
•Greater than expected product returns may exceed our reserve for returns.
•We may require additional capital to support our business growth.
•Public health emergencies or outbreaks of epidemics, pandemics, or contagious diseases have adversely affected, and could in the future, adversely affect our business and the business of our consignors and buyers.
•The failure of any bank in which we deposit our funds could reduce the amount of cash we have available.
Risks Relating to Our Strategy
•We may be unable to execute on our retail strategy.
•Expansion of our operations internationally will require significant management attention and resources.
•Our growth strategies may not be successful.
Risks Relating to Supply
•We may not be able to obtain sufficient new and recurring supply of pre-owned luxury goods.
•We may be unable to attract and retain talented sales professionals.
•Our growth and supply of product offerings are enhanced by our ability to maintain our brand partnerships.
Risks Relating to Demand
•Our continued growth depends on attracting new and retaining repeat buyers.
•National retailers and brands set their own retail prices and promotional discounts on new luxury goods, which could adversely affect our value proposition to consignors and buyers.
•We must successfully gauge and respond to changing preferences among our consignors and buyers.
•We may be unable to replicate our business model for newer categories of goods.
•We rely on consumer discretionary spending, which is adversely affected by economic downturns.
•Our industry is highly competitive and we may not be able to compete effectively.
Risks Related to Marketing and Brand Management
•Our success depends on the accuracy and reliability of our authentication processes and methods.
•We may not succeed in promoting and sustaining our brand.
•Our marketing and advertising activity may fail to efficiently drive growth in consignors and buyers.
•We rely on third parties to drive traffic to our website.
•Use of social media, emails and text messages may adversely impact our reputation or subject us to fines.
•The public disclosure of our ESG (as defined below) metrics and goals may subject us to risks.
Risks Related to Our Merchandising and Fulfillment
•We may not be able to attract, train and retain specialized personnel and skilled employees.
•We may not be able to identify and lease authentication centers in suitable geographic regions.
•We may experience damage or destruction to our authentication centers or retail stores in which we store of the majority of the consigned luxury goods we offer through our online marketplace.
•Shipping is a critical part of our business and any changes in our shipping arrangements, costs, interruptions in shipping or damage to products in transit could adversely affect our operating results.
•We may be unable to successfully leverage technology, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, to automate and drive efficiencies in our operations.
Risks Related to Data Security, Privacy and Fraud
•We rely on third parties to host our website and mobile app and to process payments.
•Failure of our data or cyber security could cause us to incur unexpected expenses or compromise our data assets.
•We may incur significant losses from fraud.
Risks Related to Our Employees
•We may be unable to attract and retain key personnel or effectively manage leadership succession.
•Labor-related matters, including labor disputes, may adversely affect our operations.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
•If we cannot successfully protect our intellectual property, our business could suffer.
Risks Relating to Litigation and Regulatory Uncertainty
•We are currently, and may be in the future, party to lawsuits and other claims.
•Our use and other processing of personal information and other data is subject to laws and obligations.
•Regulation of “cookie” tracking technologies or changes in such technologies could harm our business and operating results.
•We pay or collect sales taxes in all jurisdictions which require such taxes.
•Failure to comply with applicable laws or regulations may subject us to fines, penalties, loss of licensure, registration, facility closures or other governmental enforcement action.
•Application of existing tax laws, rules or regulations are subject to interpretation by taxing authorities.
•Our ability to use our net operating loss carryforwards and certain other tax attributes may be limited.
•If our internal control over financial reporting or our disclosure controls and procedures are not effective, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results, prevent fraud or file our periodic reports in a timely manner, which may cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information.
Risks Related to Ownership of Our Common Stock
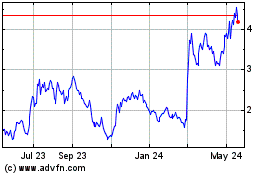
•The market price of our common stock may be volatile or may decline steeply or suddenly regardless of our operating performance and we may not be able to meet investor or analyst expectations.
•Short sellers of our stock may be manipulative and may drive down the market price of our common stock.
•Delaware law and provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws could make a merger, tender offer or proxy contest difficult, thereby depressing the trading price of our common stock.
•Our certificate of incorporation designates the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware located within the State of Delaware as the exclusive forum for substantially all disputes between us and our stockholders.
Risks Related to Our Outstanding Notes and Warrants
•We have incurred a significant amount of debt and may incur additional indebtedness in the future.
•The indentures governing our Notes (as defined below) contain restrictions and other provisions that may make it more difficult to execute our strategy or to effectively compete, or that could materially affect our financial position.
•Transactions relating to the Convertible Senior Notes or the Warrants may dilute the ownership interest of our stockholders.
•The conversion of the Convertible Senior Notes or the cash settlement of the Warrants, if triggered, may adversely affect our financial condition and operating results.
•The accounting method for the Warrants materially affects our reported financial results.
•The accounting method for the Convertible Senior Notes materially affects our reported financial results.
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should consider and read carefully all of the risks and uncertainties described below, together with all of the other information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and in our other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC"). The risks described below are not the only ones we face. The occurrence of any of the following risks or additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently believe to be immaterial could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry
We have a history of losses and we may not achieve or maintain profitability in the future.
We experienced net losses of $196.4 million, $168.5 million, and $134.2 million in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively, and as of December 31, 2024 we had an accumulated deficit of $1,253.8 million. Our key initiatives currently include growing profitable supply, improving efficiencies, and pursuing new revenue streams. If those initiatives or our investments do not prove successful or our market does not develop as we expect, we may not achieve profitability on the timeline we expect or at all, and may continue to experience losses over the long term. Any failure to increase our revenue sufficiently to keep pace with our investments and other expenses could prevent us from achieving or maintaining profitability or positive cash flow on a consistent basis. If we are unable to successfully address these risks and challenges as we encounter them, our business, financial condition and operating results could be adversely affected. We cannot assure you that we will ever achieve or sustain profitability and may continue to incur significant losses going forward.
The savings plan we implemented in February 2023 may not result in anticipated savings, could result in total costs and expenses that are greater than expected and could disrupt our business.
In February 2023, we implemented a reduction in workforce of approximately 7% and a reduction in our real estate presence to reduce our operating expenses. See “Note 11 – Restructuring” for further details.
We may not realize, in full or in part, the anticipated benefits, savings and improvements in our operating structure from these efforts due to unforeseen difficulties, delays or unexpected costs. If we are unable to realize the expected operational efficiencies and cost savings from these efforts, our operating results and financial condition, and cash flows would be adversely affected. In addition to the February 2023 workforce reduction, from time to time we have made workforce reductions, as part of cost cutting initiatives or otherwise. We cannot guarantee that we will not have to undertake additional workforce or real estate reductions in the future.
Furthermore, we may also discover that the workforce reduction will make it difficult for us to pursue new opportunities and initiatives and require us to hire qualified replacement personnel, which may require us to incur additional and unanticipated costs and expenses. We may further discover that, despite the implementation of our workforce reduction, we may require additional capital to continue expanding our business, and we may be unable to obtain such capital on acceptable terms, if at all. In addition, our real estate reduction plan could harm our brand reputation, result in unanticipated charges or disputes, constrain our ability generate new supply, and reduce demand in buyers. If we decide to open retail locations in the future, we may not be able to secure leases on comparable terms in comparable locations. Our failure to successfully accomplish any of the above activities and goals may have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We may not be able to return to historic levels of revenue growth rate or effectively manage growth or new opportunities.
Our past revenue growth should not be considered indicative of future performance. While we experienced revenue growth in 2019, 2021, 2022 and 2024, our revenue for fiscal 2023 decreased compared to 2022. Our online marketplace represents a substantial departure from the traditional resale market for luxury goods. While our business grew rapidly prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the resale market for luxury goods may not continue to develop in a manner that we expect or that otherwise would be favorable to our business. Changes in our market make it difficult to assess our future performance. You should consider our business and prospects in light of the risks and difficulties we may encounter. As we grow our business, our revenue growth rates may continue to decline in future periods due to a number of factors, including our inability to attract and retain consignors, general economic conditions, including a recession, increased market adoption against which future growth will be measured, increasing competition, slowing demand for items on our online marketplace from existing and new customers, changes to our commission structure, take rate or business model, changes in our total product mix, including as a result of our strategic shift to focus on higher value items or our failure to capitalize on growth opportunities. Our rapid growth has placed significant demands on our management and our operational and financial infrastructure. Continued growth could strain our ability to maintain reliable service levels for our consignors and buyers, develop and improve our operational, financial and management controls, enhance our reporting systems and procedures and recruit, train and retain highly skilled personnel. Failure to effectively manage the growth of our business and operations would negatively affect our reputation and brand, business, financial condition and operating results.
We may not accurately forecast revenue and appropriately plan our expenses.
We make certain assumptions when planning our expenses based on our expected revenue. These assumptions are partly based on historical results. We rely on a constant supply of consigned goods to sustain and grow our revenue, making our revenue in any given period difficult to predict. Because our operating expenses are relatively fixed in the short term, any
failure to achieve our revenue expectations would have a direct adverse effect on our business, financial condition, operating results and the price of our stock.
We have experienced seasonal and quarterly variations in our revenue and operating results.
Our business is seasonal and historically we have realized a disproportionate amount of our revenue and earnings for the year in the fourth quarter as a result of the holiday season and seasonal promotions. We expect this to continue in the future. If we experience lower than expected revenue during any fourth quarter, it may have a disproportionately large impact on our operating results and financial condition for that year. In any given year, our seasonal sales patterns may become more pronounced, strain our personnel or reduce our profit margins in a given period, which could substantially harm our business, operating results and financial condition. In anticipation of increased activity during the fourth quarter, we also incur significant additional expenses, including additional marketing spend and staffing in our sales and customer support operations. In addition, we may experience an increase in our shipping costs due to complimentary upgrades, split-shipments and additional long-zone shipments necessary to ensure timely delivery for the holiday season. Such increased costs may harm our profitability, especially if we are experiencing lower than expected revenue during the holidays.
Greater than expected product returns may exceed our reserve for returns.
We generally allow buyers to return certain purchases from our website and retail stores under our return policy. We record a reserve for returns against proceeds we receive from the sale of goods on our online marketplace and retail stores when we calculate revenue. We estimate this reserve based on historical return trends and our current expectations. The introduction of new products in the retail market, changes in consumer confidence or other competitive and general economic conditions, and higher than expected returns in connection with fourth quarter holiday buying may cause actual returns to exceed our reserve for returns. Any significant increase in returns that exceeds our reserves could adversely affect our revenue and operating results.
We may require additional capital to support business growth. If such capital is not available to us, our business operating results and financial condition may be harmed.
We may require additional funds to support our growth and respond to business challenges. To support our future growth, we may need to further develop our online marketplace services, grow our retail presence, expand our categories of pre-owned luxury goods, enhance our operating infrastructure, expand the markets in which we operate and potentially acquire complementary businesses and technologies. Accordingly, we may need to engage in equity or debt financings to secure additional funds, which may result in significant dilution to existing stockholders or the granting of new equity securities which have rights, preferences and privileges superior to those of holders of our common stock. Our 2029 Notes (as defined below) contain, and any other debt financing secured by us could also contain, restrictive covenants relating to our capital-raising activities and other financial and operational matters, which may make it more difficult for us to obtain additional capital and to pursue business opportunities in the future. In addition, we may not be able to obtain additional financing on terms favorable to us, if at all. If we are unable to obtain financing on terms satisfactory to us when we require it, our ability to support our business growth and to respond to business challenges could be significantly limited, and our business and prospects could fail or be adversely affected.
Public health emergencies or outbreaks of epidemics, pandemics, or contagious diseases such as the COVID-19 pandemic have adversely affected, and could in the future, adversely affect our business and the business of our consignors and buyers.
An epidemic, pandemic, or similar serious public health issue (a "public health issue"), and the measures undertaken by governmental authorities to address it, could significantly disrupt or prevent us from operating our business in the ordinary course for an extended period, and thereby, and/or along with any associated economic and/or social instability or distress, have a material adverse impact on our results of operations, cash flows and financial condition.
The extent to which a public health issue could impact our business, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity will depend on numerous evolving factors, known and unknown, that we cannot predict, including the duration and scope of the public health issue; government, business and individual actions that have been and continue to be taken in response; the impact of the public health issue on national and global economic activity; disruption of the financial and labor markets, including the possibility of a national or global economic recession or depression; the limitations on operations requiring employees to perform their duties in-person, such as our warehouse operations; the potential for shipping difficulties, including delayed deliveries to our buyers; and weakened consumer demand. Additionally, the increased number of employees who work remotely during a public health emergency or outbreak could introduce additional operational risk, such as an increased vulnerability to cyber-attacks, and harm productivity and collaboration. In addition, the risks and uncertainties described elsewhere in this “Risk Factors” section may be exacerbated by a public health issue.
The failure of any bank in which we deposit our funds could reduce the amount of cash we have available to pay distributions and make additional investments.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation only insures amounts up to $250,000 per depositor. It is likely that we will have cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash deposited in certain financial institutions in excess of federally insured levels. If any of the banking institutions in which we deposit funds ultimately fails, we may lose any amounts of our deposits over federally insured levels. The loss of our deposits could reduce the amount of cash we have available to distribute or invest and could result in a decline in the value of our stockholders' investment.
Risks Relating to Our Strategy
We may be unable to execute on our retail growth strategy.
We currently operate a limited number of retail stores. We believe that retail stores are effective at raising brand awareness with consignors and buyers and generating new supply. We also believe that an expansion of our brick-and-mortar presence complements our online marketplace and strengthens the omni-channel consigning and buying experience. We have in the past and may in the future continue to reassess our retail footprint and adjust our retail strategy in particular geographies. The opening and closing of retail stores brings operational challenges. We may have to enter into long-term leases before we know whether our retail strategy or a particular geography will be successful. We face a number of challenges in opening new stores, including locating retail space having a cost and geographic profile that will allow us to operate in highly desirable shopping locations, hire in-store talent and expand our retail operations in a cost-effective manner. We also have faced and may in the future face a number of challenges in closing existing stores, which may include significant exit costs, managing lease obligations and employee-related costs, including in connection with our recently announced real estate reduction plan. Closing existing stores may also limit our ability to attract new members, generate new supply and increase demand. We must provide our consignors and buyers with a consistent luxury experience across our retail locations. In the past, our stores have been the target of theft and have also experienced property damage. Any such future incidents may result in a disruption to our retail operations and significant costs if not covered by our insurance policies. In addition, the offering of unique, single-SKU products creates supply chain, merchandising and pricing challenges, as we must select the right product mix for each individual store while continuing to manage inventory at our authentication centers. If we are not able to manage or execute on our retail strategy, our business, operating results, prospects and reputation may be harmed.
Expansion of our operations internationally will require significant management attention and resources.
While we have members from outside the United States who purchase items from our online marketplace, we have not expanded our physical operations internationally. If we choose to do so, we would need to adapt to and would be subject
to new risks relating to various local cultures, languages, standards, laws and regulations and policies. Our business model we employ may not appeal to consignors and buyers outside of the United States. Furthermore, to succeed with clients in international locations, it will be necessary to locate authentication centers in foreign markets and hire local employees in those markets, and we may have to invest in such facilities before demonstrating that we can successfully run operations outside of the United States. If we invest substantial time and resources to establish and expand our operations internationally and are unable to do so successfully and in a timely manner, our operating results would suffer.
Our growth strategies may not be successfully implemented, help us achieve profitability or generate
sustainable revenue and profit.
Our growth strategies, including our initiatives to pursue new revenue streams, are evolving. For example, we have recently introduced third party advertising on our online marketplace. However, these efforts might not be successful, have been, in the case of our third-party advertising, and in other cases perceived negatively by potential consignors and buyers using our online marketplace, or we may not be able to pursue them at all. We may limit the user data shared with third-party advertising partners, which could have a negative effect on our ability to maximize our advertising revenue. In addition, we seek to balance new initiatives with our desire to provide an optimal user experience on our online marketplace, and we may not be successful in achieving a balance that continues to retain and attract consignors and buyers. If our growth strategies, including our initiatives to pursue new revenue streams, are not successful, do not generate sustainable revenue or help us achieve profitability, it could have a material adverse impact on our business and operating results.
Risks Relating to Supply
We may not be able to obtain sufficient new and recurring supply of pre-owned luxury goods.
Our success depends on our ability to generate a consistent supply of luxury goods to sell through our stores and online marketplace. To do this we must cost-effectively attract, retain and grow relationships with consignors. To expand our consignor base, we must appeal to and engage individuals new to consignment, or who have consigned through traditional brick-and-mortar shops but are unfamiliar with our business. We find new consignors by converting buyers utilizing our online marketplace, shopping in our retail stores, or utilizing our luxury consignment offices. We also reach new consignors through paid advertising, marketing materials, digital marketing, referral programs, organic word-of-mouth and other methods, such as mentions in the press, Internet search engine results and through our brand partnerships. We cannot be certain that these efforts will yield new consignors or be cost-effective. Moreover, new consignors may not choose to consign with us a second time or as frequently, or consign as many items or the same value of items, as has historically been the case with existing consignors. Therefore, the revenue generated from new consignors may not be as high as the revenue generated historically from our existing consignors or as high as we expect. Most of the luxury goods we offer through our online marketplace are initially sourced from consignors who are individuals. As a result, we may be subject to periodic fluctuations in the number, brands and quality of goods sold through our online marketplace on behalf of our consignors. In addition, a significant number of our new and existing consignors greatly prefer our concierge consultation method for consigning luxury goods, which involves our sales professionals meeting with our consignors in their homes. In November 2022, we updated our take rate structure with the goals of optimizing take rate, limiting consignment of lower value items, and increasing supply of higher value items. If our updated take rate structure is not successful in increasing the consignment of such items, our brand and reputation could be adversely affected, we may generate less revenue than expected, and we may choose to further refine the structure. We have a buy upfront program in an effort to generate additional supply. If we fail to attract new consignors or drive repeat consignments in a cost-effective manner, or fail to convert buyers to consignors, our ability to grow our business and our operating results would be adversely affected.
We may be unable to attract and retain talented sales professionals.
We rely on our sales professionals to drive our supply of luxury goods by identifying, developing and maintaining relationships with our consignors. The process of identifying and hiring sales professionals with the combination of skills and attributes required in these roles can be difficult and can require significant time. In addition, competition for qualified employees and personnel in the retail industry is intense and turnover amongst our sales professionals within a few years is not uncommon. If we are not successful in attracting and retaining effective sales professionals, the quantity and quality of the luxury goods sold through our online marketplace may be negatively impacted, which would have a material adverse effect on our business and operating results.
Our growth and supply of product offerings are enhanced by our ability to maintain our brand partnerships.
We have established brand partnerships with certain brands, and may seek to add additional brand partnerships in the future. We believe that these partnerships are important to increasing our supply and growing our business. We make direct purchases of products from our brand partners, which helps us to drive supply and expand our product offerings. To establish and maintain these partnerships, brands must trust, among other things, our authentication process and that we provide a level of customer service that matches those generally provided by luxury brands, for both consignors and buyers, online and in-store. If we are unable to provide value to our existing partners or to add new partners, the growth of our business may be harmed.
Risks Relating to Demand
Our continued growth depends on attracting new and retaining repeat buyers.
To expand our buyer base, we must appeal to and attract buyers who do not typically purchase luxury goods, who have historically purchased only new luxury goods or who used other means to purchase pre-owned luxury goods, such as traditional brick-and-mortar consignment shops, auction houses and the websites of other secondary marketplaces. We reach new buyers in part through television and digital advertising, other paid marketing, press coverage, referral programs, organic word of mouth, our brand partnerships and other methods of discovery, such as converting consignors to buyers. We expect to continue investing in these and other marketing channels in the future and cannot be certain that these efforts will yield more buyers or be cost-effective. Moreover, new buyers may not purchase through our online marketplace as frequently or spend as much with us as historically has been the case with existing buyers. As a result, the revenue generated from new buyer transactions may not be as high as the revenue generated from transactions with our existing buyers. Failure to attract new buyers and to maintain relationships with existing buyers would adversely affect our operating results and our ability to attract and retain consignors.
National retailers and brands set their own retail prices and promotional discounts on new luxury goods, which could adversely affect our value proposition to consignors and buyers.
National retailers and brands set pricing for new luxury goods that they sell and from time to time offer sales and promotional pricing, particularly during the fourth quarter holiday season, when we have historically made a substantial portion of our annual sales. Promotional pricing by these parties may lower the value of products consigned with us and our inventory and, in turn, reduce the value proposition for both our consignors and buyers. We have in the past experienced a reduction in our GMV and AOV due to fluctuations in the price of new luxury goods sold by retailers and brands, and we could experience similar reductions and fluctuations in the future. However, the timing and magnitude of such discounting can be difficult to predict and can be brought on by unique factors such as a retailer or brand going out of business and liquidating its inventory, which may happen to a greater extent as a result of macroeconomic uncertainty, inflation, geopolitical instability due in part to the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, the Israel-Hamas war and weakened consumer demand. Any of the foregoing risks could adversely affect our business, financial condition and operating results.
We must successfully gauge and respond to changing preferences among our consignors and buyers.
Our success is in large part dependent upon our ability to anticipate and identify trends in the market for pre-owned luxury goods in a timely manner and to obtain consignments of luxury goods that address those trends. We use data science to predict consignor and buyer preferences, and there can be no assurance that our data science will accurately anticipate consignor or buyer needs. Our business model limits our responsiveness to changing preferences, as the majority of our inventory consists of unique, single-SKU items. While we attempt to source goods that complement our existing inventory, we cannot ensure we will do so successfully. To the extent we do not accurately predict and successfully respond to the evolving preferences of our consignors and buyers, our ability to grow our business and our operating results would be adversely affected.
We may be unable to replicate our business model for newer categories of consigned goods or different product mixes of consigned goods.
In November 2022, we updated our take rate structure with the goals of optimizing take rate, limiting consignment of lower value items, and increasing supply of higher value items. If such higher value items are not attractive to our existing consignors or buyers, or if such items do not attract new consignors or buyers, our revenues may fall short of expectations, our brand and reputation could be adversely affected and we may incur expenses that are not offset by revenues. In addition, our business may be adversely affected if we are unable to attract new and repeat consignors that supply the necessary high-quality, appropriately priced and in-demand luxury merchandise in this high value category. Additionally, as we enter into new categories, potential consignors may demand higher commissions than our current categories, which would adversely affect our take rate and operating results. Expansion of our offerings may also strain our management and operational resources, specifically the need to hire and manage additional authentication and market experts. We may also face novel challenges in our authentication process and methods as we expand our product offerings. In addition, we may experience greater competition in specific categories from companies that are more experienced in these categories. If any of these were to occur, it could damage our reputation, limit our growth and have an adverse effect on our operating results.
We rely on consumer discretionary spending, which is adversely affected by economic downturns, including economic recession or depression, and other macroeconomic conditions or trends.
Our business and operating results are subject to global economic conditions and their impact on consumer discretionary spending, particularly in the luxury goods market. Some of the factors that may reduce luxury spending include economic downturns, including economic recession or depression, high levels of unemployment, higher consumer debt levels, higher levels of inflation, reductions in net worth, declines in asset values, including home values, and related market and economic uncertainty, including as a result of geopolitical instability and disruptions in the financial industry. Many of these factors have occurred, and may occur in the future, as a result of macroeconomic uncertainty, rising interest rates, inflationary pressures, credit constraints and geopolitical instability due in part to the conflict between Russia and Ukraine and the Israel-Hamas war. Such economic uncertainty and the resulting decrease in the rate of new luxury goods purchases in the primary market may have a corresponding impact on luxury resale, which could manifest in a number of ways, including fewer individuals choosing to consign their goods with us, resulting in a decrease of items available in our online marketplace, fewer individuals choosing to buy pre-owned luxury goods, resulting in lower active buyer growth and order volume, and lower AOV due to a combination of lower average selling price per item and/or fewer items per average order, any of which could have an adverse effect on our business and operating results.
Additionally, adverse economic changes could reduce consumer confidence, and could thereby negatively affect our operating results. In the event of a prolonged economic downturn or acute recession, significant inflation, or decreased supply, consumer spending habits could be adversely affected, and we could experience lower than expected revenue. Any of these developments could harm our business, financial condition and operating results.
Our industry is highly competitive and we may not be able to compete effectively.
We compete with vendors of new and pre-owned luxury goods, including branded luxury goods stores, department stores, traditional brick-and-mortar consignment stores, pawn shops, auction houses, specialty retailers, discount chains, independent retail stores, the online offerings of traditional retail competitors, resale players focused on niche or single categories, as well as technology-enabled marketplaces that may offer the same or similar luxury goods and services that we offer. Many of our competitors have longer operating histories, larger fulfillment infrastructures, greater brand recognition and technical capabilities, faster or lower-cost shipping, larger selections of goods for sale, greater financial, marketing, institutional and other resources and larger buyer bases than we do. As the market evolves, new competitors may emerge, including traditional retail competitors who expand their offerings to include resale. Some of our competitors may have greater resources than we do, which may allow them to derive greater revenue and profits from their existing buyer bases, acquire consignors at lower costs, achieve more favorable total product mixes or respond more quickly than we can to new or emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, and changes in consumer shopping behavior or preferences. These competitors may also adopt more aggressive pricing policies, commission structures or take rates, which may allow them to build larger consignor or buyer bases or generate revenue from their existing buyer bases more effectively than we do. New competitors may force us to decrease our take rates to remain competitive and negatively impact on our financial performance. If we fail to respond to competition effectively, our business and operating results may be adversely affected.
Risks Relating to Marketing and Brand Management
Our success depends on the accuracy and reliability of our authentication processes and methods.
Our success depends on our ability to accurately and cost-effectively determine whether an item offered for consignment is an authentic product or genuine gemstone, piece of jewelry or work of art. From time to time, we receive counterfeit goods for consignment. While we continue to invest and innovate heavily in our authentication processes and methods, and we reject any goods we believe to be counterfeit, we cannot be certain that every counterfeit item will be identified. In addition, when our authentication method does not involve taking physical possession of goods prior to the sale, our ability to identify counterfeits may decrease, and order cancellations may increase. As the sophistication of counterfeiters increases, it may be increasingly difficult to identify counterfeit products. We refund the cost of a product to a buyer if the buyer questions its authenticity and returns the item. The sale of any counterfeit goods may damage our reputation as a trusted online marketplace for authenticated, pre-owned luxury goods which may impact our ability to attract and maintain consignors, buyers and brand partners. Additionally, we have been and may in the future be subject to negative press or public allegations, including on social media, that our authentication processes and methods are inadequate. Any material failure or perceived failure in our authentication processes and methods could cause buyers and consignors to lose confidence in our platform and adversely affect our revenue.
We may not succeed in promoting and sustaining our brand.
We believe that growing The RealReal brand is critical to driving consignor and buyer engagement as well as attracting brand partners. An important goal of our brand promotion strategy is establishing and maintaining trust with our consignors, buyers and brand partners. Growing our brand will depend largely on our ability to continue providing our consignors with service that is consistent with the level of luxury associated with the goods they are consigning and delivering value for the goods they consign, all in a timely and consistent manner. For buyers, growing our brand requires that we foster trust through authentication, timely and reliable fulfillment of orders, and responsive and effective customer service. To establish and maintain relationships with existing and future brand partners, brands must trust our authentication process and that we provide a level of customer service that matches those generally provided by luxury brands, for both consignors and buyers, online and in-store. If we fail to provide consignors or buyers with the service and experience they expect, or experience consignor or buyer complaints or negative publicity about our products, services, delivery times or customer support, whether justified or not, the value of our brand would be harmed and our business may suffer.
Our marketing and advertising activity may fail to efficiently drive growth in consignors and buyers.
Our future growth and profitability depend in large part upon the effectiveness and efficiency of our marketing, promotion, public relations and advertising programs. We closely monitor the effectiveness of our advertising campaigns and changes in the advertising market, and adjust or re-allocate our advertising spend across channels, customer segments and geographic markets in real-time in an effort to optimize the effectiveness of these activities. We may increase marketing or advertising spend in future periods to drive growth. Even if our marketing and advertising expenses result in increased sales, the increase might not offset our related expenditures. We also face the unique challenge of attracting consignors and buyers to our online marketplace who may be unfamiliar with both our brand and our consignment business model. If we struggle to attract new consignors and buyers to our luxury resale model, or are unable to maintain our marketing and advertising channels on cost-effective terms or replace or supplement existing marketing and advertising channels with similarly or more effective channels, our marketing and advertising expenses could increase substantially, our consignor and buyer base could be adversely affected, and our business, operating results, financial condition and brand could suffer.
We rely on third parties to drive traffic to our website.
We rely in part on digital advertising, including search engine marketing, to promote awareness of our online marketplace, grow our business, attract new consignors and buyers and increase engagement with existing consignors and buyers. In particular, we rely on search engines and major mobile app stores as important marketing channels. If search engines change their algorithms, terms of service, display or the featuring of search results, determine we are out of compliance with their terms of service or if competition increases for advertisements, we may be unable to cost-effectively add consignors and buyers to our website and apps, which would harm our business, operating results and prospects.
Use of social media, emails and text messages may adversely impact our reputation or subject us to fines.
We use social media, emails, push notifications and text messages as part of our omni-channel approach to marketing. As laws and regulations evolve to govern the use of these channels, the failure by us, our employees or third parties acting at our direction to comply with applicable laws and regulations in the use of these channels could adversely affect our reputation or subject us to fines or other penalties. In addition, our employees or third parties acting at our direction may knowingly or inadvertently make use of social media in ways that could lead to the loss or infringement of intellectual property, as well as the public disclosure of proprietary, confidential or sensitive personal information of our business, employees, consignors, buyers or others. Information concerning us or our consignors and brands, whether accurate or not, may be posted on social media platforms at any time. The harm may be immediate without affording us an opportunity for redress or correction and could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, operating results, financial condition and prospects.
The public disclosure of our Environmental, Social and Governance (“ESG”) metrics and goals may subject us to risks.
We voluntarily report certain metrics and goals for ESG. This transparency is consistent with our commitment to operate our business with positive economic, social, and environmental impact. The perception held by our consignors or buyers, other key stakeholders, or the communities in which we do business may depend, in part, on the metrics and goals we have chosen to aspire to and whether or not we meet our goals on a timely basis, if at all. Our ability to achieve any stated goal, target or objective is subject to numerous factors and conditions, many of which are outside of our control. Also, by electing to set goals and publicly disclose our ESG metrics, we may face increased scrutiny related to our ESG activities.
In addition, we may be required to disclose various ESG metrics, progress against goals and other detailed information under applicable laws and regulations. For example, the State of California has adopted new climate change disclosure requirements, which mandate public disclosure of certain greenhouse gas emissions data and climate-related financial risk reports. Our compliance with these and other ESG-related laws, regulations and policies could be costly, and any failure to meet our goals, change in our ESG goals, priorities or strategies, change in or evolution of our methodologies for reporting ESG metrics, adjustment to previously reported information, including to reflect new or evolved methodologies for reporting ESG metrics, or perception that we fail to act responsibly in the areas in which we report, may negatively affect our reputation and the value of our brand, including by impacting employee engagement and retention, the willingness of our consignors and buyers and our partners and vendors to do business with us, or investors’ willingness to purchase or hold shares of our common stock, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial performance, and growth. Our methodologies, processes and controls for reporting ESG metrics across our operations are evolving along with multiple disparate standards for identifying, measuring and reporting ESG metrics and such standards may change over time.
Risks Related to Our Merchandising and Fulfillment
We may not be able to attract, train and retain specialized personnel and skilled employees.
To grow our business, we must continue to improve and expand our merchandising and fulfillment operations, information systems and skilled personnel in the jurisdictions in which we operate so that we have the skilled talent necessary to effectively operate our business. The operation of our business is complex and requires the coordination of multiple functions that are highly dependent on numerous employees and personnel. Each luxury item that we offer through our online marketplace is unique and requires multiple touch points, including, among others, inspection, evaluation, authentication, photography, pricing, copywriting, application of a unique single-SKU and fulfillment. The market for employees is increasingly competitive and highly dependent on geographic location. Some of our employees have specific knowledge and skills that would make it more difficult to hire replacement personnel capable of effectively performing the same tasks without substantial training. We also provide specific training to our employees in each of our business functions in order to provide our consignors and buyers with a consistent luxury experience. If we fail to successfully locate, hire, train and retain personnel in the future, our operations would be negatively impacted, which would have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and operating results.
We may not be able to identify and lease authentication centers in suitable geographic regions.
We lease facilities to store and accommodate the logistics infrastructure required to merchandise and ship the pre-owned luxury goods we sell through our online marketplace. Our ability to successfully grow our business depends on the availability and cost of leasing additional authentication centers that meet our criteria for a geographic location with access to a large, qualified talent pool as well as square footage, cost and other factors. We currently have four authentication centers - one in Arizona and three in New Jersey. Our capacity needs may grow as our business grows. Optimal space may become scarce, and where it is available, the lease terms offered by landlords may become increasingly competitive. Companies who have more financial resources and negotiating leverage than us may be more attractive tenants and, as a result, may outbid us for the facilities we seek. We also may be unable to renew our existing leases or renew them on satisfactory terms. Failure to secure adequate authentication centers could have an adverse effect on our business and operating results.
We may experience damage or destruction to our authentication centers or retail stores in which we store the majority of the consigned luxury goods we offer through our online marketplace.
We store the majority of the luxury goods we offer through our online marketplace in our authentication centers in Arizona and New Jersey, with a smaller portion of luxury goods offered for sale in our retail stores. Any large scale damage to or catastrophic loss of goods stored in such authentication centers or retail stores or any other location where goods offered through our online marketplace are stored, due to natural disasters, especially as catastrophic weather events become more frequent due to climate change, or man-made causes such as arson or theft would result in liability to our consignors for the expected commission liability for the lost items, reduction in the value of our inventory and a significant disruption to our business. In addition, while we take measures to avoid damage, conduct inspections of consigned goods and inspect returned products, we cannot control items while they are out of our possession or prevent all damage while items are stored in our authentication centers. For example, we have in the past and may in the future experience contamination, such as mold, bacteria, viruses, insects and other pests, in the goods shipped to us by our consignors, which may cause contamination of other goods stored in our authentication centers or while shipping to buyers. We may incur additional expenses and our reputation could be harmed if buyers or potential buyers believe that the luxury goods we offer on behalf of our consignors are not of high-quality or may be damaged or contain contaminants. Additionally, given the nature of the unique consigned luxury goods we offer on our online marketplace, our ability to restore the supply of consigned luxury goods on our online marketplace would take time and would result in a limitation and delay of available supply for buyers which would negatively impact our revenue and operating results. While we carry insurance for the consigned luxury goods stored in these authentication centers as well as for business interruption and loss of income, our liabilities and expenses resulting from a catastrophic event could exceed our maximum insurance coverage amounts which could have a material adverse impact on our business and operating results. For example, in May 2024, we experienced a fire on the roof of one of our leased Secaucus warehouses. As of December 31, 2024, our discussions with the insurance company remain ongoing and our liabilities and expenses are expected to exceed our maximum insurance coverage amounts.
Shipping is a critical part of our business and any changes in our shipping arrangements, costs, interruptions in shipping or damage to products in transit could adversely affect our operating results.
Our business depends on shipping vendors to meet our shipping needs. If we are not able to maintain acceptable pricing and other terms or if our vendors experience performance problems or other difficulties, including as a result of inflation, a labor strike by employees of our shipping vendors or rising shipping costs, it could negatively impact our operating results and our consignors’ and buyers’ experience. If we partner with additional vendors or switch vendors in response to such impact, we may experience a disruption in shipping, which may negatively impact our reputation with consignors and buyers. We face particular challenges in shipping internationally, including delays in shipments and customer service issues relating to the imposition of duties, which can be substantial for luxury items. Because of the seasonality of our business, any disruption to delivery services due to adverse weather, especially as climate change increases the frequency of such adverse weather, could result in delays that could adversely affect our reputation or operational results. In addition, most of the items we sell are considered highly valuable and require special handling and delivery. From time to time, such goods are damaged in transit which can increase return rates, increase our costs and harm our brand. Returned goods may also be damaged in transit as part of the return process which can significantly impact the price we are able to charge for such goods on our online marketplace. If our goods are not delivered to buyers in a timely fashion or are damaged or lost during the consignment or the delivery process, our consignors or buyers could become dissatisfied and cease using our services, which would adversely affect our business and operating results.
We may be unable to successfully leverage technology, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, to automate and drive efficiencies in our operations.
We are building automation, artificial intelligence, machine learning and other capabilities to drive efficiencies in our merchandising and fulfillment operations. As we continue to add capacity, capabilities and automation, our operations will become increasingly complex and challenging and may be subject to additional regulation. While we expect these
technologies to improve productivity in many of our merchandising operations, including pricing, copywriting, authentication, photography and photo retouching, any flaws or failures of such technologies could cause interruptions in and delays to our operations which may harm our business. Artificial intelligence technologies create specific risks that require tailored oversight. Insufficient oversight could lead to liability, financial loss, and reputational harm. We use artificial intelligence to make initial assessments on authenticity, to identify product characteristics, and to help predict consigner preferences. We have created our own purpose-built technology to operate our business, which may lack efficiency or become obsolete as we grow and we also rely on technology from third parties. If these technologies do not perform in accordance with our expectations, third parties change the terms and conditions that govern their relationships with us, or if competition increases for the technology and services provided by third parties, our business may be harmed. In addition, the evolution of these technologies may create unforeseen competitive pressures or cause disruption.
Risks Related to Data Security, Privacy and Fraud
We rely on third parties to host our website and mobile app and to process payments.
Our brand and ability to attract and retain consignors and buyers depends in part on the reliable performance of our network infrastructure and content delivery process. The continuing and uninterrupted performance of our online marketplace is critical to our success. We have experienced, and expect that in the future we will experience, interruptions, delays and outages in service and availability from time to time due to a variety of factors, including infrastructure changes, human or software errors, website hosting disruptions and capacity constraints which could affect the availability of services on our platform and prevent or inhibit the ability of members to access our online marketplace or complete purchases on our website and app. Volume of traffic and activity on our online marketplace spikes on certain days and during certain periods of the year, such as during a Black Friday promotion and generally during the fourth quarter due to the seasonality of our business, and any interruption would be particularly problematic if it were to occur at such a high volume time.
We rely on third-party payment processors to process payments made by buyers or to consignors on our online marketplace. The software and services provided by our third-party payment processors may not meet our expectations, contain errors or vulnerabilities, be compromised or experience outages. Any of these risks could cause us to lose our ability to accept online payments, make payments to consignors or conduct other payment transactions, any of which could make our platform less convenient and attractive and adversely affect our ability to attract and retain buyers and consignors.
Failure of our data or cyber security could cause us to incur unexpected expenses or compromise our data assets.
In the ordinary course of our business, we collect, process and store certain personal information (including credit card information) and other data relating to individuals, such as our consignors, buyers and employees. We also maintain other information, such as our trade secrets and confidential business information, that is sensitive and that we seek to protect. We rely substantially on commercially available systems, software, including third-party open source software, tools and monitoring to provide security for our processing, transmission and storage of personal information and other confidential information. We or our vendors, including cloud storage providers as well as other third parties with whom we do
business, could be subject to attacks from computer viruses, break-ins phishing attacks, social engineering, ransomware attacks, unauthorized use, misconduct or usage errors by our employees, attempts to overload services with denial-of-service or other attacks, which may allow hackers or other unauthorized parties, including our employees, to gain access to personal information or other data, including payment card data or confidential business information. Further, the use of open-source software may also present additional security risks because the public availability of such software may make it easier for hackers and other third parties to compromise our platform. Our members use our web and mobile e-commerce applications to consign and shop with us. These applications may become subject to account takeovers, denials of service, content scraping, or other attacks, which may result in our members' accounts being compromised.
We and our vendors, as well as other third parties with whom we do business, have faced these attacks previously and regularly must defend against or respond to such incidents. Threat actors are increasingly sophisticated and are targeting employees, contractors, service providers and third-parties through various techniques that involve social engineering and/or misrepresentation (such as phishing attempts and similar techniques). Data breaches and other cybersecurity events have become increasingly commonplace, including as a result of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. We expect to incur ongoing costs associated with the detection and prevention of security breaches and other security-related incidents. The techniques used to obtain unauthorized access or to sabotage systems change frequently and generally are not identified until they are launched against a target, and we and our vendors, as well as other third parties with whom we do business, may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative measures. Any actual or perceived compromise of our systems or data security measures or those of third parties with whom we do business, or any failure to prevent or mitigate the loss of personal or other confidential information and delays in detecting or providing notice of any such compromise or loss could disrupt our operations, damage our reputation, cause some participants to decrease or stop their use of our online marketplace and subject us to litigation, government action, increased transaction
fees, remediation costs, regulatory fines or penalties or other additional costs and liabilities, as well as reputational impact, that could adversely affect our business, financial condition and operating results. While we carry insurance related to potential data breaches, the insurance we do carry may not be adequate to cover all possible losses that our business could suffer.
We may incur significant losses from fraud.
We may fail to prevent consignors from consigning stolen or counterfeit goods. Government regulators and law enforcement officials may allege that our services violate, or aid and abet violations of certain laws, including laws restricting or prohibiting the transferability and, by extension, the resale, of stolen goods. Our form of consignor agreement includes a representation that the consignor has the necessary right and title to the goods they may consign, and we include such a rule and requirement in our terms of service prohibiting the listing of stolen or otherwise illegal products. In addition, we have implemented protective measures to detect such products. If these measures prove inadequate, we may be required to spend substantial resources to take additional protective measures which could negatively impact our operations. In addition, negative publicity relating to the actual or perceived listing or sale of stolen or counterfeit goods could damage our reputation and make our consignors and buyers reluctant to use our services.
We have in the past incurred, and may in the future incur, losses from various types of fraudulent transactions, including the use of stolen credit card numbers, claims that a consignment of a good was not authorized and that a buyer did not authorize a purchase. Under current credit card practices, we are liable for fraudulent credit card transactions because we do not obtain a cardholder’s signature. Our failure to adequately prevent fraudulent transactions could damage our reputation, result in litigation or regulatory action or lead to expenses that could substantially impact our operating results.
Risks Relating to Our Employees
We may be unable to attract and retain key personnel or effectively manage leadership succession.
Our success depends in part on our ability to attract and retain key personnel on our executive team. Senior employees have left our company in the past and others may leave in the future. We often cannot anticipate such departures and may not be able to promptly replace key leadership personnel. The loss of one or more of our key personnel or the inability to promptly identify a suitable successor to a key role could have an adverse effect on our business.
Labor-related matters, including labor disputes, may adversely affect our operations.
None of our employees are currently represented by a union. If our employees decide to form or affiliate with a union, we cannot predict the negative effects such future organizational activities will have on our business and operations. If we were to become subject to work stoppages, we could experience disruption in our operations, including delays in merchandising operations and shipping, and increases in our labor costs, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations. In addition, increased inflation rates could adversely affect us by increasing costs, including labor and employee benefit costs.
Risks Relating to Our Intellectual Property
If we cannot successfully protect our intellectual property, our business could suffer.
We rely on a combination of intellectual property rights, contractual protections and other practices to protect our brand, proprietary information, technologies and processes. We primarily rely on copyright and trade secret laws to protect our proprietary technologies and processes, including the algorithms we use throughout our business. Others may independently develop the same or similar technologies and processes, or may improperly acquire and use information about our technologies and processes, which may allow them to provide a service similar to ours, which could harm our competitive position. Our principal trademark assets include the registered trademark “The RealReal” and our logos and taglines. We also hold the rights to the “therealreal.com” Internet domain name and various related domain names, which are subject to Internet regulatory bodies and trademark and other related laws of each applicable jurisdiction. Our trademarks are valuable assets that support our brand and consumers’ perception of our services and merchandise. If we are unable to protect our trademarks or domain names, our brand recognition and reputation would suffer, we would incur significant expense reestablishing brand equity and our operating results would be adversely impacted.
Risks Relating to Litigation and Regulatory Uncertainty
We are currently, and may be in the future, party to lawsuits and other claims.
We rely on the fair use doctrine when we routinely refer to third-party intellectual property, such as trademarks, on our platform. Third parties may dispute the scope of that doctrine and challenge our ability to reference their intellectual property in the course of our business. For instance, from time to time, we are contacted by companies controlling brands of goods consignors sell, demanding that we cease referencing those brands in connection with such sales, whether in advertising or on our website. We have consistently responded by reference to the holding in Tiffany (NY), Inc. v. eBay that factual use of a brand to describe and sell a used good is not false advertising. These matters have generally been resolved with no further communications, but some have resulted in litigation against us. For example, in November 2018, Chanel filed a lawsuit against us in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York bringing various trademark and advertising-related claims under the Lanham Act and New York state law analogues. The final outcome of this litigation, including our liability, if any, with respect to Chanel’s claims, is uncertain. An unfavorable outcome in this or similar litigation could adversely affect our business and could lead to other similar lawsuits. See “Part II, Item 1 – Legal Proceedings” for a description of the Chanel litigation.
In addition, the Company, its officers and directors and the underwriters of the Company’s initial public offering (“IPO”) were named as defendants in numerous purported securities class actions in connection with the Company’s IPO (the “Securities Litigation”). See “Part II, Item 1 – Legal Proceedings” for a description of the Securities Litigation.
In addition, we have in the past and could face in the future a variety of employee claims against us, including general discrimination, privacy, wage and hour, labor and employment, disability claims and claims related to the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974. Further, the comprehensive safety measures and protocols that we have implemented may not be successful and we could face litigation or other claims related to unsafe working conditions, inadequate protection of our employees, or other similar or related claims. Any claims could also result in litigation against us or regulatory proceedings being brought against us by various federal and state agencies that regulate our business, including the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. Often these cases raise complex factual and legal issues and create risks and uncertainties. In addition, stockholders have filed securities class action litigation against us following periods of market volatility. We have been the target of litigation associated with these fluctuations and market volatility and may be the target of this type of litigation in the future.
Defending litigation is costly and can impose a significant burden on management and employees, and there can be no assurances that favorable final outcomes will be obtained. The results of any such litigation, investigations and other legal proceedings are inherently unpredictable and expensive. Although we have insurance, it provides for a substantial retention of liability and is subject to limitations and may not cover a significant portion, or any, of the expenses we may incur or be subject to in connection with shareholder class action or other litigation to which we are party. In addition, plaintiffs may seek, and we may become subject to, preliminary or provisional rulings in the course of any such litigation, including potential preliminary injunctions requiring us to cease some or all of our operations or discontinue selling consigned goods from certain brands. We may decide to settle such lawsuits and disputes on terms that are unfavorable to us. Similarly, if any litigation to which we are a party is resolved adversely, we may be subject to an unfavorable judgment that may not be reversed upon appeal. The terms of such a settlement or judgment may require us to cease some or all of our operations, discontinue selling consigned goods from certain brands or pay substantial amounts to the other party. In addition, we may have to seek a license to continue practices found to be in violation of a third-party’s rights, which may not be available on reasonable terms or at all and may significantly increase our operating costs and expenses. As a result, we may also be required to develop alternative practices or discontinue existing practices. The development of alternative practices could require significant effort and expense or may not be feasible. Our business, financial condition or operating results could be adversely affected as a result of an unfavorable resolution of the disputes and litigation referred to above.
Our use and other processing of personal information and other data is subject to laws and obligations relating to privacy and data protection.
Numerous state, federal and international laws, rules and regulations govern privacy, data protection and the collection, use and protection of personal information and other types of data we collect, use, disclose and otherwise process. These laws, rules and regulations are constantly evolving, and we expect that there will continue to be new proposed laws, regulations and industry standards concerning privacy, data protection and information security in the United States, the European Union (the "EU"), the United Kingdom (the "UK") and other jurisdictions. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (the “CCPA”), that requires covered companies to provide disclosures to California consumers and afford such consumers qualified privacy rights, such as rights of access, deletion and to opt-out of the sales and "sharing" of their personal information, which relates to "cross context behavioral advertising" or more commonly known as targeted advertising. The CCPA was amended by the California Privacy Rights Act (the “CPRA”), which went into effect on January 1, 2023. The CCPA, as amended, removes the exclusion of employment data from its auspices, adds new consumer privacy rights (such as the right to correct inaccurate personal information, or the right to opt out of the “sharing” of personal information for the purposes of cross-context behavioral advertising), expands business’s obligations to secure contractual obligations from service providers and third parties, and expands business’s obligations with respect to automated opt-out
preference signals. The new California Privacy Protection Agency completed its first round of rulemaking but has left many new requirements, such as data privacy and security risk assessments and the right to opt out of certain data profiling activities, for its second round of rulemaking, which began in March 2023 and has yet to be finalized. It remains unclear how these new amendments will be interpreted or when the second round of rulemaking activity will conclude. The CCPA may require us to modify our data processing practices and policies and to incur substantial costs and expenses in an effort to comply. Similarly, several other U.S. states, including Virginia, Connecticut, Colorado, Utah, Delaware, Iowa, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Montana, Minnesota, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Rhode Island, Tennessee and Texas have passed similar consumer data privacy laws that impose general data minimization obligations on covered businesses and also extend privacy rights to individuals, including the rights to opt out of targeted advertising and respect automated opt-out preference signals. Many of these state laws also require covered businesses to provide
consumers with the ability to opt-out of certain profiling or automated decision-making processes
Additionally, the European Commission imposes stringent EU data protection requirements across all EU Member States through the General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”). The GDPR has been transposed into national law by the UK (“UK GDPR”) and has been incorporated into the European Economic Area (“EEA”) Agreement. The GDPR and UK GDPR, as well as other statutes and regulations related to privacy and data protection, increase our compliance obligations and may affect our collection, processing, retention and transfer of certain personal data, reporting of certain security breaches, and expose us to increased penalties for non-compliance. Increased regulatory scrutiny could lead to substantial costs, require significant changes to our existing systems, limit the effectiveness of our marketing activities, and subject us to additional liabilities. Further, recent litigation in the EEA and the UK has driven significant changes in enforcement and interpretation, and we cannot yet fully determine the impact these or future laws, rules and regulations may have on our business or operations.
Given the increased legislative and regulatory enforcement focus on the use of data for advertising and artificial intelligence, we may be subject to new and unexpected regulatory interpretations and rulemaking efforts, including proposals for regulation of artificial intelligence or other automated decision-making processes. Future laws, regulations, standards and other obligations could, for example, impair our ability to collect or use information that we utilize to create targeted marketing and advertising and offer certain bespoke product features and other capabilities to drive efficiencies in our merchandising operations, thereby impairing our ability to maintain and attract new consignors and buyers, which could have a material adverse effect on our business and operating results.
These laws, rules and regulations may be inconsistent from one jurisdiction to another, subject to differing interpretations and may be interpreted to conflict with our practices. Any failure or perceived failure by us or any third parties with which we do business to comply with these laws, rules and regulations, or with other obligations to which we or such third parties are or may become subject, may result in actions against us by governmental entities, or litigation, and the expenditure of legal and other costs and of substantial time and resources, and fines, penalties or other liabilities.
Further, in view of new or modified federal, state or foreign laws and regulations, industry standards, contractual obligations and other legal obligations, or any changes in their interpretation, we may find it necessary or desirable to change our business activities and practices or to expend significant resources to modify our product or services and otherwise adapt to these changes. We may be unable to make such changes and modifications in a commercially reasonable manner or at all, and our ability to develop new products and features could be limited.
If the use of “cookie” tracking technologies is further restricted, regulated, or blocked, or if changes in technology cause cookies to become less reliable or acceptable as a means of tracking consumer behavior, the amount or accuracy of internet user information we collect would decrease, which could harm our business and operating results.
Cookies are small data files that are sent by websites and stored locally on an internet user’s computer or mobile device. We, and third parties who work on our behalf, collect data via cookies that is used to track the behavior of visitors to our websites, to provide a more personal and interactive experience, and to increase the effectiveness of our marketing. However, internet users can easily disable, delete, and block cookies directly through browser settings or through other software, browser extensions, or hardware platforms that physically block cookies from being created and stored.
Privacy regulations restrict how we deploy our cookies and this could potentially (a) increase the number of internet users that choose to proactively disable cookies on their systems or (b) cause our business partners, service providers, or vendors to no longer maintain their cookie processes. We may have to develop alternative systems to determine our clients’ behavior, customize their online experience, or efficiently market to them if clients block cookies or regulations introduce additional barriers to collecting cookie data.
We pay or collect sales taxes in all jurisdictions which require such taxes.
An increasing number of states have considered or adopted laws that impose tax collection obligations on out-of-state sellers of goods. Additionally, in 2018, the Supreme Court of the United States ruled in South Dakota v. Wayfair, Inc. et al (“Wayfair”), that online sellers can be required to collect sales tax despite not having a physical presence in the state of the customer. In response to Wayfair, or otherwise, states or local governments and taxing authorities may adopt, or begin to enforce, laws requiring us to calculate, collect and remit taxes on sales in their jurisdictions. While we currently collect and remit sales taxes in every state that requires sales taxes to be collected, including states where we do not have a physical presence, the adoption of new laws by, or a successful assertion by the taxing authorities of one or more state or local governments requiring us to collect more taxes could result in substantial additional tax liabilities, including taxes on past sales, as well as penalties and interest, which could have a material adverse impact on our business and operating results.
Failure to comply with applicable laws or regulations may subject us to fines, penalties, loss of licensure, registration, facility closures or other governmental enforcement action.
The sale of consigned goods through our online marketplace is subject to regulation, including by regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, the Federal Trade Commission, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and other international, federal, state and local governments and regulatory authorities. These laws and regulations are complex, vary from state to state and change often. We receive luxury goods on consignment from numerous consignors located in all 50 U.S. states and Puerto Rico, and the goods we receive from our consignors may contain materials such as fur, skin, ivory and other exotic animal product components, that are subject to regulation. Our standard consignor terms and conditions require consignors to comply with applicable laws when consigning their goods. Failure of our consignors to comply with applicable laws, regulations and contractual requirements could lead to litigation or other claims against us, resulting in increased legal expenses and costs. Moreover, failure by us to effectively monitor the application of these laws and regulations to our business, and to comply with such laws and regulations, may negatively affect our brand and subject us to penalties and fines.
Numerous U.S. states and municipalities, including California, New York and Florida, have regulations regarding the handling and sale of secondhand goods, and licensing requirements for secondhand dealers. Such government regulations could require us to change the way we conduct business, or our buyers to conduct their purchases in ways that increase costs, such as prohibiting or otherwise restricting the sale or shipment of certain items in some locations. To the extent we fail to comply with requirements for secondhand dealers, we may experience unanticipated permanent or temporary shutdowns of our facilities which may negatively affect our ability to increase the supply of our goods, result in negative publicity and subject us to penalties and fines.
Additionally, the luxury goods our consignors sell could be subject to recalls and other remedial actions and product safety, labeling and licensing concerns may require us to voluntarily remove selected goods from our online marketplace. Such recalls or voluntary removal of goods can result in, among other things, lost sales, diverted resources, potential harm to our reputation and increased customer service costs and legal expenses, which could have a material adverse effect on our operating results.
Application of existing tax laws, rules or regulations are subject to interpretation by taxing authorities.
The application of the income and tax laws is subject to interpretation. Although we believe our tax methodologies are compliant, a taxing authority’s final determination in the event of a tax audit could materially differ from our past or current methods for determining and complying with our tax obligations, including the calculation of our tax provisions and accruals, in which case we may be subject to additional tax liabilities, possibly including interest and penalties. Furthermore, taxing authorities have become more aggressive in their interpretation and enforcement of such laws, rules and regulations over time, as governments are increasingly focused on ways to increase revenues. This has contributed to an increase in audit activity and stricter enforcement by taxing authorities. As such, additional taxes or other assessments may be in excess of our current tax reserves or may require us to modify our business practices to reduce our exposure to additional taxes going forward, any of which may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
In addition, many of the underlying laws, rules and regulations imposing taxes and other obligations were established before the growth of the Internet and e-commerce. U.S. federal, state and local taxing authorities are currently reviewing the appropriate treatment of companies engaged in Internet commerce and considering changes to existing tax or
other laws or may change interpretation of existing tax or other laws that could levy sales, income, consumption, use or other taxes relating to our activities, and/or impose obligations on us to collect such taxes. If such tax or other laws, rules or regulations are amended or interpretations are changed, or if new unfavorable laws, rules or regulations are enacted, the results could increase our tax payments or other obligations, prospectively or retrospectively, subject us to interest and penalties, decrease the demand for our services if we pass on such costs to our buyers or consignors, result in increased costs to update or expand our technical or administrative infrastructure or effectively limit the scope of our business activities if we
decided not to conduct business in particular jurisdictions. As a result, these changes may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
Our ability to use our net operating loss carryforwards and certain other tax attributes may be limited.
We have incurred substantial net operating losses (“NOLs”) during our history. Unused NOLs may carry forward to offset future taxable income if we achieve profitability in the future, unless they expire under applicable tax laws. However, under the rules of Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change,” generally defined as a greater than 50% change (by value) in its equity ownership over a three-year period, the corporation’s ability to use its NOLs and other pre-change tax attributes to offset its post-change taxable income or taxes may be limited. The applicable rules generally operate by focusing on changes in ownership among stockholders considered by the rules as owning, directly or indirectly, 5% or more of the stock of a company, as well as changes in ownership arising from new issuances of stock by the company. In addition, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act imposes certain limitations on the deduction of NOLs generated in tax years that began on or after January 1, 2018, including a limitation on use of NOLs to offset 80% of taxable income and the disallowance of NOL carryback. Although NOLs generated in tax years before 2018 may still be used to offset future income without limitation, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act may limit our ability to use our NOLs to offset any future taxable income.
If our internal control over financial reporting or our disclosure controls and procedures are not effective, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results, prevent fraud or file our periodic reports in a timely manner, which may cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information.
We are subject to the reporting requirements under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act”) and the rules and regulations of the applicable listing standards of The Nasdaq Stock Market. Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires that we maintain effective internal control over financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures. In particular, we must perform system and process evaluations, document our controls and perform testing of our key controls over financial reporting to allow for management and our independent public accounting firm to report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. If we are not able to continue to comply with the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act or if we encounter difficulties in the timely and accurate reporting of our financial results, or if we or our independent registered public accounting firm identify deficiencies in our internal control over financial reporting that are deemed to be material weaknesses, our investors could lose confidence in our reported financial information, the market price of our stock may decline and we could be subject to lawsuits, sanctions or investigations by regulatory authorities, which would require additional financial and management resources.
Risks Relating to Ownership of Our Common Stock
The market price of our common stock may be volatile or may decline steeply or suddenly regardless of our operating performance and we may not be able to meet investor or analyst expectations.
If you purchase shares of our common stock, you may not be able to resell those shares at or above the price you paid. The market price of our common stock may fluctuate or decline significantly in response to numerous factors, many of which are beyond our control, including:
•actual or anticipated fluctuations in our consignor or buyer base, the level of consignor and buyer engagement, revenue or other operating results;
•adverse economic and market conditions, including declines in consumer discretionary spending, currency fluctuations, inflation, disruptions in the financial industry and geopolitical instability;
•the research and reports that securities or industry analysts may publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors;
•variations between our actual operating results and the expectations of securities analysts, investors and the financial community;
•any forward-looking financial or operating information we may provide to the public or securities analysts, any changes in this information or our failure to meet expectations based on this information;
•additional shares of our common stock being sold into the market by us or our existing stockholders, or the anticipation of such sales;
•hedging activities by market participants;
•sudden increased or decreased interest in our stock from retail investors;
•substantial fluctuations in the daily trading volume of our common stock;
•announcements by us or our competitors of significant products or features, technical innovations, acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments;
•changes in operating performance and stock market valuations of companies in our industry, including our competitors;
•price and volume fluctuations in the stock market, including as a result of trends in the economy;
•lawsuits threatened or filed against us;
•developments in new legislation and pending lawsuits or regulatory actions, including interim or final rulings by judicial or regulatory bodies; and
•other events or factors, including those resulting from war or incidents of terrorism, or responses to these events or threats to public health.
In addition, price and volume fluctuations in the stock markets have affected and may continue to affect many online marketplace and other technology companies’ stock prices. Stock prices often fluctuate in ways unrelated or disproportionate to the companies’ operating performance. Moreover, because of these fluctuations, comparing our operating results on a period-to-period basis may not be meaningful. You should not rely on our past results as an indication of our future performance. This variability and unpredictability could also result in our failing to meet the expectations of industry or financial analysts or investors for any period. If our revenue or operating results fall below the expectations of analysts or investors or below any forecasts we may provide to the market, or if the forecasts we provide to the market are below the expectations of analysts or investors, the price of our common stock could decline substantially. Such a stock price decline could occur even when we have met any previously publicly stated revenue or earnings forecasts that we may provide.
Short sellers of our stock may be manipulative and may drive down the market price of our common stock.
Short selling is the practice of selling securities that the seller does not own but rather has borrowed or intends to borrow from a third party. A short seller hopes to profit from a decline in the value of the securities they are shorting. As it is in the short seller’s interest for the price of the stock to decline, some short sellers publish opinions or characterizations regarding the relevant issuer intended to create negative market momentum. Issuers, like us, with securities that have historically had limited trading volumes and/or have been susceptible to relatively high volatility levels can be particularly vulnerable to such short seller attacks. Short selling may also lead to fluctuations of our stock price, particularly if retail investors or others holding “long” positions in our common stock seek to counter short selling activity by purchasing additional shares, thus making it more difficult and more expensive for short sellers to profit. No assurances can be made that declines in the market price of our common stock will not occur in the future in connection with such activity.
Delaware law and provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws could make a merger, tender offer or proxy contest difficult, thereby depressing the trading price of our common stock.
Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws contain provisions that could depress the trading price of our common stock by acting to discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of our company or changes in our management that the stockholders of our company may deem advantageous. These provisions include the following:
•establish a classified board of directors so that not all directors are elected at one time;
•permit the board of directors to establish the number of directors and fill any vacancies and newly-created directorships;
•provide that directors may only be removed for cause;
•require super-majority voting to amend some provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws;
•authorize the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock that our board of directors could use to implement a stockholder rights plan;
•prohibit stockholders from calling special meetings of stockholders;
•prohibit stockholder action by written consent;
•provide that the board of directors is expressly authorized to make, alter or repeal our bylaws;
•restrict the forum for certain litigation against us to Delaware; and
•establish advance notice requirements for nominations for election to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at annual stockholder meetings.
Any provision of our certificate of incorporation or bylaws or Delaware law that has the effect of delaying or deterring a change in control could limit the opportunity for our stockholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock, and could also affect the price that some investors are willing to pay for our common stock.
Our certificate of incorporation designates the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware located within the State of Delaware as the exclusive forum for substantially all disputes between us and our stockholders.
Our certificate of incorporation provides that, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware is the sole and exclusive forum for any derivative action or proceeding, any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty, any action arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”), our certificate of incorporation or our bylaws, any other action that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine or any other action asserting an “internal corporate claim,” as defined in the DGCL. These exclusive-forum provisions do not apply to claims under the Securities Act of 1933 (the “Securities Act”) or the Exchange Act. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in any of our securities shall be deemed to have notice of and consented to this provision. This exclusive-forum provision may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum of its choosing for disputes with us or our directors, officers or other employees. If a court were to find the exclusive-forum provision to be inapplicable or unenforceable in an action, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving the dispute in other jurisdictions, which could harm our results of operations.
Risks Related to Our Outstanding Notes and Warrants
We have incurred a significant amount of debt and may incur additional indebtedness in the future.
As of the date hereof, the principal amount of our 3.00% convertible senior notes due 2025 (the “2025 Notes”) is $26.7 million, the principal amount of our 1.00% convertible senior notes due 2028 (the “2028 Notes”) is $97.7 million, the principal amount of our 4.25%/8.75% PIK/cash senior secured notes due 2029 (the “2029 Notes”) is $134.5 million and the principal amount of our 4.00% convertible senior notes due 2031 (the “2031 Notes” and, together with the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, the “Convertible Senior Notes”) is $146.7 million (together with the 2029 Notes and the Convertible Senior Notes, the “Notes”). Additionally, the Company issued warrants to acquire an aggregate of up to 7,894,737 shares of our common stock (subject to adjustment in accordance with the terms of the Warrants). We may be required to use a substantial portion of our cash flows from operations to pay interest and principal on our indebtedness. Such payments will reduce the funds available to use for working capital, capital expenditures and other corporate purposes and limit our ability to obtain additional financing, which may in turn limit our ability to implement our business strategy, heighten our vulnerability to downturns in our business, the industry, or in the general economy, limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the industry and prevent us from taking advantages of business opportunities as they arise. If we are unable to generate such cash flow to service our debt, we may be required to adopt one or more alternatives, such as selling assets, incurring additional debt, restructuring debt or issuing additional equity on terms that may be onerous or highly dilutive. These alternatives may be insufficient to overcome macroeconomic conditions that may affect us. The duration and severity of macroeconomic uncertainty, any ensuing economic downturns, including economic recession or depression, could directly impact our ability to implement alternatives to service our debt. We may not be able to engage in any of these activities or engage in these activities on desirable terms, which could result in a default on our debt obligations.
The indentures governing our Notes contain restrictions and other provisions regarding events of default that may make it more difficult to execute our strategy or to effectively compete, or that could materially affect our financial position.
Subject to certain exceptions and qualifications, the indenture governing our 2029 Notes (the “2029 Notes Indenture”) restricts our ability to, among other things, (i) grant or incur liens securing indebtedness; (ii) incur, assume or guarantee additional indebtedness; (iii) enter into transactions with affiliates; (iv) sell or otherwise dispose of assets, including capital stock of subsidiaries; (v) in the case of the Company and any future guarantor (if any), consolidate, amalgamate or merge with or into, or sell all or substantially all of its assets to, another person; (vi) make certain restricted payments or other investments; and (vii) pay dividends or make other distributions (including loans and other advances). In addition, the 2029 Notes Indenture contains a covenant that provides that the Company may not permit liquidity (calculated as the sum of (a) unused commitments then available to be drawn under any revolving credit facility, delayed draw term loan facility or qualified securitization financing permitted thereunder (after giving effect to any borrowing base or similar limitations), plus (b) the amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held by the Company and its subsidiaries (if any)) to be less than $25 million as of the last day of any month. These restrictions, and others set forth in the 2029 Notes Indenture, may make it difficult to successfully execute our business strategy or effectively compete with companies that are not similarly restricted.
The indentures governing our Convertible Senior Notes and our 2029 Notes Indenture also set forth certain events of default after which our Notes may be declared immediately due and payable and set forth certain types of bankruptcy or insolvency events of default involving the Company or its subsidiaries. Such acceleration of our debt could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity if we are unable to negotiate mutually acceptable terms with the holders of the Notes or if alternate funding is not available to us. Furthermore, if we are unable to repay the Notes upon an acceleration or otherwise, we could be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation.
Transactions relating to our Convertible Senior Notes or the Warrants may dilute the ownership interest of our stockholders.
The conversion or exercise of some or all of our outstanding Convertible Senior Notes or Warrants would dilute the ownership interests of existing stockholders to the extent we deliver shares upon conversion or exercise of any such Convertible Senior Notes or Warrants. If the Convertible Senior Notes or Warrants become convertible or exercisable under the terms of the applicable indenture or warrant agency agreement, and if holders subsequently elect to convert or exercise the Convertible Senior Notes or Warrants, we could be required to deliver to them a significant number of shares of our common stock. Any sales or anticipated sales in the public market of the common stock issuable upon conversion of the Convertible Senior Notes or exercise of the Warrants could adversely affect prevailing market prices for our common stock. In addition, the existence of the Convertible Senior Notes and Warrants may encourage short selling by market participants because the conversion of the Convertible Senior Notes or Warrants could be used to satisfy short positions.
The conversion of the Convertible Senior Notes or the cash conversion of the Warrants, if triggered, may adversely affect our financial condition and operating results.
In the event the conditional conversion feature of the Convertible Senior Notes is triggered, holders of the Convertible Senior Notes will be entitled to convert their Convertible Senior Notes at any time during specified periods at their option. If one or more holders elect to convert their Convertible Senior Notes, unless we elect to satisfy our conversion obligation by delivering shares of our common stock (other than paying cash in lieu of delivering any fractional share), we would be required to settle a portion or all of our conversion obligation in cash, which could adversely affect our liquidity. In addition, even if holders of the Convertible Senior Notes do not elect to convert their Convertible Senior Notes, we could be required under applicable accounting rules to reclassify all or a portion of the outstanding principal of the Convertible Senior Notes as a current rather than long-term liability, which could result in a material reduction in our net working capital. Further, in the event of a fundamental change, which could occur outside the Company’s control, the Warrants may be required to be settled in cash instead of delivering shares, which could result in a material reduction in our net working capital.
The accounting method for the Warrants materially affects our reported financial results.
We account for our outstanding Warrants as liabilities at fair value on our balance sheet. The Warrants are subject to remeasurement at each balance sheet date and any change in fair value is recognized as a component of earnings in each period for which our earnings are reported. We will continue to adjust the liability for changes in fair value until the earlier of exercise or expiration of the Warrants. The volatility introduced by changes in fair value on earnings may have an adverse effect on our quarterly and annual financial results.
The accounting method for the Convertible Senior Notes materially affects our reported financial results.
Prior to the adoption of ASU 2020-06, under Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 470-20, Debt with Conversion and Other Options, we accounted for the liability and equity components of the Convertible Senior Notes separately because the Convertible Senior Notes may be settled entirely or partially in cash upon conversion in a manner that reflects our economic interest cost. This bifurcation resulted in a debt discount for Convertible Senior Notes. See “Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies— Convertible Senior Notes.” We used the effective interest method to amortize the debt discount to interest expense over the amortization period, which is the expected life of the Convertible Senior Notes. However, we adopted ASU 2020-06 as of January 1, 2022, under which we now account for the Convertible Senior Notes as a single liability measured at their amortized cost. Upon adoption, we recorded a cumulative effect adjustment of $13.4 million as a reduction to accumulated deficit and a reduction to additional paid in capital of $112.1 million related to amounts attributable to the value of the conversion options that had previously been recorded in equity. Additionally, we recorded an increase to the Convertible Senior Notes balance by an aggregate amount of $98.6 million as a result of the reversal of the separation of the convertible debt between debt and equity. As a result of the adoption of ASU 2020-06, we also derecognized $27.5 million of deferred tax liabilities and recognized $0.2 million of deferred tax assets, resulting in a $27.7 million increase to the net deferred tax assets and a corresponding increase of $27.7 million in the offsetting valuation allowance.
The adoption of this standard also significantly decreased the amount of non-cash interest expense to be recognized in periods beginning on or after January 1, 2022 as a result of eliminating the discount associated with the equity component. In addition, following adoption, we are required to calculate diluted earnings per share using the “if converted” method, which assumes that all of the Convertible Senior Notes were converted solely into shares of common stock at the beginning of the reporting period, unless the result would be anti-dilutive, which can adversely affect our diluted earnings per share. Future amendments to the accounting treatment for the Convertible Senior Notes, could adversely affect our financial results, the trading price of our common stock and the trading price of the Convertible Senior Notes.
The capped call transactions may affect the value of the 2025 Notes, the 2028 Notes and our common stock.
In connection with the pricing of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, we entered into privately negotiated capped call transactions with certain counterparties. The capped call transactions cover the number of shares of our common stock initially underlying the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes. The capped call transactions are expected to offset the potential dilution to our common stock upon any conversion of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes. In connection with establishing their initial hedges of the capped call transactions, the counterparties or their respective affiliates entered into various derivative transactions with respect to our common stock. The counterparties or their respective affiliates may modify their hedge positions by entering into or unwinding various derivatives with respect to our common stock and/or purchasing or selling our common stock or other securities of ours in secondary market transactions prior to the maturity of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes (and are likely to do so on each exercise date of the capped call transactions), or following any termination of any portion of the capped call transactions in connection with any repurchase, redemption or early conversions of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes or otherwise. This activity could also cause or avoid an increase or a decrease in the market price of our common stock.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Risk Management and Strategy
We have developed processes for assessing, identifying and managing material risks from cybersecurity threats. We review our security plans and strategies as threats and conditions evolve. The following is a summary of our cybersecurity risk management and strategy processes:
Enterprise Risk Management: Our enterprise risk management program includes management of material risks from cybersecurity threats alongside other Company risks as part of our overall risk assessment process. In 2024, as part of our Enterprise Risk Management Program, our Internal Audit team identified and prioritized the most critical risks that could impact our ability to achieve our business priorities and make risk-informed strategic decisions. With management’s input, our Board and Internal Audit team have identified cybersecurity as one of the risks that merits the highest level of prioritization. Informed by this designation, our Internal Audit team tracks cybersecurity key indicators and engages in discussions on the status, priorities and impact of cybersecurity risk response plans; reports key information to management throughout the year to inform decision making; and reports to the Audit Committee on a quarterly basis and to the full Board on the results and progress of the risk mitigation process.
In addition, we employ a range of tools and services to inform our assessment, identification and management of material risks from cybersecurity threats, which include from time to time:
•monitoring emerging data protection laws, including the California Consumer Privacy Act and the General Data Protection Regulation, and implementing responsive changes to our processes;
•undertaking periodic reviews of our policies and statements related to cybersecurity;
•conducting cybersecurity management and incident training for employees involved in our systems and processes that handle sensitive data;
•conducting phishing email simulations for employees and contractors with access to corporate email systems;
•requiring employees, as well as third-parties who provide services on our behalf, to treat information and data with care; and
•conducting tabletop exercises to simulate a response to a cybersecurity incident and using the findings to improve our processes and technologies.
Incident Response Team and Outside Resources: We have formed an Incident Response Team that monitors and mitigates material risks from cybersecurity threats. This team is composed of members from the information security, engineering and legal teams. The Incident Response Team and our internal legal team work in tandem to estimate the severity and materiality of a cybersecurity incident, create a response plan and inform other stakeholders as appropriate, including the Audit Committee or the full Board. In addition, we engage several third party service providers to monitor cybersecurity threats in the market more broadly, including in relation to phishing, data leaks on the dark web, firewalls, code security and endpoint protection. To identify risks from cybersecurity threats associated with these third-party service providers, we conduct pre-contract screening and due diligence and post-contract monitoring.
Cybersecurity Task Force: We have formed a cross-functional Cybersecurity Task Force that focuses on long-term cybersecurity strategy. The Cybersecurity Task Force is composed of members from the information security, engineering and legal teams and reports to our Chief Technology and Product Officer. The Cybersecurity Task Force meets periodically to discuss developments and best practices in cybersecurity incident response. In addition, the Cybersecurity Task Force reviews the business impact and severity of potential cybersecurity incidents, as reported by our automated systems, utilization of the bug bounty program, and public reports on the threat landscape.
For a discussion of whether and how any risks from cybersecurity threats, including as a result of any previous cybersecurity incidents, have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect the Company, including our business strategy and results of operations, see “Risk Factors – Risks Related to Data Security, Privacy and Fraud,” which are incorporated by reference into this Item 1C.
In the three most recently completed fiscal years, we have not experienced any material cybersecurity incidents and the expenses we have incurred from cybersecurity incidents were immaterial. This includes penalties and settlements, of which there were none.
Corporate Governance
Our Board of Directors provides oversight of risks from cybersecurity threats, in coordination with our Audit Committee and management team. The following is a summary of our governance processes related to cybersecurity risk management:
Board: Our full Board receives biannual updates on cybersecurity from our Chief Technology and Product Officer (the “CTPO”) or head of cybersecurity (the “CISO”) to, among other items, review cybersecurity incidents, review key metrics on our cybersecurity program and related risk management programs, and discuss our cybersecurity programs and goals. Our Board also regularly reviews cyber-related risks as part of our enterprise risk management program on a quarterly basis and receives updates from our Internal Audit team on the results of the risk monitoring and mitigation process, as described in more detail above.
Audit Committee: Our Audit Committee provides additional oversight of material risks from cybersecurity threats and engages with our CTPO or CISO regarding risk management of cybersecurity issues and to discuss potential updates to the Company’s cybersecurity risk management program, including as a result of any Cybersecurity Task Force findings. The Audit Committee receives a quarterly report from the Company’s cybersecurity team, which includes the CTPO, CISO, and members of the information security team, that summarizes progress on cyber-related key performance indicators, including product security, cloud security, risk and compliance, identity issues, and cyber defense. The Audit Committee updates the full Board on matters relating to material cybersecurity risks at least quarterly.
Management: Our CTPO is responsible for assessing and managing the Company’s material risks from cybersecurity threats, and our CISO reports directly to our CTPO regarding such threats. Our CTPO is informed about and monitors the prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation or cybersecurity incidents through the management of and participation in the Company’s Internal Audit team, Incident Response Team and Cybersecurity Task Force, as described above. As discussed above, our CTPO or CISO reports biannually to the full Board and quarterly to the Audit Committee about risks from cybersecurity threats among other cybersecurity related matters. To the extent a material cybersecurity incident occurs, our CTPO and broader management team would inform the chair of our Audit Committee of the nature, scope and impact of the incident, and involve the other members of the Audit Committee or the full Board as necessary to evaluate the risks and determine next steps. Our CTPO and CISO have served in these roles since 2023. Our CTPO has more than 20 years of experience in various senior leadership roles involving managing cybersecurity and compliance teams, including as Head of Tech and Digital at Lovevery and as Chief Technology and Product Officer at Zulilly. Our CISO has more than 20 years of experience in leadership roles focused on cybersecurity, cloud engineering, infrastructure, and technical operations, including as CISO and Head of Cloud and Infrastructure Engineering at AutoZone and as Principal Executive Advisory Consultant at Amazon Web Services.
Item 2. Properties.
Our corporate headquarters are located in San Francisco, California and are leased for a term that expires in 2027 with a right of renewal. We lease an aggregate of approximately 1.4 million square feet of space for storage, merchandising operations and fulfillment located in Arizona and New Jersey. The lease to our Arizona facility expires in 2031, and leases to our three New Jersey facilities each expire in 2029, all with a right of renewal. We lease additional offices located in Los Angeles and New York City, and we have leased several retail spaces and luxury consignment offices in other high traffic areas, including in New York City and Los Angeles.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
From time to time, the Company is subject to, and is presently involved in, litigation and other legal proceedings and from time to time, the Company receives inquiries from government agencies. Accounting for contingencies requires the Company to use judgment related to both the likelihood of a loss and the estimate of the amount or range of loss. The Company records a loss contingency when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company discloses material contingencies when a loss is not probable but reasonably possible.
On November 14, 2018, Chanel, Inc. sued the Company in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. The Complaint alleged federal and state law claims of trademark infringement, unfair competition, and false advertising. On February 1, 2019, Chanel, Inc. filed its First Amended Complaint that included substantially similar claims against the Company. On March 4, 2019, the Company filed a Motion to Dismiss the First Amended Complaint, which was granted in part and dismissed in part on March 30, 2020. The surviving claims against the Company include trademark infringement under 15 U.S.C. § 1114, false advertising under 15 U.S.C. § 1125, and unfair competition under New York common law. On May 29, 2020, the Company filed its Answer to the Amended Complaint. On November 3, 2020, the Company sought leave to amend its Answer to assert counterclaims against Chanel, Inc. for violations of the Sherman Act, 15 U.S.C. §§ 1 & 2, the Donnelly Act, N.Y. Gen. Bus. Law. § 340, and New York common law. The motion for leave to amend was granted on February 24, 2021. On February 25, 2021, the Company filed its First Amended Answer, Affirmative Defenses and Counterclaims against Chanel. The Company’s Counterclaims allege violations of the Sherman Act, 15 U.S.C. §§ 1 & 2, the Donnelly Act, N.Y. Gen. Bus. Law. § 340, and New York common law. On March 18, 2021, Chanel moved to dismiss the Company’s Counterclaims and moved to strike the Company’s unclean hands affirmative defense. Decisions on Chanel’s motion to dismiss and motion strike are pending. The parties agreed to a stay in April 2021 to engage in settlement discussions. After several mediation sessions, the parties were unable to reach a resolution, and the stay was lifted in November 2021. Chanel then sought a partial stay of discovery on the Company's counterclaims and unclean hands defense while Chanel's motion to dismiss and strike those claims are pending, and on March 10, 2022, the Court granted Chanel's request. The parties have continued to engage in fact discovery regarding Chanel's counterfeiting and false advertising claims against the Company. Fact discovery was scheduled to be completed by August 15, 2023. However, on July 19, 2023, the Court ordered a stay of the case at the parties’ request to enable the parties to attempt mediation again. The parties have continued to engage in settlement discussions facilitated by a mediator. The final outcome of this litigation, including our liability, if any, with respect to Chanel’s claims, is uncertain. An unfavorable outcome in this or similar litigation could adversely affect the Company’s business and could lead to other similar lawsuits. The Company is not able to predict or reasonably estimate the ultimate outcome or loss or range of possible losses relating to this claim.
Beginning on September 10, 2019, purported shareholder class action complaints were filed against the Company, its officers and directors and the underwriters of its IPO in the San Mateo Superior Court, Marin County Superior Court, and the United States District Court for the Northern District of California. On July 27, 2021, the Company reached an agreement in principle to settle the shareholder class action. On November 5, 2021, plaintiff filed the executed stipulation of settlement and motion for preliminary approval of the settlement with the federal court. On March 24, 2022, the court entered an order preliminarily approving the settlement. On July 28, 2022, the court entered an order finally approving the settlement and dismissing the case. The financial terms of the stipulation of settlement provide that the Company will pay $11.0 million within thirty (30) days of the later of preliminary approval of the settlement or plaintiff’s counsel providing payment instructions. The Company paid the settlement amount on March 29, 2022 with available resources and recorded approximately $11.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 under our Operating expenses as a Legal settlement. One of the plaintiffs in the Marin County case opted out of the federal settlement and is pursuing the claim in Marin County Superior Court. The stay of the state court case has been lifted, and the opt out plaintiff filed an amended complaint on October 31, 2022 alleging putative class claims under the Securities Act of 1933 (the “Securities Act”) on behalf of the two shareholders who opted out of the settlement and those who purchased stock from November 21, 2019 through March 9, 2020, based on purported new revelations. The claims are for alleged violations of Sections 11 and 15 of the Securities Act. On February 23, 2024, plaintiff filed a motion for class certification, which has been set for hearing on February 25, 2025. While the Company intends to defend vigorously against this litigation, there can be no assurance that the Company will be successful in its defense. For this reason, the Company cannot currently estimate the loss or range of possible losses it may experience in connection with this litigation.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
None.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Market Information
Our common stock, par value $0.00001 per share, is listed on the Nasdaq Global Select Market, under the symbol “REAL” and began trading on June 28, 2019. Prior to that date, there was no public trading market for our common stock.
Stockholders
As of the close of business on February 14, 2025, there were 111 stockholders of record of our common stock. The actual number of holders of our common stock is greater than this number of record holders, and includes stockholders who are beneficial owners, but whose shares are held in street name by brokers or other nominees. This number of holders of record also does not include stockholders whose shares may be held in trust by other entities.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain all available funds and future earnings, if any, to fund the development and expansion of our business, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination regarding the declaration and payment of dividends, if any, will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on then-existing conditions, including our financial condition, operating results, contractual restrictions, capital requirements, business prospects and other factors our board of directors may deem relevant. Our ability to pay cash dividends on our capital stock is limited by the terms of our existing term loans and may be limited by any future debt instruments or preferred securities.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The information required by this item with respect to our equity compensation plans will be incorporated by reference to our 2025 proxy statement set forth in the section titled “Equity Compensation Plan Information” that will be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the year ended December 31, 2024 (the “Proxy Statement”).
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
None.
Item 6. Reserved
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read together with our financial statements and related notes and other financial information included in this Annual Report. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that reflect our plans, estimates and beliefs. Our actual results could differ materially from those discussed in the forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to these differences include those discussed below and elsewhere in this Annual Report, particularly in the section titled “Risk Factors.” Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for any period in the future.
Overview
We are the world’s largest online marketplace for authenticated resale luxury goods. We are revolutionizing luxury resale by providing an end-to-end service that unlocks supply from consignors and creates a trusted, curated online marketplace for buyers globally. Since our inception in 2011, we have cultivated a loyal and engaged consignor and buyer base through our investments in our technology platform, logistics infrastructure and people. We offer a wide selection of authenticated, primarily pre-owned luxury goods on our online marketplace bearing the brands of thousands of luxury and premium designers. We offer products across multiple categories including women’s and men’s fashion, fine jewelry and watches. We have built a vibrant online marketplace that we believe expands the overall luxury market, promotes the recirculation of luxury goods and contributes to a more sustainable world.
We have transformed the luxury consignment experience by removing the friction and pain points inherent in the traditional consignment model. For consignors, we offer concierge at-home consultation and pickup as well as virtual consultations. Consignors may also drop off items at our luxury consignment offices. Our retail stores provide an alternative location to drop off consigned items and an opportunity to interact with our authentication experts. Consignors may also utilize our complimentary shipping directly to our authentication centers. We leverage our proprietary transactional database and market insights from approximately 44.5 million item sales since our inception to deliver optimal pricing and rapid sell-through. For buyers, we offer highly coveted and exclusive authenticated pre-owned luxury goods at attractive values, as well as a high-quality experience befitting the products we offer. Our online marketplace is powered by our proprietary technology platform, including consumer facing applications and purpose-built software that supports our complex, single-SKU inventory management system.
The substantial majority of our revenue is generated by consignment sales. We also generate revenue from other services and direct sales.
•Consignment revenue. When we sell goods through our online marketplace or retail stores on behalf of our consignors, we retain a percentage of the proceeds, which we refer to as our take rate. Take rates vary depending on the total value of goods sold through our online marketplace on behalf of a particular consignor as well as the category and price point of the items. In 2024 and 2023, our overall take rate on consigned goods was 38.4% and 37.5% respectively. The increase in our take rate was due to the update of our consignor commission structure (effective November 1, 2022). Additionally, we earn revenue from our subscription program, First Look, in which we offer buyers early access to the items we sell in exchange for a monthly fee.
•Direct revenue. When we accept out of policy returns from buyers, or when we make direct purchases from businesses and consignors, we take ownership of goods and retain 100% of the proceeds when the goods subsequently sell through our online marketplace or retail stores.
•Shipping services revenue. When we deliver purchased items to our buyers, we charge shipping fees to buyers for the outbound shipping and handling services. We also generate shipping services revenue from the shipping fees for consigned products returned by our buyers to us within policy. Shipping services revenue excludes the effect of buyer incentives and sales tax.
We generate revenue from orders processed through our website, mobile app and retail stores. Our omni-channel experience enables buyers to purchase anytime and anywhere. We have a global base of more than 38.6 million members as of December 31, 2024. We count as a member any user who has registered an email address on our website or downloaded our mobile app, thereby agreeing to our terms of service.
Factors Affecting Our Performance
To analyze our business performance, determine financial forecasts and help develop long-term strategic plans, we focus on the factors described below. While each of these factors presents significant opportunity for our business, collectively, they also pose important challenges that we must successfully address in order to sustain our growth, improve our operating results and achieve and maintain our profitability.
Consignors and Buyers
Consignor growth and retention. We grow our sales by increasing the supply of luxury goods offered through our consignment online marketplace. We grow our supply both by attracting new consignors and by creating lasting engagement with existing consignors. We generate leads for new consignors through our advertising activity and through the activity of our sales team. Our sales professionals, who are trained and incentivized to identify and source high-quality, coveted luxury goods, convert those leads into active consignors. Our sales professionals form a consultative relationship with consignors and deliver a high-quality, full-service consigning experience. Our existing relationships with consignors allow us to unlock valuable supply across multiple categories, including women’s fashion, men’s fashion, jewelry and watches.
We measure the ratio of demand versus supply in a given period, which we refer to as our online marketplace sell-through ratio. Sell-through ratio is defined as GMV in the period divided by the aggregate initial value of items added to our online marketplace in the period. In 2024, our online marketplace sell-through ratio was approximately 85%.
Our growth has been driven in significant part by repeat sales by existing consignors concurrent with growth of our consignor base. In 2024 and 2023, repeat consignors accounted for over 80% of GMV.
Buyer growth and retention. We grow our business by attracting and retaining buyers. We attract and retain buyers by offering highly coveted, authenticated, pre-owned luxury goods at attractive values and delivering a high-quality, luxury experience. We measure our success in attracting and retaining buyers by tracking buyer satisfaction and purchasing activity over time. If we fail to continue to attract and retain our buyer base to our online marketplace, our operating results could be adversely affected.
We believe there is substantial opportunity to grow our business by having buyers also become consignors and vice versa. As of December 31, 2024, 15% of our buyers during the last twelve months also consigned items, and 48% of our consignors also made purchases. We believe this approach effectively captures the flywheel effect that strengthens the network dynamics of our online marketplace. If we fail to continue to attract and retain our buyer base to our online marketplace, our operating results would be adversely affected. The graph below shows the percentage of GMV in each year from buyers who have participated as both buyers and consignors on our online marketplace. GMV attributable to consigning activity of such buyers is not included. Our GMV from buyers who are also consignors has increased over time due to the effectiveness of our flywheel.

Buyer acquisition cost. Our financial performance depends on effectively managing the expenses we incur to attract and retain buyers. We closely monitor our efficiency in acquiring new buyers. Our buyer acquisition cost (“BAC”) for a given period is comprised of our total advertising spend for acquiring both buyers and consignors, which is principally the cost of television, digital and direct mail advertising, divided by the number of buyers acquired in that period. We adjust or re-allocate our advertising in real-time to optimize our spend across channels, buyer demographics and geographies to improve our return on advertising spend. Our BAC has declined over time, which has been driven by improving acquisition efficiencies.

Scaling operations and technology. To support the future growth of our business, we continue to invest in physical infrastructure, technology and talent. We principally conduct our intake, authentication, merchandising and fulfillment operations in our leased authentication centers located in Arizona and New Jersey comprising an aggregate of approximately 1.4 million square feet of space. We also operate retail stores in several geographies. In addition to scaling our physical infrastructure, growing our single-SKU business operations requires that we attract, train and retain highly-skilled personnel for purposes of authentication, copywriting, merchandising, pricing and fulfilling orders. We have invested substantially in technology to automate our operations and support growth, including proprietary machine learning technology to support efficiency and quality. We continue to strategically invest in technology, as innovation positions us to scale and support growth into the future.
Seasonality. Historically, we have observed trends in seasonality of supply and demand in our business. Specifically, our supply increases in the third and fourth quarters, and our demand increases in the fourth quarter. As a result of this seasonality, we typically see stronger AOV and more rapid sell-through in the fourth quarter.
Key Financial and Operating Metrics
The key operating and financial metrics that we use to assess the performance of our business are set forth below for 2024, 2023, and 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands, except AOV and percentages) |
| GMV | $ | 1,829,463 | | | $ | 1,725,983 | | | $ | 1,815,983 | |
| NMV | $ | 1,382,875 | | | $ | 1,269,880 | | | $ | 1,335,506 | |
Consignment revenue | $ | 473,396 | | | $ | 415,572 | | | $ | 384,979 | |
Direct revenue | $ | 64,580 | | | $ | 79,160 | | | $ | 158,726 | |
| Shipping services revenue | $ | 62,508 | | | $ | 54,572 | | | $ | 59,788 | |
| Number of orders | 3,359 | | | 3,300 | | | 3,757 | |
| Take rate | 38.4 | % | | 37.5 | % | | 36.0 | % |
| Active buyers | 972 | | | 922 | | | 998 | |
| AOV | $ | 545 | | | $ | 523 | | | $ | 483 | |
| | | | | |
GMV
GMV represents the total amount paid for goods across our online marketplace in a given period. We do not reduce GMV to reflect product returns or order cancellations, which totaled 24.4%, 26.4%, and 26.5% of GMV in 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively. GMV includes amounts paid for both consigned goods and our inventory net of platform-wide discounts and excludes the effect of buyer incentives, shipping fees and sales tax. Platform-wide discounts are made available to all buyers on the online marketplace, and impact commissions paid to consignors. Buyer incentives apply to specific buyers and consist of coupons or promotions that offer credits in connection with purchases on our platform. In addition to revenue, we believe this is an important measure of the scale and growth of our online marketplace and a key indicator of the health of our consignor ecosystem. We monitor trends in GMV to inform budgeting and operational decisions to support and promote growth in our business and to monitor our success in adapting our business to meet the needs of our consignors and buyers. While GMV is the primary driver of our revenue, it is not a proxy for revenue or revenue growth (see Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Revenue Recognition—Consignment Revenue).
NMV
NMV represents the value of sales from both consigned goods and our inventory net of platform-wide discounts less product returns and order cancellations and excludes the effect of buyer incentives, shipping fees and sales tax. We believe NMV is a supplemental measure of the scale and growth of our online marketplace. Like GMV, NMV is not a proxy for revenue or revenue growth.
Consignment Revenue
Consignment revenue is generated from the sale of pre-owned luxury goods through our online marketplace and retail stores on behalf of consignors. We retain a portion of the proceeds received, which we refer to as our take rate. We recognize consignment revenue, net of allowances for product returns, order cancellations, buyer incentives and adjustments. We also generate revenue from subscription fees paid by buyers for early access to products.
Direct Revenue
Direct revenue is generated from the sales of company-owned inventory. We recognize direct revenue upon shipment of the goods sold, based on the gross purchase price net of allowances for product returns, buyer incentives and adjustments.
Shipping Services Revenue
Shipping services revenue is generated from shipping fees we charge to buyers for outbound shipping and handling activities related to delivering purchased items to our buyers. We also generate shipping services revenue from the shipping
fees for consigned products returned by our buyers to us within policy. We recognize shipping services revenue over time as the shipping activity occurs. Shipping services revenue excludes the effect of buyer incentives and sales tax.
Number of Orders
Number of orders means the total number of orders placed across our online marketplace and retail stores in a given period. We do not reduce number of orders to reflect product returns or order cancellations.
Take Rate
Take rate is a key driver of our revenue and provides comparability to other marketplaces. The numerator used to calculate our take rate is equal to net consignment sales and the denominator is equal to the numerator plus consignor commissions. Net consignment sales represent the value of sales from consigned goods net of platform-wide discounts less consignor commission, product returns and order cancellations. We exclude direct revenue from our calculation of take rate because direct revenue represents the sale of inventory owned by us, which costs are included in cost of direct revenue. Our take rate reflects the high level of service that we provide to our consignors across multiple touch points and the consistently high velocity of sales for their goods. In November 2022, we updated our take rate structure with the goals of optimizing take rate, limiting consignment of lower value items, and increasing supply of higher value items. We continue to assess our take rate structure and may implement further changes in the future.
Our take rate structure is primarily based on the category and the price point of the sold items. For example, under the current take rate structure, consignors can earn 20% commission on all sold items under $100, and up to 90% commission on watches sold for over $7,500. We launched a pricing tool for our consignors that provides detail on commission rates for specific categories and other aspects of the take rate structure. Consignors are eligible to receive additional commissions based on total net sales under an added tiered commission structure. Management assesses changes in take rates by monitoring the volume of GMV and take rate across each discrete commission grouping, encompassing commission tiers and exceptions.
Active Buyers
Active buyers include buyers who purchased goods through our online marketplace during the 12 months ended on the last day of the period presented, irrespective of returns or cancellations. We believe this metric reflects scale, brand awareness, buyer acquisition and engagement.
Average Order Value (“AOV”)
Average order value (“AOV”) means the average value of all orders placed across our online marketplace and retail stores, excluding the effect of buyer incentives, shipping fees and sales taxes. Our focus on luxury goods across multiple categories drives a consistently strong AOV. Our AOV reflects both the average price of items sold as well as the number of items per order. Our AOV is a key driver of our operating leverage.
Components of our Operating Results
Revenue
Our revenue is comprised of consignment revenue, direct revenue and shipping services revenue.
•Consignment revenue. We generate the substantial majority of our revenue from the sale of pre-owned luxury goods through our online marketplace and retail stores on behalf of consignors. For consignment sales, we retain a percentage of the proceeds received, which we refer to as our take rate. We recognize consignment revenue, net of allowances for product returns, order cancellations, buyer incentives and adjustments. Additionally, we generate revenue from subscription fees paid by buyers for early access to products, but to date our subscription revenue has not been material.
•Direct revenue. We generate direct revenue from the sale of items that we own, which we refer to as our inventory. We generally acquire inventory when we accept out of policy returns from buyers, and when we make direct purchases from businesses and consignors. We recognize direct revenue upon shipment based on the gross purchase price paid by buyers for goods, net of allowances for product returns, buyer incentives and adjustments.
•Shipping services revenue. We generate shipping services revenue from the outbound shipping and handling fees we charge when delivering purchased items to our buyers. We also generate shipping services revenue from the shipping fees for consigned products returned by our buyers to us within policy. We recognize shipping services revenue over time as the shipping activity occurs. Shipping services revenue excludes the effect of buyer incentives and sales tax.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of consignment revenue consists of credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and consignor inventory adjustments related to lost or damaged products. Cost of direct revenue consists of the cost of goods sold, credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and inventory adjustments for lower of cost or net realizable value provisions and for lost or damaged products. Cost of shipping services revenue consists of the outbound shipping and handling costs to deliver purchased items to our buyers, the shipping costs for consigned products returned by our buyers to us within policy, and an allocation of the credit card fees associated with the shipping fee charged.
Marketing
Marketing expense comprises the cost of acquiring and retaining consignors and buyers, including the cost of television, digital and direct mail advertising. Marketing expense also includes personnel-related costs for employees engaged in these activities. We expect these expenses to continue to decrease as a percentage of revenue over the longer term.
Operations and Technology
Operations and technology expense principally includes personnel-related costs for employees involved with the authentication, merchandising and fulfillment of goods sold through our online marketplace and retail stores, as well as our general information technology expense. Operations and technology expense also includes allocated facility and overhead costs, costs related to our retail stores, facility supplies, inbound consignment shipping costs, and depreciation of hardware and equipment, as well as research and development expense for technology associated with managing and improving our operations. We capitalize a portion of our proprietary software and technology development costs. As such, operations and technology expense also includes amortization of capitalized technology development costs. We expect operations and technology expense to increase in future periods to support our growth, including continuing to invest in automation and other technology improvements to support and drive efficiency in our operations. These expenses may vary from year to year as a percentage of revenue, depending primarily upon when we choose to make more significant investments. We expect these expenses to continue to decrease as a percentage of revenue over the longer term.
Selling, General and Administrative
Selling, general and administrative expense is principally comprised of personnel-related costs for our sales professionals and employees involved in finance and administration. Selling, general and administrative expense also includes allocated facilities and overhead costs and professional services, including accounting and legal advisors. We expect these expenses to continue to decrease as a percentage of revenue over the longer term.
Restructuring
Restructuring expense is primarily comprised of right-of-use asset and fixed asset impairments, severance benefits, and other related charges, including net gain on lease terminations. Impairment losses are measured and recorded for the excess of carrying value over its fair value, estimated based on expected future cash flows using discount rate and other quantitative and qualitative factors. The assumptions used such as projected future cash flows, discount rates, and determination of appropriate market comparable, are subject to volatility and may differ from actual results.
Provision for Income Taxes
Our provision for income taxes consists primarily of state minimum taxes in the United States. We have a full valuation allowance for our net deferred tax assets primarily consisting of net operating loss carryforwards, accruals and reserves, stock-based compensation, fixed assets, and other book-to-tax timing differences. We expect to maintain this full valuation allowance for the foreseeable future.
Results of Operations
The results of operations presented below should be reviewed in conjunction with the financial statements and notes included elsewhere in the Annual Report. Prior year comparisons for 2023 and 2022 are included in “Part II, Item 7 – Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023. The following tables set forth our results of operations (in thousands) and such data as a percentage of revenue for the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Revenue: | | | | | |
| Consignment revenue | $ | 473,396 | | | $ | 415,572 | | | $ | 384,979 | |
Direct revenue | 64,580 | | | 79,160 | | | 158,726 | |
| Shipping services revenue | 62,508 | | | 54,572 | | | 59,788 | |
Total revenue | 600,484 | | | 549,304 | | | 603,493 | |
| Cost of revenue: | | | | | |
| Cost of consignment revenue | 53,801 | | | 58,120 | | | 56,963 | |
Cost of direct revenue | 55,809 | | | 74,343 | | | 141,661 | |
| Cost of shipping services revenue | 43,353 | | | 40,563 | | | 56,178 | |
Total cost of revenue | 152,963 | | | 173,026 | | | 254,802 | |
| Gross profit | 447,521 | | | 376,278 | | | 348,691 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
Marketing | 55,256 | | | 58,275 | | | 62,988 | |
Operations and technology | 260,827 | | | 257,041 | | | 278,628 | |
Selling, general and administrative | 187,737 | | | 183,793 | | | 195,342 | |
| Restructuring | 196 | | | 43,462 | | | 896 | |
Total operating expenses | 504,016 | | | 542,571 | | | 537,854 | |
| Loss from operations | (56,495) | | | (166,293) | | | (189,163) | |
Change in fair value of warrant liability | (68,167) | | | — | | | — | |
Gain on extinguishment of debt | 4,177 | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest income | 7,943 | | | 8,805 | | | 3,191 | |
| Interest expense | (21,384) | | | (10,701) | | | (10,472) | |
Other income, net | — | | | — | | | 171 | |
| Loss before provision for income taxes | (133,926) | | | (168,189) | | | (196,273) | |
| Provision for income taxes | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | |
| Net loss | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenue: | | | | | |
| Consignment revenue | 79 | % | | 76 | % | | 64 | % |
Direct revenue | 11 | | | 14 | | | 26 | |
| Shipping services revenue | 10 | | | 10 | | | 10 | |
Total revenue | 100 | | | 100 | | | 100 | |
| Cost of revenue: | | | | | |
| Cost of consignment revenue | 9 | | | 11 | | | 9 | |
Cost of direct revenue | 9 | | | 14 | | | 24 | |
| Cost of shipping services revenue | 7 | | | 7 | | | 9 | |
Total cost of revenue | 25 | | | 32 | | | 42 | |
| Gross profit | 75 | | | 68 | | | 58 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
Marketing | 9 | | | 11 | | | 11 | |
Operations and technology | 43 | | | 47 | | | 46 | |
Selling, general and administrative | 31 | | | 33 | | | 33 | |
Restructuring | — | | | 8 | | | — | |
Total operating expenses | 83 | | | 99 | | | 90 | |
| Loss from operations | (8) | | | (31) | | | (32) | |
Change in fair value of warrant liability | (11) | | | — | | | — | |
Gain on extinguishment of debt | 1 | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest income | 1 | | | 2 | | | 1 | |
| Interest expense | (4) | | | (2) | | | (2) | |
Other income, net | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Loss before provision for income taxes | (21) | | | (31) | | | (33) | |
| Provision for income taxes | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Net loss | (21) | % | | (31) | % | | (33) | % |
Comparison of 2024 and 2023
Consignment Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
Consignment revenue | $ | 473,396 | | | $ | 415,572 | | | $ | 57,824 | | | 14 | % |
Consignment revenue increased by $57.8 million, or 14%, in 2024 compared to 2023. The increase in revenue was driven primarily by an increase in consignment GMV, a 4% increase in our AOV and a 240 basis point improvement in our take rate during the year ended December 31, 2024. Overall GMV increased by 6% during the year ended December 31, 2024. The increase in GMV is driven by an increase in consignment GMV, slightly offset by a decrease in direct GMV. Our take rate increased to 38.4% from 37.5% during the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to last year due to the update of our consignor commission structure which went into effect on November 1, 2022.
Direct Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Direct revenue | $ | 64,580 | | | $ | 79,160 | | | $ | (14,580) | | | (18) | % |
Direct revenue decreased by $14.6 million, or 18%, in 2024 compared to 2023. The decrease was primarily driven by our planned actions to rebalance vendor-purchased company-owned inventory as the margin profile of our direct revenue is lower than consignment revenue. We recognize direct revenue upon shipment of the purchased good to the buyer. Direct revenue as a percentage of total revenue may vary from period to period primarily based on the amount of consignment revenue.
Shipping Services Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Shipping services revenue | $ | 62,508 | | | $ | 54,572 | | | $ | 7,936 | | | 15 | % |
Shipping services revenue increased by $7.9 million, or 15%, in 2024 compared to 2023 primarily due to an increase in the standard shipping fee per order.
Cost of Consignment Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Cost of consignment revenue | $ | 53,801 | | | $ | 58,120 | | | $ | (4,319) | | | (7) | % |
| As a percent of consignment revenue | 11 | % | | 14 | % | | | | |
Cost of consignment revenue decreased by $4.3 million, or 7%, in 2024 compared to 2023, driven by a decrease in overhead costs, including packaging, employee compensation related expenses and website hosting fees, partially offset by costs directly associated with the increase in consignment revenue.
Consignment revenue gross margin increased by 262 basis points in the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to the year ended December 31, 2023, driven by the improvement in take rate and the reduction in overhead costs.
Cost of Direct Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Cost of direct revenue | $ | 55,809 | | | $ | 74,343 | | | $ | (18,534) | | | (25) | % |
| As a percent of direct revenue | 86 | % | | 94 | % | | | | |
Cost of direct revenue decreased by $18.5 million, or 25%, in 2024 compared to 2023. The decrease was primarily attributable to the 18% decrease in direct revenue compared to the prior year as a result of our planned actions to rebalance vendor-purchased company-owned inventory.
Direct revenue gross margin increased by 750 basis points in the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to the year ended December 31, 2023, primarily driven by strategic liquidation of company owned inventory sold at discounted prices, which resulted in the sell through of inventory that was previously reserved. The margin profile of our direct revenue is lower than the margin profile of our consignment revenue.
Cost of Shipping Services Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Cost of shipping services revenue | $ | 43,353 | | | $ | 40,563 | | | $ | 2,790 | | | 7 | % |
| As a percent of shipping services revenue | 69 | % | | 74 | % | | | | |
Cost of shipping services revenue increased by $2.8 million, or 7%, in the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to the year ended December 31, 2023, primarily due to increased cost per shipment.
Shipping services revenue gross margin increased by 497 basis points in the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to the year ended December 31, 2023, primarily due to the increase in the standard shipping fee per order.
Total Gross Margin
Our total gross margin increased by 603 basis points in the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to the year ended December 31, 2023 primarily driven by the increase in higher margin consignment revenue and decrease in lower margin direct revenue. Gross margin may vary from period to period.
Marketing
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Marketing | $ | 55,256 | | | $ | 58,275 | | | $ | (3,019) | | | (5) | % |
Marketing expense decreased by $3.0 million, or 5%, in 2024 compared to 2023. The decrease was primarily due to a decrease in advertising costs.
As a percentage of revenue, marketing expense decreased to 9% in 2024 from 11% and 2023. These expenses may vary from period to period as a percentage of revenue, depending primarily upon our marketing investments. We expect these expenses to decrease as a percentage of revenue over the longer term.
Operations and Technology
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Operations and technology | $ | 260,827 | | | $ | 257,041 | | | $ | 3,786 | | | 1 | % |
Operations and technology expense increased by $3.8 million, or 1%, in 2024 compared to 2023. The increase was primarily due to higher employee costs and software and service expenses, partially offset by a decrease in stock based compensation expense.
As a percentage of revenue, operations and technology expense decreased to 43% in 2024 from 47% in 2023 due to an increase in consignment revenue. These expenses may vary from period to period as a percentage of revenue, depending primarily upon when we choose to make more significant investments. We expect these expenses to decrease as a percentage of revenue over the longer term.
Selling, General and Administrative
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Selling, general and administrative | $ | 187,737 | | | $ | 183,793 | | | $ | 3,944 | | | 2 | % |
Selling, general and administrative expense increased by $3.9 million, or 2%, in 2024 compared to 2023. The increase was primarily due to increased employee compensation related expenses due to an increase in headcount compared to the prior period.
As a percentage of revenue, selling, general and administrative decreased to 31% in 2024 from 33% in 2023. These expenses may vary from period to period as a percentage of revenue. We expect these expenses to decrease as a percentage of revenue over the longer term.
Restructuring
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
Restructuring | $ | 196 | | | $ | 43,462 | | | $ | (43,266) | | | (100) | % |
Restructuring decreased by $43.3 million, or over 100%, in 2024 compared to 2023. We incurred charges to reduce our real estate presence and operating expenses through the closure of certain retail and office locations and workforce reduction during 2023, which were substantially completed during 2023.
Change in Fair Value of Warrant Liability
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
Change in fair value of warrant liability | $ | (68,167) | | | $ | — | | | $ | (68,167) | | | 100 | % |
The fair value of warrant liability increased by $68.2 million, or 100% in 2024 compared to 2023. The Company issued warrants to acquire an aggregate of up to 7,894,737 shares (subject to adjustment in accordance with the terms of the warrants) of the Company's common stock as part of the 2024 Note Exchange (as defined below) in February 2024. The change was due to the unrealized loss on the change in fair value of the warrant liability from the issuance date to December 31, 2024 (See Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net).
Gain on Extinguishment of Debt
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
Gain on extinguishment of debt | $ | 4,177 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,177 | | | 100 | % |
Gain on extinguishment of debt increased by $4.2 million, or 100% in 2024 compared to 2023. The increase was due to the gain recorded from the extinguishment of the Exchanged Notes (as defined below) and the issuance of the 2029 Notes (See Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net).
Interest Income
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Interest income | $ | 7,943 | | | $ | 8,805 | | | $ | (862) | | | (10) | % |
Interest income decreased by $0.9 million, or 10%, in the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to the year ended December 31, 2023 due to lower average cash balances.
Interest Expense
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except percentage) |
| Interest expense | $ | (21,384) | | | $ | (10,701) | | | $ | 10,683 | | | 100 | % |
Interest expense increased by $10.7 million, or 100%, for the year ended December 31, 2024 compared to the year ended December 31, 2023 due to the contractual interest expense related to the 2029 Notes issued in February 2024.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2024, we had cash and cash equivalents of $172.2 million and an accumulated deficit of $1,253.8 million. We had restricted cash of $14.9 million as of December 31, 2024, consisting of cash deposited with a financial institution as collateral for our letters of credit, facility leases and credit cards. Since our inception, we have generated negative cash flows from operations and have primarily financed our operations through equity and convertible debt financings. In July 2019, we received net proceeds of $315.5 million upon completion of our IPO on July 2, 2019. In June 2020, we received net proceeds of $143.3 million from the issuance of our 2025 Notes and the related capped call transactions. In March 2021, we received net proceeds of $244.5 million from our 2028 Notes and the related capped call transactions. In February 2024, we exchanged $145.8 million of the 2025 Notes and $6.5 million of the 2028 Notes for $135.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2029 Notes (the “2024 Note Exchange”). As a result of the 2024 Note Exchange, we significantly extended the average maturity date of our outstanding indebtedness (see Note 6 - Non-convertible Notes, Net).
On February 10, 2025, we entered into an exchange agreement with certain holders of our 2028 Notes (the “2025 Exchange Agreement”). Under the terms of the 2025 Exchange Agreement, certain holders of the 2028 Notes agreed to exchange $183.3 million aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes for $146.7 million aggregate principal amount of our new 2031 Notes (the “2025 Notes Exchange”). The 2031 Notes bear cash interest at a rate of 4.00% per annum payable semi-annually in arrears and mature on February 15, 2031.
We expect that operating losses and negative cash flows from operations could continue in the foreseeable future. We believe our existing cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2024 will be sufficient to meet our working capital and capital expenditures needs for at least the next 12 months.
Our primary capital requirements include contractual obligations related to our operating leases, our indebtedness, certain non-cancellable contracts and compensation and benefits payments to support our strategic plans. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to, those set forth under the heading “Risk Factors” in this Annual Report, and our ability to grow our revenues and the timing of investments to support growth in our business, such as the build-out of our authentication centers and, to a lesser extent, the opening of new retail stores. We may seek additional equity or debt financing. In the event that additional financing is required from outside sources, we may not be able to raise it on terms acceptable to us or at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital when desired, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the periods indicated. Prior year comparisons are included in "Park II, Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Net cash (used in) provided by: | | | | | |
Operating activities | $ | 26,846 | | | $ | (61,268) | | | $ | (91,557) | |
Investing activities | (25,587) | | | (42,128) | | | (36,922) | |
Financing activities | (4,759) | | | 226 | | | 4,101 | |
Net decrease in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | (3,500) | | | $ | (103,170) | | | $ | (124,378) | |
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
During 2024, net cash provided by operating activities was $26.8 million, which consisted of a net loss of $134.2 million, adjusted by non-cash charges of $158.2 million and cash inflows due to a net change of $2.8 million in our operating assets and liabilities. The net change in our operating assets and liabilities was primarily the result of cash inflows due to an increase of $11.5 million in consignor payables and an increase of $13.1 million in other accrued and current liabilities, partially offset by cash outflows due to a decrease of $20.9 million in operating lease liabilities. Our primary uses of cash in operating activities include operating costs such as operating lease obligations, compensation and benefits, marketing, and other expenditures necessary to support our business growth.
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities
During 2024, net cash used in investing activities was $25.6 million, which consisted of $14.2 million for purchases of property and equipment, net, including leasehold improvements, and $11.8 million for capitalized proprietary software costs.
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
During 2024, net cash used in financing activities was $4.8 million, which primarily consisted of cash outflows of $5.3 million for debt issuance costs related to the 2024 Note Exchange and $1.6 million of taxes related to restricted stock units vesting, partially offset by $1.4 million of proceeds from the issuance of common stock related to the Company's employee stock purchase plan.
Convertible Senior Notes
As of December 31, 2024, we had 2025 Notes outstanding in an aggregate principal amount of $26.7 million and 2028 Notes outstanding in an aggregate principal amount of $281.0 million. A portion of the net proceeds from the sale of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes was used to fund the net cost of entering into the capped call transactions described below.
The 2025 Notes are convertible into cash, shares of our common stock or a combination of cash and shares of our common stock, at the Company’s election, at an initial conversion rate of 56.2635 shares of our common stock per $1,000 principal amount of the 2025 Notes, which is equivalent to an initial conversion price of approximately $17.77 per share of our common stock. The initial conversion price of the 2025 Notes represents a premium of approximately 27.5% over the $13.94 closing price of our common stock on June 10, 2020. The 2028 Notes are convertible into cash, shares of our common stock or a combination of cash and shares of our common stock, at the Company’s election, at an initial conversion rate of 31.4465 shares of our common stock per $1,000 principal amount of the 2028 Notes, which is equivalent to an initial conversion price of approximately $31.80 per share of our common stock. The initial conversion price of the notes represents a premium of approximately 32.5% over the $24.00 closing price of our common stock on March 3, 2021.
In connection with the the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, we entered into privately negotiated capped call transactions, with certain of the initial purchasers or their affiliates. The capped call transactions cover, subject to anti-dilution adjustments, the number of shares of common stock underlying the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes sold in the offering. The capped call transactions are generally expected to reduce potential dilution to our common stock upon any conversion of the notes and/or offset any cash payments we are required to make in excess of the principal amount of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, as the case may be, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap. The cap price of the capped call transactions related to the 2025 Notes was initially $27.88 per share, which represents a premium of 100.0% over the closing price of our common stock of $13.94 per share on June 10, 2020, and is subject to certain adjustments under the terms of the capped call transactions. The cap price of the capped call transactions related to the 2028 Notes was initially $48.00 per share, which represents a premium of 100.0% over the closing price of our common stock of $24.00 per share on March 3, 2021, and is subject to certain adjustments under the terms of the capped call transactions.
On February 10, 2025, pursuant to the 2025 Notes Exchange, we issued $146.7 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2031 Notes in exchange for $183.3 million in aggregate principal amount of our 2028 Notes. The 2031 Notes are convertible into cash, shares of our common stock or a combination of cash and shares of our common stock, at the Company’s election, at an initial conversion rate of 95.5795 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount, which is equivalent to an initial conversion price of approximately $10.46 per share of our common stock. The initial conversion price represents a premium of approximately 26.9% over the $8.24 closing price of our common stock on February 10, 2025. As a result of the 2025 Notes Exchange, we have $97.7 million outstanding in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes as of the date hereof. We did not receive any cash proceeds from the issuance of the 2031 Notes in the 2025 Notes Exchange.
For additional details related to our Convertible Senior Notes, please see “Note 7 – Convertible Senior Notes, Net” and "Note 17 — Subsequent Events" to the financial statements included in this report.
2029 Notes and Warrants
On February 29, 2024, the Company entered into exchange agreements with certain holders (the “Exchange Holders”) of its Convertible Senior Notes to exchange (i) $145.8 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2025 Notes and (ii) $6.5 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes (together, the “Exchanged Notes”) for $135.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the Company’s 4.25%/8.75% PIK/Cash Senior Secured Notes due 2029 (the “2029 Notes”), pursuant to an indenture. The 2029 Notes bear interest at a rate of 13.00% per annum, consisting of cash interest at a rate of 8.75% per annum payable semi-annually in arrears and payment in-kind interest at a rate of 4.25% per annum payable semi-annually. The 2029 Notes will mature on the earlier of (a) March 1, 2029 and (b) any date, if any, on or after December 1, 2027 on which (a) the aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes then outstanding is greater than $20 million and (b) the difference between (i) the amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held by the Company and its subsidiaries (if any) as of such date of determination and (ii) the aggregate principal amount of 2028 Notes outstanding as of such date of determination is less than $75 million. In connection with the 2024 Note Exchange, the Company issued warrants to acquire an aggregate of up to 7,894,737 shares (subject to adjustment in accordance with the terms of the warrants) of the Company’s common stock to the holders of the Exchanged Notes at an exercise price of $1.71, subject to certain cashless exercise provisions and adjustment in accordance with the terms of the warrants (the “Warrants”) (see “Note 4 – Fair Value Measurement” to the financial statements included in this report for further details on the terms of the Warrants).
For additional details related to our 2029 Notes, please see “Note 6 – Non-convertible Notes, Net” to the financial statements included in this report.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
Adjusted EBITDA
Adjusted EBITDA is a key performance measure that our management uses to assess our operating performance. Because Adjusted EBITDA facilitates internal comparisons of our historical operating performance on a more consistent basis, we use this measure as an overall assessment of our performance, to evaluate the effectiveness of our business strategies and for business planning purposes and for incentive and compensation purposes. Adjusted EBITDA may not be comparable to similarly titled metrics of other companies.
Adjusted EBITDA means net loss before interest income, interest expense, provision for income taxes, and depreciation and amortization, further adjusted to exclude stock-based compensation, payroll taxes on employee stock transactions, restructuring, CEO separation benefits and transition costs, gain on extinguishment of debt, change in fair value of warrant liability and certain one time expenses. Adjusted EBITDA provides a basis for comparison of our business operations between current, past and future periods by excluding items that we believe are not indicative of our core operating performance. Adjusted EBITDA is a non-GAAP measure. Adjusted EBITDA has certain limitations as the measure excludes the impact of certain expenses that are included in our statements of operations that are necessary to run our business and should not be considered as an alternative to net loss or any other measure of financial performance calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP.
In particular, the exclusion of certain expenses in calculating Adjusted EBITDA facilitates operating performance comparisons on a period-to-period basis and, in the case of exclusion of the impact of stock-based compensation and the related employer payroll tax expense on employee stock transactions, excludes an item that we do not consider to be indicative of our core operating performance. Investors should, however, understand that stock-based compensation and the related employer payroll tax expense will be a significant recurring expense in our business and an important part of the compensation provided to our employees. Accordingly, we believe that Adjusted EBITDA provides useful information to investors and others in understanding and evaluating our operating results in the same manner as our management and board of directors.
The following table provides a reconciliation of net loss to Adjusted EBITDA (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Adjusted EBITDA Reconciliation: | | | | | |
| Net loss | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
| Add (deduct): | | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | 33,100 | | | 31,695 | | | 27,669 | |
| Interest income | (7,943) | | | (8,805) | | | (3,191) | |
Interest expense (1) | 21,384 | | | 10,701 | | | 10,472 | |
| Provision for income taxes | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | |
| EBITDA | (87,385) | | | (134,598) | | | (161,323) | |
Stock-based compensation (2) | 29,082 | | | 34,273 | | | 46,138 | |
CEO separation benefits and transition costs (3) | 782 | | | 159 | | | 2,499 | |
| Payroll taxes on employee stock transactions | 371 | | | 195 | | | 451 | |
Legal settlements (4) | 600 | | | 1,340 | | | 456 | |
Restructuring (5) | 196 | | | 43,462 | | | 896 | |
Gain on extinguishment of debt (6) | (4,177) | | | — | | | — | |
Change in fair value of warrant liability (7) | 68,167 | | | — | | | — | |
One time expenses (8) | 1,672 | | | — | | | (1,571) | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 9,308 | | | $ | (55,169) | | | $ | (112,454) | |
(1) As of December 31, 2024, interest expense includes $4.8 million of accrued PIK interest which is a non-cash interest expense. PIK interest is added to the principal balance of the 2029 Notes semi-annually.
(2) The stock-based compensation expense for the year ended December 31, 2022 includes a one time charge of $1.0 million related to the modification of certain equity awards pursuant to the terms of the transition and separation agreement entered into with our founder, Julie Wainwright, in connection with her resignation as Chief Executive Officer ("CEO") on June 6, 2022 (the "Separation Agreement").
(3) The CEO separation benefits and transition costs for the year ended December 31, 2024 consist of severance and benefits payable to John Koryl pursuant to his separation agreement. The CEO separation benefits and transition costs for the year ended December 31, 2023 consists of retention bonuses for certain executives incurred in connection with our founder's resignation in 2022. The CEO separation benefits and transition costs for the year ended December 31, 2022 consist of separation benefits for the 2022 fiscal year, as well as general and administrative fees, including legal and recruiting expenses, as well as retention bonuses for certain executives incurred in connection with our founder's resignation on June 6, 2022.
(4) The legal settlement charges for the year ended December 31, 2023 reflect legal settlement expenses arising from the settlement of two former employees’ individual claims and California Private Attorney General Actions initiated against the Company on behalf of such former employees and those similarly situated.
(5) Restructuring for the year ended December 31, 2023 consists of impairment of right-of-use assets and property and equipment, employee severance charges, gain on lease terminations, and other charges, including legal and transportation expenses. Restructuring for the year ended December 31, 2022 consists of employee severance payments and benefits.
(6) The gain on extinguishment of debt for the year ended December 31, 2024 reflects the difference between the carrying value of the Exchanged Notes and the fair value of the 2029 Notes.
(7) The change in fair value of warrant liability for the year ended December 31, 2024 reflects the remeasurement of the warrants issued by the Company in connection with the 2024 Note Exchange in February 2024.
(8) One time expenses for the year ended December 31, 2024 consists of vendor services settlement and estimated losses, net of estimated insurance recoveries related to the fire at one of our New Jersey authentication centers. See "Note 12 - Commitments and Contingencies" in the notes to the audited financial statements for disclosure regarding the event. One time expense for the year ended December 31, 2022 primarily consists of insurance reimbursement of $1.4 million related to a legal settlement expense.
Material Contractual and Other Obligations
Our material contractual and other obligations as of December 31, 2024 consist of:
•Operating Leases. As of December 31, 2024, our cash requirements related to our operating leases on our authentication centers, retail stores, and corporate offices that are included in our balance sheet were $124.5 million, of which $28.8 million is expected to be paid within the next 12 months.
•Convertible Senior Notes. As of December 31, 2024, our cash requirements related to our Convertible Senior Notes that are included on our balance sheet and the related periodic interest payments were $287.0 million, of which $30.0 million is expected to be paid within the next 12 months. Our 2025 Notes will mature on June 15, 2025, unless earlier redeemed or repurchased by the Company or converted and our 2028 Notes will mature on March 1, 2028, unless earlier redeemed or repurchased by the Company or converted.
•Non-convertible Notes. As of December 31, 2024, our cash requirements related to our Non-convertible Notes that are included on our balance sheet and the related periodic interest payments were $225.8 million, of which $12.2 million is expected to be paid within the next 12 months.
•Non-cancellable purchase commitments. Our cash requirements related to certain other non-cancellable purchase commitments associated primarily with software services and hosting arrangements, were approximately $17.6 million, of which approximately $8.1 million is expected to be paid within the next 12 months.
On February 10, 2025, pursuant to the 2025 Notes Exchange, we issued $146.7 million in aggregate principal amount of our 2031 Notes in exchange for $183.3 million in aggregate principal amount of our 2028 Notes.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Our management’s discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based on our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires our management to make judgments and estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, as well as the reported revenue generated, and expenses incurred during the reporting periods. Our estimates are based on our historical experience and on various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these judgments and estimates under different assumptions or conditions and any such differences may be material.
While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, we believe that the accounting estimates discussed below involve a significant level of estimation uncertainty by management.
2024 Note Exchange
During the year ended December 31, 2024, we accounted for the 2024 Note Exchange as a debt extinguishment and recorded a gain on extinguishment as the difference between the carrying amount of the Exchanged Notes and the fair value of the 2029 Notes. We estimated fair value of the 2029 Notes by using projected future payments of interest and principal discounted at the effective yield. The fair value of the 2029 Notes is considered a critical estimate because the judgment in the valuation methods utilized and assessing an interest rate that would be available to us for a similar debt instrument.
Warrants
The Warrants are accounted for as liabilities under ASC 480 as the warrants may be required to be settled in cash in case of a fundamental change, which could occur outside of our control. The fair value of the warrant liability is estimated using the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model, which incorporates inherent uncertainties and generally requires significant judgement including factors such as the risk-free interest rate and the expected volatility of the price of the underlying stock. Changes in fair value are recognized on our statements of operations.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” to our financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for recently issued accounting pronouncements not yet adopted as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
We are a smaller reporting company as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act and are not required to provide the information otherwise requested under this item.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
Please refer to the Financial Statements and Notes to Financial Statements in this Form 10-K which is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of December 31, 2024. Based on this evaluation, our CEO and CFO concluded that, as of December 31, 2024, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level in ensuring that (a) the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms, and (b) such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management, including our CEO and CFO, is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of our financial reporting and the preparation of our financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our CEO and CFO, we have conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Based on evaluation under these criteria, management determined that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2024.
KPMG LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, has audited management's assertion on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, as stated in their report which is included in Part IV —Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting identified in connection with the evaluation required by Rule 13a-15(d) and 15d-15(d) of the Exchange Act that occurred during the year ended December 31, 2024 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations on Effectiveness of Controls
Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, believes that our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting are designed to provide reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and are effective at the reasonable assurance level. However, our management does not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision making can be faulty, and that breakdowns can occur because of a simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by the collusion of two or more people or by management override of controls. The design of any system of controls is also based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions; over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or the degree of compliance with policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of the inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected.
Item 9B. Other Information.
Rule 10b5-1 Trading Plans
During the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2024, none of our directors or officers adopted or terminated a "Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement" or a "non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement," as those terms are defined in Regulation S-K, Item 408.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections.
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
Information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our proxy statement for our 2025 annual meeting of stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024 (the “Proxy Statement”).
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our Proxy Statement.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our Proxy Statement.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our Proxy Statement.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
Our independent registered public accounting firm is KPMG LLP, San Francisco, CA, Auditor ID: 185.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our Proxy Statement.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
(a)Please refer to the Financial Statements, Notes to Financial Statements and the Exhibit Index in this Form 10-K which is incorporated herein by reference.
(b)Please refer to the Exhibit Index in this Form 10-K which is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
Exhibit Index
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | |
Exhibit Number | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed
Herewith |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 3.1 | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 3.2 | | June 17, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 3.2 | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 3.4 | | June 6, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.1 | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 4.1 | | June 17, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.2 | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 4.7 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.3 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 4.1 | | June 16, 2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.4 | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 4.2 | | August 7, 2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.5 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 4.1 | | March 8, 2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.6 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 4.1 | | March 8, 2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.7 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 4.1 | | February 10, 2025 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.8 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 4.2 | | February 10, 2025 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.1+ | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.1 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.2# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.3 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.3# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.4 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.4# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.5 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.5# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.6 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | |
Exhibit Number | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed
Herewith |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.6# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.7 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.7# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.8 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.8# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.9 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.9# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.10 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.10# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.11 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.11# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.12 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.12# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.13 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.13# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.14 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.14# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.15 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.15# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.16 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.16# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.17 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.17# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.19 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | |
Exhibit Number | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed
Herewith |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.18# | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.20 | | May 31, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.19+ | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.21 | | June 17, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.20+ | | | | S-1 | | 333-231891 | | 10.22 | | June 17, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.21+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | August 14, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.22+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.25 | | March 11, 2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.23+ | | | | 10-Q | | 011-38953 | | 10.1 | | November 7, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.24 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | June 16, 2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.25 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | June 23, 2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.26# | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | November 10, 2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.27 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | March 8, 2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.28 | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | March 16, 2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.29+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | May 10, 2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.30+ | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | September 29, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.31+ | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.20 | | September 29, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | |
Exhibit Number | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed
Herewith |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.32+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.34 | | February 28, 2022 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.33+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | August 9, 2022 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.34+ | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | January 25, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.35+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.35 | | February 28, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.37+ | | | | S-8 | | 333-270281 | | 99.1 | | March 3, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.38+ | | | | S-8 | | 333-270281 | | 99.2 | | March 3, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.39+ | | | | S-8 | | 333-270281 | | 99.3 | | March 3, 2023 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.40+ | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | February 21, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.41* | | | | 10-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.41 | | March 1, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.42 | | | | 10-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.42 | | March 1, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.43 | | | | 10-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.43 | | March 1, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.44 | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.5 | | May 7, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.45+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | November 4, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.46+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.2 | | November 4, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.47+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.3 | | November 4, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | |
Exhibit Number | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed
Herewith |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.48+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-38953 | | 10.4 | | November 4, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.49* | | | | 8-K | | 001-38953 | | 10.1 | | February 10, 2025 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 19 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 23.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 31.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 31.2 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 32.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 32.2 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 97 | | | | 10-K | | 001-38953 | | | | March 1, 2024 | |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.INS | | XBRL Instance Document | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.SCH | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.CAL | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.DEF | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.LAB | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.PRE | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as inline XBRL with applicable taxonomy extension information contained in Exhibits 101.INS, 101.SCH, 101.CAL, 101.DEF, 101.LAB, and 101.PRE). | | | | | | | | | | |
___________________________________________
+ Indicates management contract or compensatory plan.
# Certain information contained in this agreement has been omitted because it both (i) is not material and (ii) would be competitively harmful if publicly disclosed.
* Certain schedules and exhibits omitted pursuant to Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K promulgated by the SEC. The Company agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of any omitted schedule or exhibit to the SEC upon request.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the Registrant has duly caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | |
| The RealReal, Inc. |
| | |
| Date: February 21, 2025 | By: | /s/ Ajay Madan Gopal |
| | Ajay Madan Gopal |
| | Chief Financial Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Name | | Title | | Date |
/s/ Rati Sahi Levesque | | Chief Executive Officer and Director | | February 21, 2025 |
Rati Sahi Levesque | | (Principal Executive Officer) | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Ajay Madan Gopal | | Chief Financial Officer | | February 21, 2025 |
Ajay Madan Gopal | | (Principal Financial Officer) | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Steve Lo | | Senior Vice President, Chief Accounting Officer | | February 21, 2025 |
| Steve Lo | | (Principal Accounting Officer) | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Chip Baird | | Director | | February 21, 2025 |
| Chip Baird | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Caretha Coleman | | Director | | February 21, 2025 |
| Caretha Coleman | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Karen Katz | | Director | | February 21, 2025 |
| Karen Katz | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Rob Krolik | | Director | | February 21, 2025 |
| Rob Krolik | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Niki Leondakis | | Director | | February 21, 2025 |
| Niki Leondakis | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Carol Melton | | Director | | February 21, 2025 |
| Carol Melton | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ James Miller | | Director | | February 21, 2025 |
| James Miller | | | | |
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors
The RealReal, Inc.:
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of The RealReal, Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively, the financial statements). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2024, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated February 21, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of a critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Sufficiency of the audit evidence over the IT elements of revenue recognition
As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, the Company recognizes consignment revenue by providing a service to sell pre-owned luxury goods on behalf of consignors to buyers through its online marketplace and retail stores. Direct revenue is recognized from the sale of Company-owned inventory on its online marketplace and retail stores. The Company reported $600 million in total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2024.
We identified the evaluation of the sufficiency of audit evidence over the information technology (IT) elements of revenue recognition as a critical audit matter. A high degree of complex auditor judgment was required to evaluate the nature and extent of audit evidence obtained related to consignment and direct revenue due to the complexity and number of IT systems. IT professionals with specialized skills and knowledge were required to understand and assess the Company’s internally developed IT systems used in the revenue recognition process.
The following are the primary procedures we performed to address this critical audit matter. We applied auditor judgment to determine the nature and extent of procedures to be performed over the IT elements of revenue recognition. We involved IT professionals with specialized skills and knowledge, who assisted in:
•gaining an understanding of the systems used in the Company’s recognition of revenue
•evaluating the design and testing the operating effectiveness of certain internal controls related to the IT applications used in the revenue recognition process. This included IT controls, IT application controls, data configurations, and interface controls over the transfer of relevant data between systems.
We performed a software-assisted data analysis to test the relationships among certain revenue transactions. On a sample basis, we also tested certain revenue transactions by comparing the recorded amounts to underlying documentation. We evaluated the sufficiency of audit evidence obtained by assessing the results of procedures performed, including the appropriateness of the nature and extent of such evidence.
/s/ KPMG LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2013.
San Francisco, California
February 21, 2025
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors
The RealReal, Inc.:
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited The RealReal, Inc.'s (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively, the financial statements), and our report dated February 21, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ KPMG LLP
San Francisco, California
February 21, 2025
THE REALREAL, INC.
Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Assets | | | |
| Current assets | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | 175,709 | |
Accounts receivable | 13,961 | | | 17,226 | |
Inventory, net | 23,583 | | | 22,246 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 22,913 | | | 20,766 | |
Total current assets | 232,669 | | | 235,947 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 94,443 | | | 104,087 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 75,714 | | | 86,348 | |
| Restricted cash | 14,911 | | | 14,914 | |
| Other assets | 5,358 | | | 5,627 | |
Total assets | $ | 423,095 | | | $ | 446,923 | |
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Deficit | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | |
Accounts payable | $ | 11,004 | | | $ | 8,961 | |
Accrued consignor payable | 89,718 | | | 77,122 | |
Operating lease liabilities, current portion | 22,835 | | | 20,094 | |
Convertible senior notes, net, current portion | 26,653 | | | — | |
Other accrued and current liabilities | 98,466 | | | 82,685 | |
Total current liabilities | 248,676 | | | 188,862 | |
| Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion | 85,790 | | | 104,856 | |
| Convertible senior notes, net | 276,807 | | | 452,421 | |
Non-convertible notes, net | 134,470 | | | — | |
Warrant liability | 78,584 | | | — | |
| Other noncurrent liabilities | 6,144 | | | 4,083 | |
Total liabilities | 830,471 | | | 750,222 | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) | | | |
Stockholders’ deficit: | | | |
Common stock, $0.00001 par value; 500,000,000 shares authorized as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023; 111,242,479 and 104,670,500 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively | 1 | | | 1 | |
Additional paid-in capital | 846,450 | | | 816,325 | |
Accumulated deficit | (1,253,827) | | | (1,119,625) | |
Total stockholders’ deficit | (407,376) | | | (303,299) | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit | $ | 423,095 | | | $ | 446,923 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE REALREAL, INC.
Statements of Operations
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenue: | | | | | |
| Consignment revenue | $ | 473,396 | | | $ | 415,572 | | | $ | 384,979 | |
| Direct revenue | 64,580 | | | 79,160 | | | 158,726 | |
| Shipping services revenue | 62,508 | | | 54,572 | | | 59,788 | |
| Total revenue | 600,484 | | | 549,304 | | | 603,493 | |
| Cost of revenue: | | | | | |
| Cost of consignment revenue | 53,801 | | | 58,120 | | | 56,963 | |
| Cost of direct revenue | 55,809 | | | 74,343 | | | 141,661 | |
| Cost of shipping services revenue | 43,353 | | | 40,563 | | | 56,178 | |
| Total cost of revenue | 152,963 | | | 173,026 | | | 254,802 | |
| Gross profit | 447,521 | | | 376,278 | | | 348,691 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Marketing | 55,256 | | | 58,275 | | | 62,988 | |
| Operations and technology | 260,827 | | | 257,041 | | | 278,628 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 187,737 | | | 183,793 | | | 195,342 | |
| Restructuring | 196 | | | 43,462 | | | 896 | |
| Total operating expenses | 504,016 | | | 542,571 | | | 537,854 | |
| Loss from operations | (56,495) | | | (166,293) | | | (189,163) | |
Change in fair value of warrant liability | (68,167) | | | — | | | — | |
Gain on extinguishment of debt | 4,177 | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest income | 7,943 | | | 8,805 | | | 3,191 | |
| Interest expense | (21,384) | | | (10,701) | | | (10,472) | |
Other income, net | — | | | — | | | 171 | |
| Loss before provision for income taxes | (133,926) | | | (168,189) | | | (196,273) | |
| Provision for income taxes | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | |
Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (1.24) | | | $ | (1.65) | | | $ | (2.05) | |
Shares used to compute net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | 107,878,366 | | | 101,806,000 | | | 95,921,246 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE REALREAL, INC.
Statements of Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
(In thousands, except share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-in
Capital | | | | Accumulated
Deficit | | Total
Stockholders’
Equity
(Deficit) |
| Shares | | Amount |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | | 92,960,066 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 841,255 | | | | | $ | (768,128) | | | $ | 73,128 | |
| Cumulative effect adjustment due to adoption of ASU 2020-06 | | — | | | — | | | (112,052) | | | | | 13,420 | | | (98,632) | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options | | 1,929,265 | | | — | | | 2,906 | | | | | — | | | 2,906 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes | | 3,587,964 | | | — | | | (216) | | | | | — | | | (216) | |
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP | | 610,877 | | | — | | | 1,400 | | | | | — | | | 1,400 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | — | | | — | | | 47,767 | | | | | — | | | 47,767 | |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (196,445) | | | (196,445) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | | 99,088,172 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 781,060 | | | | | $ | (951,153) | | | $ | (170,092) | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options | | 8,511 | | | — | | | 19 | | | | | — | | | 19 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes | | 4,708,141 | | | — | | | (690) | | | | | — | | | (690) | |
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP | | 865,676 | | | — | | | 886 | | | | | — | | | 886 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | — | | | — | | | 35,050 | | | | | — | | | 35,050 | |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (168,472) | | | (168,472) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | | 104,670,500 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 816,325 | | | | | $ | (1,119,625) | | | $ | (303,299) | |
Settlement of capped calls | | — | | | — | | | 396 | | | | | — | | | 396 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options | | 136,658 | | | — | | | 376 | | | | | — | | | 376 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes | | 5,868,967 | | | — | | | (1,646) | | | | | — | | | (1,646) | |
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP | | 566,354 | | | — | | | 1,413 | | | | | — | | | 1,413 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | — | | | — | | | 29,586 | | | | | — | | | 29,586 | |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (134,202) | | | (134,202) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2024 | | 111,242,479 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 846,450 | | | | | $ | (1,253,827) | | | $ | (407,376) | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE REALREAL, INC.
Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net loss | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 33,100 | | | 31,695 | | | 27,669 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 29,082 | | | 34,273 | | | 46,138 | |
| Reduction of operating lease right-of-use assets | 15,192 | | | 16,746 | | | 19,602 | |
| Bad debt expense | 2,498 | | | 1,962 | | | 1,680 | |
Non-cash interest expense | 8,684 | | | — | | | — | |
Issuance costs allocated to liability classified warrants | 374 | | | — | | | — | |
| Accretion of debt discounts and issuance costs | 2,127 | | | 2,573 | | | 2,368 | |
Property, plant, equipment, and right-of-use asset impairments | — | | | 39,739 | | | — | |
Provision for inventory write-downs and shrinkage | 2,590 | | | 9,783 | | | 4,077 | |
Gain on debt extinguishment | (4,177) | | | — | | | — | |
Change in fair value of warrant liability | 68,167 | | | — | | | — | |
Loss related to warehouse fire, net | 740 | | | — | | | — | |
| Other adjustments | (165) | | | (515) | | | 702 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | 767 | | | (6,981) | | | (6,120) | |
| Inventory, net | (3,677) | | | 10,938 | | | 23,971 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 701 | | | 2,001 | | | (2,952) | |
| Other assets | 76 | | | (3,050) | | | (409) | |
| Operating lease liability | (20,883) | | | (26,478) | | | (17,764) | |
| Accounts payable | 910 | | | (425) | | | 4,947 | |
| Accrued consignor payable | 11,470 | | | (4,421) | | | 10,501 | |
| Other accrued and current liabilities | 13,090 | | | (464) | | | (9,823) | |
| Other noncurrent liabilities | 382 | | | (172) | | | 301 | |
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 26,846 | | | (61,268) | | | (91,557) | |
| Cash flow from investing activities: | | | | | |
Insurance proceeds related to warehouse fire | 461 | | | — | | | — | |
| Capitalized proprietary software development costs | (11,800) | | | (12,951) | | | (14,061) | |
| Purchases of property and equipment | (14,248) | | | (29,177) | | | (22,861) | |
Net cash used in investing activities | (25,587) | | | (42,128) | | | (36,922) | |
| Cash flow from financing activities: | | | | | |
Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 376 | | | 19 | | | 2,906 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of stock in connection with the Employee Stock Purchase Program | 1,413 | | | 886 | | | 1,400 | |
| Taxes paid related to restricted stock vesting | (1,646) | | | (679) | | | (205) | |
Cash received from settlement of capped calls in conjunction with the 2024 Note Exchange | 396 | | | — | | | — | |
Issuance costs paid related to the 2024 Note Exchange | (5,298) | | | — | | | — | |
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (4,759) | | | 226 | | | 4,101 | |
Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | (3,500) | | | (103,170) | | | (124,378) | |
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | | | | | |
| Beginning of period | 190,623 | | | 293,793 | | | 418,171 | |
| End of period | $ | 187,123 | | | $ | 190,623 | | | $ | 293,793 | |
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information | | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | $ | 10,680 | | | $ | 8,127 | | | $ | 8,104 | |
| Cash paid for income taxes | 200 | | | 227 | | | 256 | |
| Supplemental disclosures of non-cash investing and financing activities | | | | | |
Property and equipment additions not yet paid in cash | 1,818 | | | 1,757 | | | 13,860 | |
Capitalized proprietary software development costs not yet paid in cash | 654 | | | 1,122 | | | 1,590 | |
| Stock-based compensation capitalized to proprietary software development costs | 504 | | | 777 | | | 1,629 | |
Liability classified warrants issued in connection with the 2024 Note Exchange | 10,417 | | | — | | | — | |
Net decrease in principal amount of debt due to the 2024 Note Exchange | (17,232) | | | — | | | — | |
| Tax withholding liability for restricted stock | — | | | 11 | | | 11 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE REALREAL, INC.
Notes to Financial Statements
Note 1. Description of Business and Basis of Presentation
Organization and Description of Business
The RealReal, Inc. (the “Company”) is an online marketplace for authenticated, consigned luxury goods across multiple categories, including women’s fashion, men’s fashion, and jewelry and watches. The Company was incorporated in the state of Delaware on March 29, 2011 and is headquartered in San Francisco, California.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and, in the opinion of management, reflect all adjustments necessary to state fairly the Company’s financial position, results of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the periods presented. For the years ended 2024, 2023, and 2022, comprehensive loss is equal to net loss as the Company has no other comprehensive income (loss) item in the periods presented. The Company’s functional and reporting currency is the U.S. dollar.
The Company has made a presentation change to the Company's statements of operations to reclassify its legal settlements expense to selling, general, and administrative expenses. Additionally, the Company has made a presentation change to reclassify loss on disposal of property and equipment, impairment of capitalized proprietary software, and gain on lease termination to other adjustments within operating cash flows in the statements of cash flows. Changes to reclassify amounts in the prior periods have been made to conform to the current period presentation.
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period. Significant items subject to such estimates and assumptions include those related to revenue recognition, including the returns reserve, standalone selling price related to consignment revenue transactions, valuation of inventory, software development costs, stock-based compensation, fair value of warrant liability, initial fair value of non-convertible notes issued as part of the 2024 Note Exchange (see Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net), incremental borrowing rates related to lease liability, valuation of deferred taxes, and other contingencies. The Company evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors and adjusts those estimates and assumptions when facts and circumstances dictate. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Net Loss per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
The Company follows the two-class method when computing net loss per common share when shares are issued that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method determines net loss per common share for each class of common stock and participating securities according to dividends declared or accumulated and participation rights in undistributed earnings. The two-class method requires income (loss) available or attributable to common stockholders for the period to be allocated between common stock and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive dividends as if all income for the period had been distributed.
The Company’s convertible senior notes are participating securities as they give the holders the right to receive dividends if dividends or distributions declared to the common stockholders is equal to or greater than the last reported sale price of the Company’s common stock on the trading day immediately preceding the ex-dividend date for such dividend or distribution as if the instruments had been converted into shares of common stock. No undistributed earnings were allocated to the participating securities as the contingent event is not satisfied as of the reporting date.
For periods in which the Company reports net losses, diluted net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders is the same as basic net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders, because potentially dilutive common shares and assumed conversion of the convertible senior notes are not assumed to have been issued within the calculation, if their effect is anti-dilutive.
Segments
The Company has one operating segment and one reportable segment as its chief operating decision maker, who is its Chief Executive Officer, reviews financial information on a consolidated basis for purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance. All long-lived assets are located in the United States and substantially all revenue is attributed to consignors and buyers based in the United States.
Revenue Recognition
The Company generates revenue from the sale of pre-owned luxury goods through its online marketplace and retail stores. Revenue is recognized upon transfer of control of promised products or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for those products or services. The Company enters into contracts that include products and services that are capable of being distinct and accounted for as separate performance obligations as described below. The transaction price requires an allocation across consignment services, sales of Company-owned inventory, and shipping services. Estimation is required in the determination of the services' stand-alone selling price (“SSP”).
Consignment Revenue
The Company provides a service to sell pre-owned luxury goods on behalf of consignors to buyers through its online marketplace and retail stores. The Company retains a percentage of the proceeds received as payment for its consignment service, which the Company refers to as its take rate. SSP is estimated using observable stand-alone consignment sales which are conducted without shipping services. The Company reports consignment revenue on a net basis as an agent and not the gross amount collected from the buyer. Title to the consigned goods remains with the consignor until transferred to the buyer upon purchase of the consigned goods and expiration of the allotted return period. The Company does not take title of consigned goods at any time except in certain cases where returned goods become Company-owned inventory.
The Company recognizes consignment revenue upon purchase of the consigned good by the buyer as its performance obligation of providing consignment services to the consignor is satisfied at that point. Consignment revenue is recognized net of estimated returns, cancellations, buyer incentives and adjustments. The Company recognizes a returns reserve based on historical experience, which is recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets (see Note 5). Sales tax assessed by governmental authorities is excluded from revenue.
Certain transactions provide consignors with a material right resulting from the tiered consignor commission plan. Under this plan, the amount an individual consignor receives for future sales of consigned goods may be dependent on previous consignment sales for that consignor within his/her consignment period. Accordingly, in certain consignment transactions, a small portion of the Company’s consignment revenue is allocated to such material right using the portfolio method and recorded as deferred revenue, which is recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets. The impact of the deferral has not been material to the financial statements.
The Company also generates subscription revenue from monthly memberships allowing buyers early access to shop for luxury goods. The buyers receive the early access and other benefits over the term of the subscription period, which represents a single stand-ready performance obligation. Therefore, the subscription fees paid by the buyer are recognized over the monthly subscription period. Subscription revenue was not material in 2024, 2023, and 2022.
Direct Revenue
The Company generates direct revenue from the sale of Company-owned inventory. The Company recognizes direct revenue on a gross basis upon shipment of the purchased good to the buyer as the Company acts as the principal in the transaction. SSP is estimated using observable stand-alone sales of Company-owned inventory which are conducted without shipping services, when available, or a market assessment approach. Direct revenue is recognized net of estimated returns, buyer incentives and adjustments. Sales tax assessed by governmental authorities is excluded from revenue. Cost of direct revenue is also recognized upon shipment to the buyer in an amount equal to that paid to the consignor from the original consignment sale, an amount equal to that paid as a direct purchase from a third party, or the lower of cost of the inventory purchased and its net realizable value.
Shipping Services Revenue
The Company provides a service to ship purchased items to buyers and a service to ship items from buyers back to the Company. The Company determines itself to be the principal in this arrangement. The Company charges a fee to buyers
for this service and has elected to treat shipping and handling activities performed as a separate performance obligation. For shipping services revenue, the Company's SSP is estimated using a market approach considering external and internal data points on the stand-alone sales price of the shipping service. All outbound shipping and handling costs for buyers are accounted for as cost of shipping services and recognized as the shipping activity occurs. The Company also generates shipping services revenue from the shipping fees for consigned products returned by buyers to the Company within policy. The Company recognizes shipping revenue and associated costs over time as the shipping activity occurs, which is generally one to three days after shipment.
Incentives
Incentives, which include platform-wide discounts and buyer incentives, may periodically be offered to buyers. Platform-wide discounts are made available to all buyers on the online marketplace. Buyer incentives apply to specific buyers and consist of coupons or promotions that offer credits in connection with purchases on the Company’s platform, and do not impact the commissions paid to consignors. These are treated as a reduction of consignment revenue and direct revenue. Additionally, the Company periodically offers commission exceptions to the standard consignment rates to consignors to optimize its supply. These are treated as a reduction of consignment revenue at the time of sale. The Company may offer a certain type of buyer incentive in the form of site credits to buyers on current transactions to be applied towards future transactions, which are included in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets.
Contract Liabilities
The Company’s contractual liabilities primarily consist of deferred revenue for material rights primarily related to the tiered consignor commission plan, which are recognized as revenue using a portfolio approach based on the pattern of exercise, and certain buyer incentives. Contract liabilities are recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets and are generally expected to be recognized within one year. Contract liabilities were immaterial as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of consignment revenue consists of credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and consignor inventory adjustments relating to lost or damaged products. Cost of direct revenue consists of the cost of goods sold, credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and inventory adjustments. Cost of shipping services revenue consists of the outbound shipping and handling costs to deliver purchased items to buyers, the shipping costs for consigned products returned by buyers to the Company within policy, and an allocation of the credit card fees associated with the shipping fee charged.
Marketing
Marketing expense is comprised of the cost of acquiring new consignors and buyers for our online platform and physical stores, including the cost of television, digital and direct mail advertising. Marketing expense also includes personnel-related costs, including stock-based compensation, of employees engaged in these activities. Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and were $42.9 million, $48.4 million, and $49.0 million in 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Operations and Technology
Operations and technology expense is comprised of costs associated with the authentication, merchandising and fulfillment of goods sold through our online marketplace and retail stores, as well as general information technology expense. The principal component of operations and technology expense is personnel-related costs, including stock-based compensation, of employees engaged in these activities. Operations and technology expense also includes allocated facility and overhead costs, costs related to our retail stores, facility supplies, inbound consignment shipping costs, and depreciation of hardware and equipment, as well as research and development expense for technology associated with managing and improving our operations. In 2024, 2023, and 2022, the Company capitalized proprietary software developments costs of $11.8 million, $13.3 million, and $15.6 million, respectively. As such, operations and technology expense also includes amortization of capitalized technology development costs, which is taken on straight-line basis over three years once the technology is ready for its intended use.
Selling, General and Administrative
Selling, general and administrative expense is principally comprised of the personnel-related costs for employees involved in sales, finance and administration, and includes stock-based compensation expense. Selling, general and
administrative expense also includes allocated facility and overhead costs and professional services, including accounting and legal advisors.
Stock-based Compensation
The Company incurs stock-based compensation expense from stock options, restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance based restricted stock units (“PSUs”) subject to performance or market conditions, and employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”) purchase rights. Stock-based compensation expense related to employees and nonemployees is measured based on the grant-date fair value of the awards. The Company estimates the fair value of stock options granted and the purchase rights issued under the ESPP using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The fair value of RSUs is estimated based on the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant, which is determined based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock. Compensation expense is recognized in the statements of operations over the period during which the employee is required to perform services in exchange for the award (the vesting period of the applicable award) using the straight-line method for awards with only a service condition.
To determine the grant-date fair value of the Company's stock-based payment awards for PSUs subject to performance conditions, the quoted stock price on the date of grant is used. The stock-based compensation expense for PSUs with performance conditions is recognized based on the estimated number of shares that the Company expects will vest and is adjusted on a quarterly basis using the estimated achievement of financial performance targets. For PSUs subject to market conditions, the grant-date fair value is determined using the Monte Carlo simulation model which utilizes multiple input variables to estimate the probability that market conditions will be achieved. These variables include the Company's expected stock price volatility over the expected term of the award, the risk-free interest rate for the expected term of the award, and expected dividends. For PSUs with market conditions, the stock-based compensation expense is recognized on a tranche by tranche basis over the requisite service period using the fair value derived from the Monte Carlo simulation model. The compensation expense will be recognized regardless of whether the market condition is ever satisfied, provided the requisite service period is satisfied. For all awards, the Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur.
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less from the purchase date to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents primarily consist of investments in short-term money market funds.
Restricted cash consists of cash deposited with a financial institution as collateral for the Company’s letters of credit for its facility leases and the Company’s credit cards. The Company had $14.9 million in restricted cash as of December 31, 2024 and 2023.
The following table provides a reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash for the year ended December 31, 2024 that sum to the total of the same amounts shown in the statements of cash flows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | 175,709 | | | $ | 293,793 | |
| Restricted cash | 14,911 | | | 14,914 | | | — | |
| Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 187,123 | | | $ | 190,623 | | | $ | 293,793 | |
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivables are recorded at the amounts billed to buyers and do not bear interest. Accounts receivables result from credit card transactions, the majority of which are settled within two business days.
Inventory, Net
Inventory consists of finished goods arising from goods returned after the title has transferred from the buyer to the Company as well as finished goods from direct purchases from vendors and consignors. The cost of inventory is an amount equal to that paid to the consignor or vendors. Inventory is valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value using the specific identification method and the Company records provisions, as appropriate, to write down obsolete and excess inventory to estimated net realizable value. After the inventory value is reduced, adjustments are not made to increase it from the estimated net realizable value. Additionally, inventory is recorded net of an allowance for shrinkage
which represents the risk of physical loss of inventory. Provisions for inventory shrinkage are estimated based on historical experience and are adjusted based upon physical inventory counts. Provisions to write down inventory to net realizable value and provisions for inventory shrinkage were $2.6 million and $9.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Return reserves, which reduce revenue and cost of sales, are estimated using historical experience. Liabilities for return allowances are included in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets and were $22.4 million and $22.2 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023. Included in inventory on the Company’s balance sheets are assets totaling $4.8 million and $5.2 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, for the rights to recover products from customers associated with its liabilities for return reserves.
Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment, net is recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. Repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred.
The estimated useful lives of our assets are as follows:
| | | | | |
| Proprietary software | 3 years |
| Furniture and equipment | 3-5 years |
| Vehicles | 5 years |
| Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life |
Software Development Costs
Proprietary software includes the costs of developing the Company’s internal proprietary business platform and automation projects. The Company capitalizes qualifying proprietary software development costs that are incurred during the application development stage. Capitalization of costs begins when two criteria are met: (1) the preliminary project stage is completed and (2) it is probable that the software will be completed and used for its intended function. Such costs are capitalized in the period incurred. Capitalization ceases and amortization begins when the software is substantially complete and ready for its intended use, including the completion of all significant testing. Costs related to preliminary project activities and post-implementation operating activities are expensed as incurred.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
The carrying amounts of long-lived assets, including right-of-use assets, property and equipment, net and capitalized proprietary software, are periodically reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable or that the useful life is shorter than originally estimated. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by comparing the carrying amount of assets to future undiscounted net cash flows the assets are expected to generate over their remaining life.
If the assets are considered to be impaired, the amount of any impairment is measured as the difference between the carrying value and the fair value of the impaired assets. If the useful life is shorter than originally estimated, the Company amortizes the remaining carrying value over the revised shorter useful life.
Leases
Contracts that have been determined to convey the right to use an identified asset are evaluated for classification as an operating or finance lease. For the Company’s operating leases, the Company records a lease liability based on the present value of the lease payments at lease inception, using the applicable incremental borrowing rate. The Company estimates the incremental borrowing rate by developing its own synthetic credit rating, corresponding yield curve, and the terms of each lease at the lease commencement date. The corresponding right-of-use asset is recorded based on the corresponding lease liability at lease inception, adjusted for payments made to the lessor at or before the commencement date, initial direct costs incurred and any tenant incentives allowed for under the lease. The Company does not include optional renewal terms or early termination provisions unless the Company is reasonably certain such options would be
exercised at the inception of the lease. Operating lease right-of-use assets, current portion of operating lease liabilities, and operating lease liabilities, net of current portion are included on the Company’s balance sheet.
The Company has elected the practical expedients that allows for the combination of lease components and non-lease components and to record short-term leases as lease expense on a straight-line basis on the statements of operations. Variable lease payments are recorded as expense as they are incurred.
The Company has finance leases for vehicles and equipment, and the amounts of finance lease right-of-use assets and finance lease liabilities have been immaterial to date.
Convertible Senior Notes, Net
Prior to the adoption of ASU 2020-06 on January 1, 2022, convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash or other assets, or partially in cash, upon conversion, were separately accounted for as long-term debt and equity components (or conversion feature). The debt component represented the Company’s contractual obligation to pay principal and interest and the equity component represented the Company’s option to convert the debt security into equity of the Company or the equivalent amount of cash. Upon issuance, the Company allocated the debt component on the basis of the estimated fair value of a similar liability that does not have an associated convertible feature and the remaining proceeds are allocated to the equity component. The bifurcation of the debt and equity components resulted in a debt discount for the aforementioned notes. The Company uses the effective interest method to amortize the debt discount to interest expense over the amortization period which is the expected life of the debt. Following the adoption of ASU 2020-06, there is no bifurcation of the liability and equity components of the 3.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2025 (the “2025 Notes”) and the 1.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2028 (the “2028 Notes” and, together with the 2025 Notes, the “Notes”), and the entire principal of the Notes are accounted for as debt.
Debt
The Company initially recognizes incurred debt, net of any discounts, premiums and issuance costs related to the debt offering. All debt issuance costs are presented as a direct deduction from the related principal debt amounts on the balance sheet. Debt obligations due within 12 months are classified as current liabilities. Debt discounts, premiums and issuance costs are amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt using the effective interest method. When multiple instruments are issued in the same transaction, the Company allocates any issuance costs to the instruments on the same basis as the allocation of proceeds. Issuance costs allocated to instruments measured at fair value are expensed in the period incurred.
Capped Call Transactions
In June 2020 and March 2021, in connection with the issuance of its convertible senior notes, the Company entered into capped call transactions (see Note 7 - Convertible Senior Notes, Net). The capped call transactions are expected generally to reduce the potential dilution to the holders of the Company’s common stock upon any conversion of the convertible senior notes and/or offset any cash payments the Company is required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted convertible senior notes, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap based on the cap price. The Capped Calls (as defined below) are classified in stockholders’ equity as a reduction to additional paid-in capital and are not subsequently remeasured as long as the conditions for equity classification continue to be met. The Company monitors the conditions for equity classification, which continue to be met as of December 31, 2024.
Debt Issuance Costs
Debt issuance costs, which consist of direct incremental legal, consulting, banking and accounting fees related to the anticipated debt offering, are amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt based on the effective interest method. The Company presents debt issuance costs on the balance sheets as a direct deduction from the associated debt. The Company adopted ASU 2020-06 as of January 1, 2022 using the modified retrospective method. Prior to the adoption of ASU 2020-06 on January 1, 2022, a portion of debt issuance costs incurred in connection with the convertible senior notes issued in June 2020 and March 2021 was allocated to the equity component and was recorded as a reduction to additional paid in capital and was not amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt. Following the adoption of ASU 2020-06, the debt issuance costs previously allocated to the equity component of both series of Notes were reclassified to debt. As such, all of the debt issuance costs are recorded as a direct deduction from the related principal debt amounts on the balance sheet, and are all amortized to interest expense over the estimated remaining life of the related debt.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled.
The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in loss in the period of enactment. The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs.
Concentrations of Credit Risks
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and accounts receivable. At times, such amount may exceed federally-insured limits. The Company is closely monitoring ongoing events involving limited liquidity, defaults, non-performance or other adverse developments that affect financial institutions or other companies in the financial services industry or the financial services industry generally. The Company reduces credit risk by placing its cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and investments with major financial institutions with high credit ratings within the United States. The Company has not experienced any realized losses on cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash to date; however, no assurances can be provided.
As of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there were no customers that represented 10% or more of the Company’s accounts receivable balance and there were no customers that individually exceeded 10% of the Company’s total revenue for each of the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures requires disclosures about significant segment expenses that are regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The Company adopted the standard during the year ended December 31, 2024 and applied it retrospectively to the periods presented. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company's financial statements.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures. This new guidance is designed to enhance the transparency and decision usefulness of income tax disclosures. The amendments of this update are related to the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid, requiring (1) consistent categories and greater disaggregation of information in the rate reconciliation and (2) income taxes paid disaggregated by jurisdiction. ASU 2023-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-03, Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses, which requires companies to disclose in the notes to the financial statements the disaggregation of certain expense categories included within the income statement expense captions. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2027 on a prospective basis with optional retrospective application. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-04, Debt with Conversion and Other Options. This new guidance is designed to clarify requirements for determining whether certain settlements of convertible debt instruments should be accounted for as an induced conversion. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2025 and for interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements.
Note 3. Cash and Cash Equivalents
The following tables summarize the estimated value of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents (in thousands) and do not include restricted cash. There are no unrealized gains or losses related to the restricted cash balance.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
| Amortized Cost | | Unrealized Gain | | Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value |
| Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | |
Cash | $ | 24,870 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 24,870 | |
Money market funds | 147,342 | | | — | | | — | | | 147,342 | |
| Total cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 172,212 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 |
| Amortized Cost | | Unrealized Gain | | Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value |
| Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | |
Cash | $ | 50,947 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 50,947 | |
Money market funds | 124,762 | | | — | | | — | | | 124,762 | |
| Total cash and cash equivalents | $ | 175,709 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 175,709 | |
Note 4. Fair Value Measurement
Assets and liabilities recorded at fair value on a recurring basis on the balance sheets are categorized based upon the level of judgment associated with the inputs used to measure their fair values. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or an exit price that would be paid to transfer a liability in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The authoritative guidance on fair value measurements establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy for disclosure of fair value measurements as follows:
Level 1—Observable inputs such as unadjusted, quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities at the measurement date.
Level 2—Inputs (other than quoted prices included in Level 1) are either directly or indirectly observable for the asset or liability. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active.
Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities.
There were no transfers between Level 1, Level 2 or Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy during the periods presented.
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
The following table sets forth the Company's financial instruments on the balance sheet that were measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the period indicated by level within the fair value hierarchy (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 | | |
| Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | | | | | | | |
Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Money market funds | $ | 147,342 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 147,342 | | | | | | | | | |
Total | $ | 147,342 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 147,342 | | | | | | | | | |
Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Warrants | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 78,584 | | | $ | 78,584 | | | | | | | | | |
Total | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 78,584 | | | $ | 78,584 | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2023, the Company held $124.8 million in money market funds. Such amounts are considered Level 1 and the Company held no other assets or liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis.
Fair Value Measurements of Other Financial Instruments
The following table presents the carrying amounts and estimated fair values of the financial instruments that are not recorded at fair value on the balance sheets (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Net Carrying Amount | | Estimated Fair Value | | Net Carrying Amount | | Estimated Fair Value |
| 2025 Convertible senior notes | $ | 26,653 | | | $ | 26,493 | | | $ | 170,564 | | | $ | 128,219 | |
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | $ | 276,807 | | | $ | 216,291 | | | $ | 281,857 | | | $ | 99,978 | |
2029 Non-convertible notes | $ | 134,470 | | | $ | 140,889 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
The principal amounts of the 2025 Notes, the 2028 Notes and the 2029 Notes are $26.7 million, $281.0 million, and $137.9 million, respectively. The difference between the principal amounts of such notes and their respective net carrying amounts are the unamortized debt issuance costs and debt premiums.
As of December 31, 2024, the fair value of the 2025 Notes, the 2028 Notes and the 2029 Notes, which differs from their carrying value, is determined based on the quoted bid prices of such notes in an over-the counter market using the latest trading information of the reporting period.
Fair Value Measurement of Warrants
In connection with the 2024 Note Exchange (defined in Note 6 – Non-convertible Notes, Net), the Company issued warrants (the "Warrants") to acquire an aggregate of up to 7,894,737 shares (subject to adjustment in accordance with the terms of the Warrants) of the Company’s common stock to the holders of the Exchanged Notes at an exercise price of $1.71, subject to certain cashless exercise provisions and adjustment in accordance with the terms of the Warrants. The Warrants are exercisable from the date of issuance until they expire on March 1, 2029. The Warrants are accounted for as liabilities under ASC 480 since the warrants may be required to be settled in cash in case of a fundamental change, which could occur outside of the Company’s control. Changes in fair value are recognized within change in fair value of warrant liability on the Company’s statements of operations. Issuance costs allocated to the Warrants are included in selling, general and administrative on the Company’s statements of operations.
The aggregate fair value of the Warrants upon issuance and as of December 31, 2024 was $10.4 million and $78.6 million, respectively, determined using a Black-Scholes Model with the following inputs:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| On issuance | | December 31, 2024 |
| Stock price | $1.77 | | $10.93 |
| Exercise price | $1.71 | | $1.71 |
Expected life in years | 5.00 | | 4.17 |
Expected volatility | 94.84 | % | | 96.75 | % |
Expected dividends | — | % | | — | % |
Discount rate | 4.26 | % | | 4.38 | % |
The following table presents the activity related to the Warrants during the year ended December 31, 2024.
| | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
Opening balance | $ | — | |
| Issuance of warrants | 10,417 | |
| Change in fair value | 68,167 | |
Balance as of December 31, 2024 | $ | 78,584 | |
Note 5. Balance Sheet Components
Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment, net is recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. Property and equipment, net consists of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 |
Proprietary software | $ | 47,416 | | | $ | 44,964 | |
Furniture and equipment | 51,959 | | | 47,389 | |
Automobiles | 2,036 | | | 2,069 | |
Leasehold improvements | 88,840 | | | 84,138 | |
| Property and equipment, gross | 190,251 | | | 178,560 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (95,808) | | | (74,473) | |
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 94,443 | | | $ | 104,087 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense on property and equipment was $32.7 million, $31.0 million, and $26.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company recorded $8.6 million of impairment of leasehold improvements and disposal of fixed assets related to the closures of several of its office and retail locations as part of the savings plan the Company implemented. The impairment charges are included in restructuring in the statements of operations. The Company did not record impairment of leasehold improvements or disposal of fixed assets related to the savings plan during the year ended December 31, 2024.
Other Accrued and Current Liabilities
Other accrued and current liabilities consist of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 |
| Returns reserve | $ | 22,409 | | | $ | 22,204 | |
| Accrued compensation | 24,749 | | | 20,086 | |
| Accrued sales tax and other taxes | 9,727 | | | 8,118 | |
Site credit and gift card liability | 15,542 | | | 14,058 | |
| Accrued marketing and outside services | 6,403 | | | 5,012 | |
| Accrued shipping | 3,270 | | | 4,244 | |
| Accrued interest | 4,996 | | | 1,166 | |
| Deferred revenue | 2,441 | | | 2,214 | |
| Other | 8,929 | | | 5,583 | |
| Other accrued and current liabilities | $ | 98,466 | | | $ | 82,685 | |
Note 6. Non-convertible Notes, Net
2024 Note Exchange
On February 29, 2024 (the “Closing Date”), the Company entered into exchange agreements with certain holders (the “Exchange Holders”) of its 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes to exchange (i) $145.8 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2025 Notes and (ii) $6.5 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes (together, the “Exchanged Notes”) for $135.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the Company’s 4.25%/8.75% PIK/Cash Senior Secured Notes due 2029 (the “2029 Notes”), pursuant to an indenture (the “2024 Note Exchange”). The 2029 Notes bear interest at a rate of 13.00% per annum, consisting of cash interest at a rate of 8.75% per annum payable semi-annually in arrears and payment in-kind (“PIK”) interest at a rate of 4.25% per annum payable semi-annually. During the year ended December 31, 2024, $2.9 million was added to the principal amounts outstanding due to accrued PIK interest. The 2029 Notes will mature on the earlier of (a) March 1, 2029 and (b) any date, if any, on or after December 1, 2027 on which (a) the aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes then outstanding is greater than $20 million and (b) the difference between (i) the amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held by the Company and its subsidiaries (if any) as of such date of determination and (ii) the aggregate principal amount of 2028 Notes outstanding as of such date of determination is less than $75 million. In connection with the 2024 Note Exchange, the Company issued the Warrants (see Note 4 – Fair Value Measurement for further details on the terms of the Warrants). As a result of the 2024 Note Exchange, the Company’s principal debt balance decreased $17.2 million.
As the terms of the 2029 Notes were deemed to have substantially different terms from the Exchanged Notes, the 2024 Note Exchange was accounted for as an extinguishment of the Exchanged Notes. In connection with debt extinguishment accounting, the Company recorded a gain of $4.2 million as the difference between the carrying amount of the Exchanged Notes and the fair value of the 2029 Notes. Included in the recorded gain are unamortized debt discounts and issuance costs related to the Exchanged Notes and the fair value of the Warrants as they represent fees paid to the Exchange Holders as part of the 2024 Note Exchange.
The Company allocated issuance costs to the Warrants and the 2029 Notes based on relative fair value. The Company allocated $0.4 million of issuance costs to the Warrants with the balance being allocated to the 2029 Notes. Issuance costs related to the 2029 Notes are being amortized to interest expense through the expected maturity of the 2029 Notes at an effective interest rate of 13.35%.
The indenture governing the 2029 Notes contains certain covenants, which include (i) a covenant by the Company not to permit liquidity (calculated as the sum of (a) unused commitments then available to be drawn under any revolving credit facility, delayed draw term loan facility or qualified securitization financing permitted thereunder (after giving effect to any borrowing base or similar limitations), plus (b) the amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held by the Company and its subsidiaries (if any)) to be less than $25 million as of the last day of any month, (ii) limitations on the Company’s and certain of its future subsidiaries’ (if any) ability to, among other things, (a) grant or incur liens securing indebtedness, (b) incur assume or guarantee additional indebtedness, (c) enter into transactions with affiliates, (d) sell or
otherwise dispose of assets, including capital stock of subsidiaries, (e) make certain restricted payments or other investments, or (f) pay dividends or make other distributions (including loans and other advances and (iii) limitations, in the case of the Company and any future guarantor (if any), to consolidate, amalgamate or merge with or into, or sell all or substantially all of its assets to, another person. As of December 31, 2024 the Company was in compliance with all covenants.
The indenture governing the 2029 Notes sets forth certain events of default after which the 2029 Notes may be declared immediately due and payable and sets forth certain types of bankruptcy or insolvency events of default involving the Company or its subsidiaries.
The 2029 Notes are guaranteed by certain of the Company’s future wholly-owned domestic subsidiaries (if any) on a senior secured basis. The 2029 Notes and the guarantees (if any), together with any future indebtedness secured on a pari passu basis with the 2029 Notes and the guarantees (if any), are secured by a first priority lien on substantially all of the assets of the Company and the guarantors (if any), subject to certain exceptions.
On or after March 1, 2025, the Company may redeem the 2029 Notes at its option, in whole at any time or in part from time to time, at the following redemption prices (expressed as percentages of principal amount) plus accrued and unpaid interest, to, but excluding, the applicable redemption date (subject to the right of holders of record of the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date), if redeemed during the following periods: March 1, 2025 to (but excluding) March 1, 2026 - 113.0%; March 1, 2026 to (but excluding) October 1, 2026 - 106.5%; and October 1, 2026 and thereafter - 100.0%. In addition, prior to March 1, 2025, the Company may redeem the 2029 Notes at its option, in whole at any time or in part from time to time, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 2029 Notes redeemed plus the applicable premium as of, and accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the applicable redemption date (subject to the right of holders of record of the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date). Notwithstanding the foregoing, at any time and from time to time on or prior to March 1, 2025, the Company may redeem in the aggregate up to 40% of the original aggregate principal amount of the 2029 Notes (calculated after giving effect to the issuance of any PIK payments) with the net proceeds of one or more equity offerings to the extent the net cash proceeds thereof are contributed to the common equity capital of the Company or are used to purchase capital stock (other than disqualified stock) of the Company, at a redemption price of 113.0%, plus accrued and unpaid interest, to, but excluding, the applicable redemption date (subject to the right of holders of record on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date), provided at least 60% of the original aggregate principal amount of the 2029 Notes (calculated after giving effect to any PIK payments) remains outstanding after each such redemption.
A schedule of the Company's future maturities for the 2029 Notes with interest components included in principal, is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | Amount |
| Fiscal Year | | 2029 Notes |
2025 through 2028 | | $ | — | |
2029 | | 166,631 | |
Total expected payments at maturity | | 166,631 | |
Less unamortized debt issuance costs and debt premium, net | | (3,430) | |
Less amounts related to PIK interest | | (28,730) | |
Net carrying amount | | $ | 134,470 | |
Note 7. Convertible Senior Notes, Net
In June 2020, the Company issued an aggregate principal of $172.5 million of its 2025 Notes, pursuant to an indenture, in a private offering to qualified institutional buyers. The 2025 Notes will mature on June 15, 2025, unless earlier redeemed or repurchased by the Company or converted. In February 2024, certain of the 2025 Notes were extinguished in connection with the 2024 Note Exchange (see Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net).
At issuance, the Company received net proceeds from the 2025 Notes offering of approximately $165.8 million, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and commission and offering expenses. The Company used approximately $22.5 million of the net proceeds from the 2025 Notes offering to fund the net cost of entering into the capped call
transactions described below. The Company intends to use the remainder of the net proceeds for general corporate purposes.
In March 2021, the Company issued an aggregate principal of $287.5 million of its 2028 Notes, pursuant to an indenture, in a private offering to qualified institutional buyers. The 2028 Notes will mature on March 1, 2028, unless earlier redeemed or repurchased by the Company or converted. In February 2024, certain of the 2028 Notes were extinguished in connection with the 2024 Note Exchange (see Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net).
At issuance, the Company received net proceeds from the 2028 Notes offering of approximately $278.1 million, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and commission and offering expenses. The Company used approximately $33.7 million of the net proceeds from the 2028 Notes offering to fund the net cost of entering into the capped call transactions described below. The Company intends to use the remainder of the net proceeds for general corporate purposes.
The 2025 Notes accrue interest at a rate of 3.00% per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning on December 15, 2020. The initial conversion rate applicable to the 2025 Notes is 56.2635 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of 2025 Notes (which is equivalent to an initial conversion price of approximately $17.77 per share of the Company’s common stock). The 2028 Notes accrue interest at a rate of 1.00% per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year, beginning on September 1, 2021. The initial conversion rate applicable to the 2028 Notes is 31.4465 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of 2028 Notes (which is equivalent to an initial conversion price of approximately $31.80 per share of the Company’s common stock). The conversion rate is subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of certain specified events but will not be adjusted for accrued and unpaid interest. In addition, upon the occurrence of a corporate event, the Company will, in certain circumstances, increase the conversion rate by a number of additional shares for a holder that elects to convert its 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes in connection with such corporate event.
The 2025 Notes will be redeemable, in whole or in part, at the Company’s option at any time, and from time to time, on or after June 20, 2023, and the 2028 Notes will be redeemable, in whole or in part, at the Company's option at any time, and from time to time, on or after March 5, 2025, in each case if the last reported sale price per share of the Company’s common stock exceeds 130% of the conversion price then in effect for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive), including the trading day immediately preceding the date on which the Company provides notice of redemption, during any 30 consecutive trading day period ending on, and including, the trading day immediately before the date the Company sends the related redemption notice. In addition, calling any Note for redemption will constitute a make-whole fundamental change with respect to that Note, in which case the conversion rate applicable to the conversion of that Note will be increased in certain circumstances if it is converted after it is called for redemption.
Prior to March 15, 2025, in the case of the 2025 Notes, and December 1, 2027, in the case of the 2028 Notes, the applicable Convertible Senior Notes will be convertible only under the following circumstances:
•During any calendar quarter (and only during such calendar quarter), if, the last reported sale price per share of the Company’s common stock exceeds 130% of the applicable conversion price on each applicable trading day for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) in the period of the 30 consecutive trading day period ending on, and including, the last trading day of the immediately preceding calendar quarter;
•During the five business day period after any five consecutive trading day period in which, for each day of that period, the trading price per $1,000 principal amount of 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes for such trading day was less than 98% of the product of the last reported sale price of the Company’s common stock and the applicable conversion rate on such trading day;
•Upon the occurrence of specified corporate transactions; or
•If the Company calls any 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes for redemption.
On and after March 15, 2025, in the case of the 2025 Notes, and December 1, 2027, in the case of the 2028 Notes, until the close of business on the scheduled trading day immediately preceding the maturity date, holders may convert all or a portion of their 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes, in multiples of $1,000 principal amount, at any time, regardless of the foregoing circumstances. Upon conversion, the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes will be settled, at the Company’s election, in cash, shares of the Company’s common stock, or a combination of cash and shares of the Company’s common stock. It is the Company’s current intent to settle conversions of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes through combination settlement,
which involves repayment of the principal portion in cash and any excess of the conversion value over the principal amount in shares of its common stock. The conditions allowing holders of either the 2025 Notes or the 2028 Notes to convert were not met as of December 31, 2024.
The 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes are unsecured and unsubordinated obligations of the Company and will rank senior in right of payment to any of future indebtedness of the Company that is expressly subordinated in right of payment to the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes; rank equal in right of payment to any existing and future unsecured indebtedness of the Company that is not so subordinated; be effectively subordinated in right of payment to any secured indebtedness of the Company to the extent of the value of the assets securing such indebtedness; and be structurally subordinated to all existing and future indebtedness and other liabilities and obligations incurred by future subsidiaries of the Company.
If bankruptcy, insolvency, or reorganization occurs with respect to the Company (and not solely with respect to a significant subsidiary of the Company), then the principal amount of, and all accrued and unpaid interest on, all of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes then outstanding will immediately become due and payable without any further action or notice by any person. If an event of default (other than bankruptcy, insolvency, or reorganization with respect to the Company and not solely with respect to a significant subsidiary of the Company) occurs and is continuing, then, with the exception of certain reporting events of default, the trustee, by notice to the Company, or noteholders of at least 25% of the aggregate principal amount of 2025 Notes or 2028 Notes, as applicable, then outstanding, by notice to us and the trustee, may declare the principal amount of, and all accrued and unpaid interest on, all of the 2025 Notes or 2028 Notes, as applicable, the outstanding to become due and payable immediately.
The carrying amount of the 2025 Notes is $26.7 million as of December 31, 2024, with principal of $26.7 million, net of unamortized issuance costs of $0.1 million. The 2025 Notes were classified as short-term liabilities as of December 31, 2024. The issuance costs related to the 2025 Notes are being amortized to interest expense over the expected life of the 2025 Notes or approximately its five-year term at an effective interest rate of 3.74%. The carrying amount of the 2028 Notes is $276.8 million as of December 31, 2024, with principal of $281.0 million, net of unamortized issuance costs of $4.2 million. The 2028 Notes were classified as long term liabilities as of December 31, 2024. The issuance costs related to the 2028 Notes are being amortized to interest expense over the expected life of the 2028 Notes or approximately its seven-year term at an effective interest rate of 1.45%.
The following table sets forth the amounts recorded in interest expense related to the 2025 Notes as of the dates indicated (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Contractual interest expense | $ | 1,531 | | | $ | 5,175 | | | $ | 5,175 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 383 | | | 1,268 | | | 1,080 | |
Total interest and amortization expense | $ | 1,914 | | | $ | 6,443 | | | $ | 6,255 | |
The following table sets forth the amounts recorded in interest expense related to the 2028 Notes as of the dates indicated (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Contractual interest expense | $ | 2,821 | | | $ | 2,875 | | | $ | 2,875 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 1,308 | | | 1,305 | | | 1,288 | |
Total interest and amortization expense | $ | 4,129 | | | $ | 4,180 | | | $ | 4,163 | |
A schedule of the Company's future maturities for the 2025 and 2028 Notes, is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amount |
| Fiscal Year | 2025 Notes | | 2028 Notes |
2025 | $ | 26,749 | | | $ | — | |
2026 | — | | | — | |
2027 | — | | | — | |
2028 | — | | | 281,019 | |
Total principal payments | 26,749 | | | 281,019 | |
Less unamortized debt issuance costs | (96) | | | (4,212) | |
Net carrying amount | $ | 26,653 | | | $ | 276,807 | |
Capped Call Transactions with Respect to the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes
In connection with the issuance of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes, including the initial purchasers’ exercise of the option to purchase additional Notes, the Company entered into capped call transactions with respect to its common stock with certain financial institutions (collectively, the “Counterparties”). The Company paid an aggregate amount of approximately $22.5 million to the Counterparties in connection with the 2025 capped call transactions (the “2025 Capped Calls”) and $33.7 million to the Counterparties in connection with the 2028 capped call transactions and (the “2028 Capped Calls” and, together with the 2025 Capped Calls, the “Capped Calls”). The 2025 Capped Calls and 2028 Capped Calls initially covered approximately 9,705,454 shares and 9,040,869 shares of the Company’s common stock at a strike price that corresponds to the initial conversion price of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, respectively. The 2025 Capped Calls and the 2028 Capped Calls are subject to anti-dilution adjustments that are intended to be substantially identical to those in the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, as applicable, and are exercisable upon conversion of the 2025 Notes or the 2028 Notes, as applicable. The Capped Calls are subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of specified extraordinary events affecting the Company, including merger events, tender offer and announcement events. In addition, the Capped Calls are subject to certain specified additional disruption events that may give rise to a termination of the Capped Calls, including nationalization, insolvency or delisting, changes in law, failures to deliver, insolvency filings and hedging disruptions. The 2025 Capped Calls settle in components commencing on April 16, 2025 with the last component scheduled to expire on June 12, 2025. The 2028 Capped Calls settle in components commencing on December 31, 2027 with the last component scheduled to expire on February 28, 2028.
The cap price of the 2025 Capped Call is initially $27.88 per share, which represents a premium of 100.0% over the closing price of the Company’s common stock of $13.94 per share on June 10, 2020, and is subject to certain adjustments under the terms of the capped call transactions. The cap price of the 2028 Capped Call is initially $48.00 per share, which represents a premium of 100.0% over the closing price of the Company’s common stock of $24.00 per share on March 3, 2021, and is subject to certain adjustments under the terms of the capped call transactions. The Company expects to receive from the Counterparties a number of shares of the Company’s common stock or, at the Company’s election (subject to certain conditions), cash, with an aggregate market value (or, in the case of cash settlement, in an amount) approximately equal to the product of such excess times the number of shares of the Company’s common stock relating to the 2025 Capped Calls and 2028 Capped Calls being exercised.
These Capped Call instruments meet the conditions outlined in ASC 815-40 to be classified in stockholders’ equity, are not accounted for as derivatives, and are not subsequently remeasured as long as the conditions for equity classification continue to be met. The Company recorded a reduction to additional paid-in capital of approximately $22.5 million and $33.7 million related to the premium payments for the 2025 Capped Call and 2028 Capped Call transactions.
In connection with the 2024 Note Exchange, the Company received $0.4 million in cash in connection with settling certain Capped Calls. After giving effect to such settlements, the 2025 Capped Calls and 2028 Capped Calls outstanding cover approximately 1,504,992 and 8,837,095 shares of the Company's common stock, respectively. As the Capped Calls were equity classified, the proceeds from settlement of these Capped Calls were recorded to additional paid in capital.
Note 8. Common Stock
The Company had reserved shares of common stock for issuance, on an as-converted basis, as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 |
| Options issued and outstanding | 917,370 | | | 1,119,676 | |
| Outstanding restricted stock units | 14,305,562 | | | 12,695,176 | |
| Shares available for grant under the 2019 equity incentive plan | 5,490,650 | | | 7,654,656 | |
| Shares available for issuance under 2019 ESPP | 4,135,266 | | | 3,654,915 | |
Warrants to purchase common stock | 7,894,737 | | | — | |
Total | 32,743,585 | | | 25,124,423 | |
Note 9. Share-based Compensation Plans
2019 Equity Incentive Plan
In connection with the Company’s initial public offering, the Company adopted the 2019 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2019 Plan”). The 2019 Plan allows the Company to grant stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units and performance awards to participants. Subject to the terms and conditions of the 2019 Plan, the initial number of shares authorized for grants under the 2019 Plan is 8,000,000. These available shares increase annually by an amount equal to the lesser of 8,000,000 shares, 5% of the number of shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31, or the number of shares determined by the Company’s board of directors.
The Company’s board of directors approved an increase of shares available for grant under the 2019 Plan by 4,465,083 shares on May 5, 2021, by 4,648,003 shares on February 23, 2022, by 4,954,409 shares on February 13, 2023, and by 5,233,525 shares on February 20, 2024.
Activity under the Company’s stock option plan is set forth below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of
Options | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise
Price Per
Share | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(in thousands) |
| Balances at December 31, 2023 | 1,119,676 | | | 7.79 | | | 4.2 | | $ | 15 | |
| Options granted | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Options exercised | (136,658) | | | 3.05 | | | | | |
| Options cancelled | (65,648) | | | 8.53 | | | | | |
| Balances at December 31, 2024 | 917,370 | | | 8.44 | | | 3.5 | | 3,445 | |
| Options vested and exercisable— December 31, 2024 | 917,370 | | | 8.44 | | | 3.5 | | 3,445 | |
There were no stock options granted in 2024 and in 2023. The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $0.3 million, zero and $5.3 million, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised is the difference between the fair value of the underlying common stock on the date of exercise and the exercise price for in-the-money stock options.
In February 2022, the Company granted PSUs with financial performance targets to certain employees of the Company. The number of shares of the Company's common stock issued upon settlement will depend on the achievement of financial metrics relative to the approved performance targets, and can range from 0% to 150% of the target amount. The PSUs are subject to continuous service with the Company and will vest after approximately three years. The PSUs are measured using the fair value at the date of grant. The compensation expense associated with PSUs is recognized based on the estimated number of shares that the Company expects will vest and may be adjusted based on interim estimates of performance against the performance condition. During the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company has not recognized stock-based compensation expense as attainment of financial performance targets is not considered probable.
In March 2023, the Company granted PSUs under the 2019 Plan subject to the achievement of both market and service conditions to certain employees of the Company. The number of shares of the Company's common stock issued upon settlement will depend on the achievement of approved market conditions and continuous service with the Company. The PSUs are eligible to vest in three tranches over a five-year performance period. The PSUs are measured using the Monte Carlo simulation to obtain the fair value at the date of grant based on the probability that the market conditions will be met. The compensation expense associated with the PSUs is based on the fair value and is recognized over the requisite service period. The compensation expense will be recognized regardless of whether the market condition is ever satisfied, provided the requisite service period is satisfied.
In March and October 2024, the Company granted PSUs with financial performance targets to certain employees of the Company. The number of shares of the Company's common stock issued upon settlement will depend on the achievement of financial metrics relative to the approved performance targets, and can range from 0% to 200% of the target amount. The PSUs are subject to continuous service with the Company and will vest after approximately three years from the grant date. The PSUs are measured using the fair value at the date of grant. The compensation expense associated with PSUs is recognized based on the estimated number of shares that the Company expects will vest and may be adjusted based on interim estimates of performance against the performance condition.
Inducement Grants
The Company granted stock-based awards outside of the 2019 Plan to the certain executives. These awards were granted as inducements material to their commencement of employment and entry into offer letters with the Company, in accordance with Nasdaq Listing Rule 5635(c)(4).
The inducement pool consisted of a total of 5,625,000 shares of the Company's common stock, which includes (a) 2,050,000 shares of PSUs that are eligible to vest based on market and service conditions in four tranches over a five-year performance period and (b) 3,575,000 shares of RSUs generally subject to the same terms and conditions as grants that are made under the 2019 Plan. The unvested PSUs and RSUs held by the Company's former Chief Executive Officer John Koryl were forfeited upon his separation from the Company on October 28, 2024. The activity in the inducement pool is included in the summary of RSU activity table below.
RSUs
A summary of RSU activity for the year ended December 31, 2024 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of
Shares | | Restricted Stock Units
Weighted-
Average Grant
Date Fair
Value | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value
(in thousands) |
| Unvested December 31, 2023 | 12,695,176 | | | $ | 4.07 | | | $ | 25,517 | |
| Granted | 13,109,475 | | | 3.33 | | | |
| Vested | (6,312,012) | | | 4.56 | | | |
| Forfeited | (5,187,077) | | | 3.23 | | | |
| Unvested December 31, 2024 | 14,305,562 | | | $ | 3.48 | | | $ | 156,360 | |
Included in the table above for the year ended December 31, 2024 are 2,535,000 PSUs granted, 98,000 PSUs vested, and 1,979,678 PSUs forfeited. The weighted average grant date fair value per share of the PSUs granted, vested and forfeited in the year ended December 31, 2024 was $3.31, $1.63 and $2.53, respectively.
The total fair value as of the respective vesting dates of RSUs that vested during the year ended December 31, 2024 was $21.7 million.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In connection with the Company’s initial public offering, the Company adopted the Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”). The Employee Stock Purchase Plan permits employees to purchase shares of common stock during six-month offering periods at a purchase price equal to the lesser of (1) 85% of the fair market value of a share of common stock on the first business day of such offering period and (2) 85% of the fair market value of a share of common stock on
the last business day of such offering period. The initial number of shares of common stock that could be issued under the employee stock purchase plan was 1,750,000 shares. These available shares increase by an amount equal to the lesser of 1,750,000 shares, 1% of the number of shares of common stock outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31, or the number of shares determined by the Company’s board of directors.
The Company's board of directors approved an increase in the shares available for grant under the ESPP by 893,016 shares on May 5, 2021, by 929,601 shares on February 23, 2022, by 990,882 shares on February 13, 2023, and by 1,046,705 shares on February 20, 2024.
During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, employees purchased 566,354, 865,676, and 610,877 shares, respectively, at an average price of $2.49, $1.02 and $2.29, respectively.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had an immaterial amount of unrecognized stock-based compensation cost related to purchase rights under the employee stock purchase plan.
Stock-based Compensation
In determining the fair value of the stock-based awards, the Company uses the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and assumptions discussed below.
Fair Value of Common Stock— The fair value of the shares of common stock has historically been determined by the Company’s board of directors as there was no public market for the common stock. Subsequent to our IPO, the fair value per share of common stock is the closing price of the Company’s common stock as reported on the applicable grant date.
Expected Term —The expected term represents the period that the Company’s stock options are expected to be outstanding and is determined using the simplified method (based on the mid-point between the vesting date and the end of the contractual term) as the Company has concluded that its stock option exercise history does not provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term.
Volatility —Because the Company was privately held and did not have an active trading market for its common stock for a sufficient period of time, the expected volatility was estimated based on the average volatility for comparable publicly-traded companies, over a period equal to the expected term of the stock option grants.
Risk-free Rate —The risk-free rate assumption is based on the U.S. Treasury zero coupon issues in effect at the time of grant for periods corresponding with the expected term of the option.
Dividends —The Company has never paid dividends on its common stock and does not anticipate paying dividends on common stock. Therefore, the Company uses an expected dividend yield of zero.
The following assumptions were used to estimate the fair value of stock options granted in 2019, as there were no stock options granted in 2024, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| Expected term (in years) | 5.0 – 6.1 |
| Expected volatility | 44.2% – 47.8% |
| Average risk-free rate | 1.9% – 2.6% |
| Dividend yield | — |
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had approximately $43.3 million of unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to RSUs and PSUs, which the Company expects to recognize over the remaining weighted-average vesting period of approximately 2.2 years. As of December 31, 2024, the Company had no unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to options.
Total stock-based compensation expense by function was as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Marketing | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,550 | | | $ | 2,209 | |
| Operations and technology | 9,930 | | | 12,534 | | | 19,822 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 18,220 | | | 20,189 | | | 24,107 | |
Total | $ | 29,082 | | | $ | 34,273 | | | $ | 46,138 | |
During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company recognized compensation expense of $1.0 million within selling, general and administrative associated with the modification of certain outstanding equity awards pursuant to the terms of the transition and separation agreement the Company entered into with its founder, Julie Wainwright, in connection with her resignation as Chief Executive Officer on June 6, 2022.
During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company capitalized $0.5 million, $0.8 million, and $1.6 million of stock-based compensation expense to proprietary software, respectively.
Note 10. Leases
The Company leases its corporate offices, retail spaces and authentication centers under various noncancelable operating leases with terms ranging from one year to fifteen years.
The Company recorded operating lease costs of $20.9 million, $22.8 million and $29.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company incurred $5.5 million, $5.2 million and $5.6 million of variable lease costs for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, which is comprised primarily of the Company’s proportionate share of operating expenses, property taxes and insurance.
Due to the office and store closures in the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company reviewed its right-of-use assets for impairment. Impairment losses are measured and recorded for the excess of carrying value over its fair value, estimated based on expected future cash flows using discount rate and other quantitative and qualitative factors. As a result, the Company recorded $31.1 million related to the impairment of certain office and store right-of-use assets during the year ended December 31, 2023. No impairment charges were recorded during the year ended December 31, 2024. The impairment charges are included in restructuring in the statements of operations.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company entered into agreements to amend certain of its operating leases. The Company treated the lease termination amendments as lease modifications for accounting purposes as of the applicable effective dates of such terminations which resulted in a decrease of $7.7 million to the related lease liabilities, and a decrease of $1.4 million to the related right-of-use assets for the year ended December 31, 2023. The Company recorded a net gain on the lease terminations of $0.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The net gain on lease terminations is included in restructuring in the statements of operations.
Maturities of operating lease liabilities by fiscal year for the Company’s operating leases are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| Fiscal Year | | Amount |
| 2025 | | $ | 28,761 | |
| 2026 | | 28,649 | |
| 2027 | | 24,699 | |
| 2028 | | 21,991 | |
| 2029 | | 11,615 | |
| Thereafter | | 8,822 | |
| Total future minimum payments | | $ | 124,537 | |
| Less: Imputed interest | | (15,912) | |
| Present value of operating lease liabilities | | $ | 108,625 | |
Supplemental cash flow information related to the Company’s operating leases are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Operating cash flows used for operating leases | $ | 27,939 | | | $ | 34,118 | | | $ | 27,097 | |
Operating lease assets obtained in exchange for operating lease liabilities (including remeasurement of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities due to lease modifications) | $ | 4,558 | | | $ | 6,272 | | | $ | 2,245 | |
The weighted average remaining lease term and discount rate for the Company’s operating leases are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2024 | | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Weighted average remaining lease term | 4.6 years | | 5.5 years |
| Weighted average discount rate | 6.2 | % | | 6.1 | % |
The Company has leases for certain vehicles and equipment that are classified as finance leases. The finance lease right-of-use asset and finance lease liabilities for these vehicle and equipment leases are immaterial as of December 31, 2024 and 2023.
Note 11. Restructuring
In February 2023, the Company announced a savings plan to reduce its real estate presence and operating expenses through closure of certain retail and office locations and workforce reduction.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company recognized $43.5 million in restructuring which consisted of right-of-use asset impairment charge of $31.1 million, leasehold improvements impairment charge of $8.6 million, employee severance of $3.0 million, and other related charges of $1.5 million, partially offset by a $0.7 million gain on lease terminations. The Company recorded an immaterial amount of restructuring for the year ended December 31, 2024. The restructuring related charges were recorded on a separate line item in the Company's statements of operations.
Note 12. Commitments and Contingencies
Fire at Secaucus, New Jersey Authentication Center
In May 2024, the Company experienced a fire at one of its authentication centers in Secaucus, New Jersey. The damage was primarily limited to fixed assets, leasehold improvements, supplies, and consigned and owned inventories. The Company maintains property, cargo, general liability and business interruption insurance coverage.
As of December 31, 2024, discussions with the insurance company are still ongoing. Based on the provisions of the Company’s insurance policies, the Company recorded insurance recoveries for fire related costs for which recovery was deemed probable.
The Company recorded losses related to the fire, net of insurance recoveries, of $0.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2024 within Operations and Technology on the statements of operations.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company recorded $2.5 million of insurance receivables within prepaid and other current assets on the balance sheet. The Company has received $3.9 million in payments from insurers towards its claims to cover immediate impacts of the fire. $3.4 million of the payments are included within net cash flows from operating activities and $0.5 million of the payments are included within net cash flows from investing activities in the statements of cash flows due to the nature of the advance insurance payments.
Noncancelable Purchase Commitments
Our contractual commitments primarily consist of software and other services in the ordinary course of business that are noncancellable with varying expiration dates through 2027. As of December 31, 2024, the future minimum payments under the Company’s noncancelable purchase commitments were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| Year Ending December 31, | | Purchase
Commitments |
| 2025 | | $ | 8,072 | |
| 2026 | | 7,665 | |
| 2027 | | 1,825 | |
| 2028 | | — | |
| 2029 | | — | |
| Total future minimum payments | | $ | 17,562 | |
Contingencies
From time to time, the Company is subject to, and it is presently involved in, litigation and other legal proceedings and from time to time, the Company receives inquiries from government agencies. Accounting for contingencies requires the Company to use judgment related to both the likelihood of a loss and the estimate of the amount or range of loss. The Company records a loss contingency when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company discloses material contingencies when a loss is not probable but reasonably possible.
On November 14, 2018, Chanel, Inc. sued the Company in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. The Complaint alleged federal and state law claims of trademark infringement, unfair competition, and false advertising. On February 1, 2019, Chanel, Inc. filed its First Amended Complaint that included substantially similar claims against the Company. On March 4, 2019, the Company filed a Motion to Dismiss the First Amended Complaint, which was granted in part and dismissed in part on March 30, 2020. The surviving claims against the Company include trademark infringement under 15 U.S.C. § 1114, false advertising under 15 U.S.C. § 1125, and unfair competition under New York common law. On May 29, 2020, the Company filed its Answer to the Amended Complaint. On November 3, 2020, the Company sought leave to amend its Answer to assert counterclaims against Chanel, Inc. for violations of the Sherman Act, 15 U.S.C. §§ 1 & 2, the Donnelly Act, N.Y. Gen. Bus. Law. § 340, and New York common law. The motion for leave to amend was granted on February 24, 2021. On February 25, 2021, the Company filed its First Amended Answer, Affirmative Defenses and Counterclaims against Chanel. The Company’s Counterclaims allege violations of the Sherman Act, 15 U.S.C. §§ 1 & 2, the Donnelly Act, N.Y. Gen. Bus. Law. § 340, and New York common law. On March 18, 2021, Chanel moved to dismiss the Company’s Counterclaims and moved to strike the Company’s unclean hands affirmative defense. Decisions on Chanel’s motion to dismiss and motion strike are pending. The parties agreed to a stay in April 2021 to engage in settlement discussions. After several mediation sessions, the parties were unable to reach a resolution, and the stay was lifted in November 2021. Chanel then sought a partial stay of discovery on the Company's counterclaims and unclean hands defense while Chanel's motion to dismiss and strike those claims are pending, and on March 10, 2022, the Court granted Chanel's request. The parties have continued to engage in fact discovery regarding Chanel's counterfeiting and false advertising claims against the Company. Fact discovery was scheduled to be completed by August 15, 2023. However, on July 19, 2023, the Court ordered a stay of the case at the parties’ request to enable the parties to attempt mediation again. The parties have continued to engage in settlement discussions facilitated by a mediator. The final outcome of this litigation, including our liability, if any, with respect to Chanel’s claims, is uncertain. An unfavorable outcome in this or similar litigation could adversely affect the Company’s business and could lead to other similar lawsuits. The Company is not able to predict or reasonably estimate the ultimate outcome or loss or range of possible losses relating to this claim.
Beginning on September 10, 2019, purported shareholder class action complaints were filed against the Company, its officers and directors and the underwriters of its IPO in the San Mateo Superior Court, Marin County Superior Court, and the United States District Court for the Northern District of California. On July 27, 2021, the Company reached an agreement in principle to settle the shareholder class action. On November 5, 2021, plaintiff filed the executed stipulation of settlement and motion for preliminary approval of the settlement with the federal court. On March 24, 2022, the court entered an order preliminarily approving the settlement. On July 28, 2022, the court entered an order finally approving the settlement and dismissing the case. The financial terms of the stipulation of settlement provide that the Company will pay $11.0 million within thirty (30) days of the later of preliminary approval of the settlement or plaintiff’s counsel providing payment instructions. The Company paid the settlement amount on March 29, 2022 with available resources and recorded approximately $11.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 under our Operating expenses as a Legal settlement.
One of the plaintiffs in the Marin County case opted out of the federal settlement and is pursuing the claim in Marin County Superior Court. The stay of the state court case has been lifted, and the opt out plaintiff filed an amended complaint on October 31, 2022 alleging putative class claims under the Securities Act of 1933 (the “Securities Act”) on behalf of the two shareholders who opted out of the settlement and those who purchased stock from November 21, 2019 through March 9, 2020, based on purported new revelations. The claims are for alleged violations of Sections 11 and 15 of the Securities Act. On February 23, 2024, plaintiff filed a motion for class certification, which has been set for hearing on February 25, 2025. While the Company intends to defend vigorously against this litigation, there can be no assurance that the Company will be successful in its defense. For this reason, the Company cannot currently estimate the loss or range of possible losses it may experience in connection with this litigation.
Indemnifications
In the ordinary course of business, the Company may provide indemnifications of varying scope and terms to vendors, directors, officers and other parties with respect to certain matters including, but not limited to, losses arising out of the breach of such agreements, intellectual property infringement claims made by third parties and other liabilities relating to or arising from the Company's various services, or its acts or omissions. The Company has not incurred any material costs as a result of such indemnifications and have not accrued any liabilities related to such obligations in its financial statements.
Note 13. Income Taxes
The components of the Company’s income tax provision consisted of (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Current: | | | | | |
Federal | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
State | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | |
| Total current tax expense | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | |
| Deferred: | | | | | |
Federal | — | | | — | | — |
State | — | | | — | | — |
| Total deferred tax expense | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total provision for income taxes | $ | 276 | | | $ | 283 | | | $ | 172 | |
The reconciliation of the Federal statutory income tax provision for the Company’s effective income tax provision (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
Tax at federal statutory rate | $ | (28,144) | | | $ | (35,290) | | | $ | (41,209) | |
State taxes, net of federal effect | (7,627) | | | (9,554) | | | (11,257) | |
| Stock-based compensation | 3,192 | | | 8,956 | | | 419 | |
Non-deductible items | 1,988 | | | 504 | | | 524 | |
| Tax credits | (169) | | | (531) | | | (563) | |
| | | | | |
Warrant liability fair value adjustment | 18,333 | | | — | | | — | |
| Adoption of ASU 2020-06 | — | | | — | | | (28,045) | |
Provision to return adjustments | (1,927) | | | 9,259 | | | — | |
Valuation allowance | 14,651 | | | 26,501 | | | 80,254 | |
| Other | (21) | | | 438 | | | 49 | |
| Provision for income taxes | $ | 276 | | | $ | 283 | | | $ | 172 | |
The Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 230,303 | | | $ | 232,259 | |
Fixed assets and intangibles | 10,461 | | | 6,364 | |
Capitalized research and development (1) | 18,679 | | | 13,835 | |
Accruals and reserves | 18,685 | | | 12,477 | |
| Stock options | 1,536 | | | 840 | |
Operating lease liabilities | 29,424 | | | 33,683 | |
| Capped calls | 15,011 | | | 15,065 | |
| Convertible debt | — | | | 2,329 | |
| Tax credits | 2,738 | | | 2,569 | |
Other | 4,621 | | | — | |
| Gross deferred tax assets | 331,458 | | | 319,421 | |
Less: valuation allowance | (306,948) | | | (292,297) | |
| Total deferred tax assets | 24,510 | | | 27,124 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
Operating lease right-of-use assets | (21,641) | | | (24,416) | |
| | | |
Other | (2,869) | | | (2,708) | |
| Gross deferred tax liabilities | (24,510) | | | (27,124) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
(1) Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, research and development costs are no longer fully deductible when incurred and are required to be capitalized and amortized for U.S. tax purposes effective January 1, 2022. The mandatory capitalization requirement increases our gross deferred tax assets, which are fully offset by the valuation allowance.
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, the Company evaluates all available positive and negative evidence by considering whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be recognized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon future taxable income, future reversals of existing taxable temporary difference, taxable income in carryback years and tax-planning strategies. The Company believes it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets in the U.S. will not be realized; accordingly, a valuation allowance has been established against the Company's U.S. deferred tax assets. The net change in the valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023 was an increase of $14.7 million and an increase of $26.5 million, respectively.
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company has a net operating loss carryforward of $861.8 million and $871.3 million for federal tax purposes, respectively, and $818.6 million and $817.5 million for state tax purposes, respectively. If not utilized, these losses will expire beginning in 2025 for state tax purposes. However, beginning in tax year 2018 and forward, the Federal law has changed such that net operating losses generated after December 31, 2017 may be carried forward indefinitely. Accordingly, $157.6 million of the federal net operating losses will begin to expire in 2033. However, $704.2 million of the federal net operating losses will not expire.
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company has a credit carryforward of $4.7 million and $4.3 million for federal tax purposes, respectively, and $1.0 million for state tax purposes. If not utilized, these credits will expire beginning in 2041 for federal tax purposes and do not expire for state tax purposes.
The Tax Reform Act of 1986 limits the use of net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards in certain situations where changes occur in the stock ownership of a company. During 2019, the Company analyzed whether any of the reported net operating losses would be limited because of these rules. Based on the analysis the Company believes $3.3 million of the Federal and $2.1 million of California net operating losses will not be available to offset future taxable income because of the limitation. The reported net operating losses have been adjusted based on this analysis.
The Company files tax returns as prescribed by the tax laws of the jurisdictions in which it operates. In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by federal, state and local, jurisdictions, where applicable. As of
December 31, 2024 and 2023, all years generally remain open to examination. Additionally, net operating loss carryforwards are subject to examination by the Internal Revenue Service and the California Franchise Tax Board for up to three and four years, respectively, after utilization.
Uncertain Income Tax Positions
The following table reflects the changes to the Company's unrecognized tax benefits (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
Unrecognized tax benefits beginning balance | $ | 2,678 | | | $ | 1,525 | |
Increases related to current year tax positions | 169 | | | 531 | |
Increases related to prior year tax positions | — | | | 622 | |
Unrecognized tax benefits ending balance | $ | 2,847 | | | $ | 2,678 | |
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company had unrecognized tax benefits of $2.8 million and $2.7 million, respectively, none of which, if recognized, would favorably impact the Company’s effective tax rate. The unrecognized tax benefits relate to federal and state research and development credits. The Company's policy is to include interest and penalties as a component to the statements of operations, however there were no associated interest and penalties during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023. The Company estimates that there will be no material changes in its uncertain tax positions in the next 12 months.
Note 14. Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
A reconciliation of the numerator and denominator used in the calculation of the basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is as follows (in thousands, except share and per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Numerator | | | | | |
Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
| Denominator | | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding used to calculate net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | 107,878,366 | | | 101,806,000 | | | 95,921,246 | |
Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (1.24) | | | $ | (1.65) | | | $ | (2.05) | |
The following securities were excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders for the periods presented, because including them would have been anti-dilutive (on an as-converted basis):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Options to purchase common stock | 917,370 | | | 1,119,676 | | | 1,754,776 | |
| Restricted stock units | 14,305,562 | | | 12,695,176 | | | 11,369,021 | |
| Estimated shares issuable under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 248,523 | | | 367,074 | | | 695,782 | |
Assumed conversion of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes | 10,342,056 | | | 18,746,323 | | | 18,746,323 | |
Warrants to purchase common stock | 7,894,737 | | | — | | | — | |
Total | 33,708,248 | | | 32,928,249 | | | 32,565,902 | |
The 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes issued in June 2020 and in March 2021, respectively, are convertible, based on the applicable conversion rate, into cash, shares of the Company’s common stock or a combination thereof, at the Company’s election. The impact of the assumed conversion to diluted net loss per share is computed on an as-converted basis.
Note 15. Retirement Plan
The Company has a defined-contribution 401(k) retirement plan covering substantially all of its employees. Eligible employees are permitted to contribute up to an amount not to exceed an annual statutory maximum. The Company matches employee contributions at a rate of 25% of vested contributions, up to a maximum of $2,000 per participant per year. The Company’s contributions to the 401(k) plan were $1.4 million, $0.8 million, and $1.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Note 16. Segment Information
The Company has one reportable segment as its chief operating decision maker (the "CODM"), who is its Chief Executive Officer, reviews financial information on a consolidated basis. The Company generates revenue from the sale of pre-owned luxury goods through its online marketplace and retail stores. Revenue is comprised of consignment revenue, direct revenue, and shipping services revenue. The Company does not have intra-entity sales or transfers.
The chief operating decision maker assesses performance and allocates resources based on net loss, as reported on the statements of operations. Net loss is used to monitor budget versus actual results. The CODM does not evaluate operating segments using asset or liability information.
The following table presents selected financial information with respect to the Company's single operating segment (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Total revenue | $ | 600,484 | | | $ | 549,304 | | | $ | 603,493 | |
| Less: | | | | | |
| Cost of consignment revenue | 53,801 | | | 58,120 | | | 56,963 | |
| Cost of direct revenue | 55,809 | | | 74,343 | | | 141,661 | |
| Cost of shipping services revenue | 43,353 | | | 40,563 | | | 56,178 | |
| Total cost of revenue | 152,963 | | | 173,026 | | | 254,802 | |
| Gross Profit | 447,521 | | | 376,278 | | | 348,691 | |
| Less: | | | | | |
People costs | 283,002 | | | 274,229 | | | 297,676 | |
Software and purchased services | 108,866 | | | 104,454 | | | 103,695 | |
| Occupancy expense | 37,295 | | | 37,718 | | | 44,911 | |
Depreciation and amortization(1) | 32,764 | | | 31,695 | | | 27,669 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 29,082 | | | 34,273 | | | 46,138 | |
Administration and other segment expenses (2) | 12,811 | | | 16,740 | | | 16,869 | |
Restructuring (3) | 196 | | | 43,462 | | | 896 | |
| Total operating expenses | 504,016 | | | 542,571 | | | 537,854 | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | (68,167) | | | — | | | — | |
| Gain on extinguishment of debt | 4,177 | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest income | 7,943 | | | 8,805 | | | 3,191 | |
| Interest expense | (21,384) | | | (10,701) | | | (10,472) | |
| Other income (expense), net | — | | | — | | | 171 | |
Provision for income taxes | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
(1) Expenses reported in operating expenses, excludes depreciation and amortization recorded in cost of revenue.
(2) Administration and other segment expenses include insurance, supplies, and taxes.
(3) Restructuring expenses for the year ended December 31, 2024 and 2022 consist of employee severance charges. For the year ended December 31, 2023 it consists of impairment of right-of-use assets and property and equipment, employee severance charges, gain on lease terminations, and other charges.
Note 17. Subsequent Events
On February 10, 2025, the Company entered into an exchange agreement with certain holders of its 2028 Notes to exchange $183.3 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes for $146.7 million in aggregate principal amount of new convertible senior notes due 2031 (“2031 Notes”), issued pursuant to an Indenture, dated February 10, 2025. The exchange was consummated, and the 2031 Notes were issued in a private placement, on February 10, 2025.
The 2031 Notes bear cash interest at a rate of 4.00% per annum payable semi-annually in arrears on February 15 and August 15 of each year, beginning on August 15, 2025 (with additional interest being paid solely on the first interest payment date of the 2031 Notes in consideration for the accrued and unpaid interest on the 2028 Notes exchanged for the 2031 Notes) and will mature on February 15, 2031. The 2031 Notes are convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Indenture. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this transaction on its financial statements.
The RealReal - Insider Trading Policy
The RealReal, Inc. (the Company or TRR), has established this Insider Trading Policy in accordance with the Company’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and Insider Trading laws.
This Insider Trading Policy applies to the Company and all of the following Insiders:
•all employees of the Company;
•all consultants, contractors, vendors or other persons associated with the Company who may have access to Material Non-Public Information about the Company; and
•all members of the Company’s Board of Directors.
This Insider Trading Policy is organized in question and answer format. All bolded terms are defined in this document. If you have any questions about this Insider Trading Policy, please contact InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com.
Table of Contents
| | | | | | | | |
1. | Background and Definitions |
| 1.1 | What is Insider Trading? |
| 1.2 | What is Material Non-Public Information? |
| 1.3 | Does my family or do members of my household have to comply with this Insider Trading Policy? |
| 1.4 | Who are Designated Insiders? |
| 1.5 | What is a Trading Window, or what is a Blackout Period? |
| 1.6 | When does the Trading Window Open? |
| 1.7 | When does the Trading Window Close? |
| 1.8 | Will I receive reminders when the Trading Window opens and closes? |
| 1.9 | What is a Special Blackout Period? |
| 1.10 | What if I am unsure if I am in possession of Material Non-Public Information? |
| 1.11 | Who do I contact if I have questions about, or to report violations of, this Insider Trading Policy? |
2. | Compliance with this Insider Trading Policy |
| 2.1 | What types of transactions does this Insider Trading Policy apply to? |
| 2.2 | What is prohibited by this Insider Trading Policy? |
| 2.3 | What are the penalties for Insider Trading or violating this Insider Trading Policy? |
| 2.4 | Are there exceptions to this Insider Trading Policy? |
| 2.5 | What do I need to do to trade Company securities in an Open Trading Window? |
3. | Rule 10b5-1 Plans |
| 3.1 | What is a Rule 10b5-1 Plan? |
| 3.2 | How do I put a Rule 10b5-1 Plan in place? |
| 3.3 | What are the requirements for putting a Rule 10b5-1 Plan in place? |
| 3.4 | May I use my regular broker for a Rule 10b5-1 Plan? |
| 3.5 | May I trade alongside my Rule 10b5-1 Plan or have multiple Rule 10b5-1 Plans? |
| 3.6 | May I trade in the open market if my Rule 10b5-1 Plan expires? |
| 3.7 | May I amend or terminate my Rule 10b5-1 Plan? |
| 3.8 | What is the record retention requirement for Rule 10b5-1 Plans? |
4. | Administration of this Policy |
5. | Training |
6. | Document Review and Approval Requirements |
1.Background and Definitions
To promote compliance with Insider Trading Laws, which include applicable laws, rules, regulations and listing standards, it is the Company’s policy not to engage in transactions of Securities in violation of Insider Trading Laws. Policies and procedures with respect to individuals and other entities subject to this Insider Trading Policy are reflected below.
1.1.What is Insider Trading?
The term Insider Trading generally refers to the illegal trading in a company’s stock (and or securities as defined below) on the basis of Material Non-Public Information whether or not intentional. Sharing Material Non-Public Information about the Company with anyone, whether or not you received any compensation for, is known as ”tipping” or a “tip”, and is another form of prohibited Insider Trading.
Securities include common stock, options, preferred stock, debt securities, convertible securities or any similar securities, as well as any derivative securities relating to any of the securities whether you received the securities from the issuer of such securities (i.e. the Company in the case of TRR Securities) or obtained, or plan to obtain, such securities from third-parties or on the open market.
*Please note: Your obligation not to disclose Material Non-Public Information is in addition to any other confidentiality obligations applicable to you as a result of your employment by, or other relationship with, the Company. Maintaining the confidentiality of Company information is essential for competitive, security and other business reasons, as well as to comply with federal Insider Trading Laws.
1.2.What is Material Non-Public Information?
In general, Material Non-Public Information is defined broadly and includes any information that is not widely available to the public and that a reasonable person would consider important when making an investment decision.
For information to be considered available to the public, it needs to be shared in a way designed to reach investors generally, and investors must be given an opportunity to absorb it. Practically speaking that means that the information: (a) has been disclosed through a press release or a filing with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), or through a widely attended conference call or presentation that is available to the public through a webcast or dial-in number; and (b) two full trading days need to have passed to allow the news to be “digested” by the public. While it is not possible to define all categories of material information some examples are:
▪Financial performance or projections such as earnings, planned guidance and liquidity
▪Proposed acquisitions, divestitures or restructurings, a possible change in control or other major transactions
▪Major personnel or significant changes in senior management
▪Actual or threatened, or resolution of, major litigation or governmental investigation exposure or developments
▪Development of a significant new product, product line, service or process, including technology
▪Unanticipated changes in sales, orders, costs or expenses
▪Awards of significant new contracts, orders, or the loss thereof
▪Cybersecurity incidents
▪Significant accounting developments
▪Potential changes to credit ratings
▪Major marketing changes
▪Proposed dividends or stock splits, public or private securities offerings
Whether information is Material Non-Public Information is difficult to evaluate in the abstract and, unfortunately, is typically assessed with the benefit of hindsight. Either positive or negative information may be Material Non-Public Information and does not have to relate specifically to the Company’s business.
You should treat all information you learn about the Company or its business plans as confidential and proprietary to the Company. Inadvertent disclosure of confidential information may expose you and the Company to significant risk of investigation and litigation.
Accordingly, it is important that responses to inquiries about the Company by the press, investment analysts or any other inquiries are made only through authorized individuals. Please contact investorrelations@therealreal.com and press@therealreal.com if you receive any inquiries.
1.3.Does my family or do members of my household or entities I control have to comply with this Insider Trading Policy?
Any member of your immediate family, and any person who resides in your household, adult or minor and whether or not related to you, and any entity over which you have control or influence with respect to a transaction in Securities (e.g., a trustee of a trust or an executor of an estate) or in which you have a material financial interest (for example, a trust of which the employee is a beneficiary, must comply with this Insider Trading Policy. Likewise, when we refer to “you,” we also mean each of the people and entities listed above with respect to you. Because the people and entities listed above are covered by this Insider Trading Policy, you will be responsible for their transactions in TRR Securities and, in order to maintain your compliance with this Insider Trading Policy, you should ensure that they do not transact in TRR Securities without your clearance. If any member of your immediate family or your household or an entity you control is charged with Insider Trading, you will also likely be charged with Insider Trading. In addition, you should ensure that you do not share Material Non-Public Information or other confidential information about the Company with anyone else, including parents, siblings, cousins, aunts, uncles, etc., or with anyone you are otherwise affiliated with, such as business partners or associates or other advisors.
1.4.Who are Designated Insiders?
Designated Insiders are subject to additional trading restrictions under this Insider Trading Policy. The term Designated Insiders includes:
▪all employees of the Company who are:
•at the level of “director” or above,
•a member of the legal or finance teams
•at the level of “manager” and above and a member of the product team, or
•otherwise have access to Material Non-Public Information about the Company;
▪all consultants, vendors or other persons associated with the Company who may have access to Material Non-Public Information about the Company;
▪all members of the Company’s Board of Directors.
1.5.What is a Trading Window, or what is a Blackout Period?
To ensure compliance with this Insider Trading Policy and to avoid even the appearance of trading on the basis of Material Non-Public Information, the Company will close the Trading Window for Designated Insiders when the Company’s quarterly financial results could be “deemed” known by Designated Insiders, which is generally the middle of the last month of each quarter. The Trading Window will generally open again two (2) full trading days after the Company announces its quarterly earnings. You should not expect that the Trading Window will open on any particular date or remain open for any minimum period of time. The timeframe when the Trading Window is closed is also referred to as a Blackout Period. For more information about the timing of the Trading Window opening and closing, please see Section 1.6 and Section 1.7 below.
*Please Note: Trading in TRR Securities when the Trading Window is open and you have been granted clearance to do so is not a guarantee that you have not illegally engaged in Insider Trading. You may be in possession of Material Non-Public Information and you should use good judgement at all times. Any questions should be directed to InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com before you trade in TRR Securities.
**You are responsible at all times for compliance with the prohibitions against Insider Trading.
1.6.When does the Trading Window Open?
As discussed in Section 1.5 above, additional trading restrictions apply to Designated Insiders. Each quarter, the Trading Window for Designated Insiders generally opens two (2) full trading days after the Company’s quarterly earnings announcement.
Any questions should be directed to InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com before you trade in any TRR Securities.
1.7.When does the Trading Window Close?
Each quarter, the Trading Window generally closes for Designated Insiders on the 15th day of the last month of every quarter (March 15th, June 15th, September 15th, December 15th), subject to any Special Blackout Period as described in Section 1.9 below. If you are a Designated Insider, this generally means that the last trading day is the 14 th of the last month of every quarter.
If the 14 th day falls on a weekend, then the last trading day is the preceding Friday. If the 14th day falls on a holiday, then the last trading day is the trading day before the 14 th.
Any questions should be directed to InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com before you trade in any TRR Securities.
1.8.Will I receive reminders when the Trading Window opens and closes?
If you are a Designated Insider, you will receive a courtesy email confirming the date that the Trading Window will open and when the Trading Window is expected to close.
Also, approximately one week before the Trading Window closes, if you are a Designated Insider, you will typically receive a courtesy email confirming the date that the Trading Window will close.
When you receive these emails, please make note of the relevant dates.
If you will be unable to access your TRR email, for example if you are on leave or holiday, please provide InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com with an alternate email. You are responsible for observing the closed Trading Window whether or not you receive the courtesy email. Your account in eTrade will be blocked for trading when the Trading Window closes. However, if your account in eTrade is inadvertently left unblocked, you are still responsible for observing the closed Trading Window.
*Please Note: You are responsible for observing the closed Trading Window whether or not you receive these courtesy emails.
1.9.What is a Special Blackout Period?
The Company may need to impose a Special Blackout Period and you may receive an email notification that a Special Blackout Period is in effect and that you may not trade in TRR Securities until the Special Blackout Period has ended. Special Blackout Periods may apply to all Insiders, not just Designated Insiders. You may not disclose the existence of the Special Blackout Period to any other person. Failure to receive an email of a Special Blackout Period will not protect you from allegations of Insider Trading or violating this Insider Trading Policy if you are in possession of Material Non-Public Information and trade in TRR Securities.
1.10.What if I am unsure if I am in possession of Material Non-Public Information?
Please contact InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com if you have any questions.
1.11.Who do I contact if I have questions about, or wish to report a violation of, this Insider Trading Policy?
Please contact InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com if you have any questions or concerns or to report a violation of this policy. You may also report any violations of this Insider Trading Policy via the Company’s anonymous ethics hotline 24 hours, 7 days a week at 1-844-288-5309 or www.therealreal.ethicspoint.com. If you become aware of any violation of this Insider Trading Policy, you should report it immediately. You will not be disciplined or retaliated against in any way for reporting violations of this Insider Trading Policy in good faith.
2.Compliance with this Insider Trading Policy
2.1.What types of transactions does this Insider Trading Policy apply to?
This Insider Trading Policy applies to all of the following Restricted Transactions involving Securities (whether undertaken directly by you or indirectly by anyone else on your behalf):
•Purchase
•Sale
•Exercise of stock options
•Put or call
•Short sale
•Hedging
•Gifts
•Transfers for estate planning purposes
•Pledging or margin account
•Any transactions similar to the above
Securities include common stock, options, preferred stock, debt securities, convertible securities or any similar securities, as well as any derivative securities relating to any of the securities whether you received the securities from the issuer of such securities (i.e. the Company in the case of TRR Securities) or obtained, or plan to obtain, such securities from third-parties or on the open market.
Derivative Securities include any trade in any interest or position relating to the future price of securities, such as a put, call or short sale, or any hedging transactions with the securities or using securities as collateral for margin accounts or pledging of securities.
You MAY NOT engage in Derivative Transactions in TRR Securities AT ANY TIME.
If you are in possession of Material Non-Public Information when you cease to be an Insider, this Insider Trading Policy will continue to apply until that Material Non-Public Information has become public or is no longer material.
If you have any questions about whether a transaction is subject to this Insider Trading Policy, please contact InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com before engaging in that transaction.
2.2.What is prohibited by this Insider Trading Policy?
You MAY NOT engage in Restricted Transactions in TRR Securities (subject to the exceptions below), while you are in possession of Material Non-Public Information about the Company. This prohibition also applies to transactions in the securities of other companies about which you may learn Material Non-Public Information while working for the Company.
You MAY NOT communicate Material Non-Public Information to anyone who may trade in TRR Securities (or any other securities). You may not have another person trade TRR Securities (or any other securities) for you if you are in possession of Material Non-Public Information relevant to those securities.
You MAY NOT engage in Derivative Transactions in TRR Securities AT ANY TIME.
Derivative Transactions include any trade in any interest or position relating to the future price of TRR Securities, such as a put, call or short sale, or any hedging transactions with the TRR Securities or using TRR Securities as collateral for margin accounts or pledging of securities.
*Please Note: It is your responsibility to determine whether you are in possession of Material Non-Public Information even if the Trading Window is open and you have been granted clearance to trade. Any questions should be directed to InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com before you trade in any TRR Securities.
** You MAY NOT trade in the securities of any company if you have Material Non-Public Information about that company.
2.3.What are the penalties for Insider Trading or violating this Insider Trading Policy?
The consequences of violating the Insider Trading Laws can be severe and can include civil and criminal sanctions and penalties, including imprisonment. If you fail to comply with this Insider Trading Policy, you will be subject to TRR-imposed sanctions, including dismissal, regardless of whether your failure to comply with this Insider Trading Policy results in a violation of law. The Company reserves the right to determine, in its own discretion and on the basis of the information available to it, whether you have violated this Insider Trading Policy. The Company is not required to wait for the filing or conclusion of a civil or criminal action by the SEC or the Department of Justice or any other entity or person.
If you provide any Material Non-Public Information to any other person who purchased or sold TRR Securities while in possession of such Material Non-Public Information, you will also be subject to severe civil and criminal sanctions and penalties, including imprisonment.
2.4.Are there exceptions to this Insider Trading Policy?
The only exceptions to this Insider Trading Policy are:
▪Cash Option Exercises. You may exercise a TRR stock option for cash. However, this exception does not apply to a cashless exercise of your stock options in which shares are sold in the market (i.e. a net exercise of your stock options).
▪Rule 10b5-1 Plans. You may sell or purchase TRR Securities pursuant to a Rule 10b5-1 Plan (see Section 3 below).
▪Employee Stock Purchase Plan. Purchases of common stock made on your behalf pursuant to the Company Employee Stock Purchase Plan, if any, resulting from periodic contributions of money to the plan made in accordance with the terms of the Company Employee Stock Purchase Plan.
▪Permitted Transactions. Any other transaction designated by the Company’s Board of Directors or any board committee or the Chief Legal Officer, with reference to this Policy, as a Permitted Transaction.
Please Note: You must contact the InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com if you wish to utilize one the above exceptions prior to undertaking any of the actions above.
2.5.What do I need to do to trade TRR securities when the Trading Window is open?
All Designated Insiders must comply with the Company’s Pre-Clearance process as follows:
▪Complete the Pre-Clearance Request Form provided to you in the courtesy email reminder that the Trading Window is opening.
▪Email the Pre-Clearance Request Form to Preclearancerequest@therealreal.com not less than two (2) business days prior to the date you wish to trade in the TRR Securities.
▪You will receive a response prior to your proposed trading date.
▪You will have five (5) days from your proposed trading date or until the Trading Window
closes, whichever is sooner, to complete your trade in TRR Securities.
If you are not a Designated Insider, you DO NOT need to comply with this Pre-Clearance process before trading in TRR Securities.
3.Rule 10b5-1 Plans
3.1.What is a Rule 10b5-1 Plan?
A Rule 10b5-1 Plan allows trades in your TRR Securities to take place even when the Trading Window is closed or you are in possession of Material Non-Public Information. A Rule 10b5-1 Plan is a written trading plan that you must sign in an open Trading Window and when you ARE NOT in possession of any Material Non-Public Information. The Rule 10b5-1 Plan is evidence that you made these future decisions about trading in TRR securities at the time that you signed the Rule 10b5-1 Plan.
A Rule 10b5-1 Plan provides an affirmative defense to prosecution for Insider Trading for transactions that you make in TRR securities. A Rule 10b5-1 Plan IS NOT a safe harbor from prosecution for Insider Trading.
3.2.How do I put a Rule 10b5-1 Plan in place?
If you would like to put a Rule 10b5-1 Plan in place, please contact InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com.
3.3.What are the requirements for putting a Rule 10b5-1 Plan in place?
You must sign a Rule 10b5-1 Plan in place when (i) the Trading Window is open (if you are a Designated Insider) and (ii) you ARE NOT otherwise in possession of Material Non-Public Information.
Your Rule 10b5-1 Plan must be reviewed, approved and counter-signed by the Company and must comply in all respects with the requirements of Rule 10b5-1, which include the following:
▪a cooling-off period for directors and Officers (as defined by Rule 16a-1(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) of the later of (1) 90 days following plan adoption; or (2) two business days following the disclosure in certain periodic reports of
the Company’s financial results for the fiscal quarter in which the plan was adopted (but not to exceed 120 days following plan adoption) before any trading can commence under the plan;
▪a cooling-off period of 30 days for other persons;
▪a condition for directors and Officers to include a representation in their Rule 10b5-1 Plan certifying, at the time of the adoption, that: (1) they are not aware of Material Non-Public Information about the Company or its Securities; and (2) they are adopting the plan in good faith and not as part of a plan or scheme to evade the prohibitions of Rule 10b-5;
▪a limitation on using multiple overlapping Rule 10b5-1 plans (except as otherwise permitted by Rule 10b5-1);
▪a limitation on the ability of anyone other than issuers to rely on the affirmative defense for a single trade plan to one such plan during any consecutive 12-month period; and
▪a condition that all persons entering into a Rule 10b5-1 Plan must act in good faith with respect to that plan.
3.4.What broker may I use for my Rule 10b5-1 Plan?
You must use eTrade as the broker for your Rule 10b5-1 Plan, unless you are using your own broker at the time that this Insider Trading Policy is effective.
In exceptional circumstances where you wish to use your own broker, please email our Chief Legal Officer. Any exceptions to this requirement are at the sole discretion of the Chief Legal Officer.
3.5.May I trade alongside my Rule 10b5-1 Plan or have multiple Rule 10b5-1 Plans?
You ARE PROHIBITED from engaging in any trades of TRR Securities outside of your Rule 10b5-1 Plan. You may not have more than one Rule 10b5-1 Plan in effect at any time, except as expressly permitted by Rule 10b5- 1.
3.6.May I trade in the open market if my Rule 10b5-1 Plan expires?
If your Rule 10b5-1 Plan expires, you may trade in the open market in TRR Securities after that date if (i) the Trading Window is open and (ii) you ARE NOT otherwise in possession of Material Non-Public Information.
3.7.May I amend or terminate my Rule 10b5-1 Plan?
Your Rule 10b5-1 Plan MAY NOT be amended or terminated by you after you establish it unless approved by the Chief Legal Officer. Any modification or termination of your Rule 10b5-1 Plan may expose you to prosecution for Insider Trading as such modification or termination calls into question your “good faith” in establishing a Rule 10b5-1 Plan.
If you terminate your Rule 10b5-1 Plan and then wish to establish a new Rule 10b5-1 Plan, the first trade under the new Rule 10b5-1 Plan may not occur until the applicable cooling off period has expired as described in Section 3.3, and subject to all other requirements in Section 3.3.
If you modify your Rule 10b5-1 Plan in a manner that is treated as a termination under Rule 10b5-1 (for example, any modification or change to the amount, price or timing of the purchase or sale of the securities underlying the plan, or the substitution or removal of a broker that changes the price or date on which purchases or sales are to be executed), the modification will be treated as a termination of the Rule 10b5-1 Plan and the modified plan will be treated as the adoption of a new 10b5-1 Plan subject to the requirements of Section 3.3 of this Insider Trading Policy (including a new cooling off period).
3.8.What is the record retention requirement for Rule 10b5-1 Plans?
You must keep a copy of your Rule 10b5-1 Plan for five (5) years after its termination.
4.Administration of this policy
The Legal Department is responsible for administering this Insider Trading Policy.
If you have any questions regarding this Insider Trading Policy or its applicability to any proposed transaction or event, please contact InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com.
5.Training
The Legal Department will provide training about Insider Trading and this Insider Trading Policy on a periodic basis.
If you have any questions about Insider Trading or this Insider Trading Policy, please contact InsiderTradingPolicy@therealreal.com.
6.Document Review and Approval Requirements
This Insider Trading Policy will be periodically reviewed and updated by the Legal Department, subject to approval by the Company’s Board of Directors or a sub-committee thereof.
(February 2023)
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
We consent to the incorporation by reference in the registration statements (No. 333-232528, 333-255981, 333-264837, 333-270281, 333-277638, and 333-279214) on Form S-8 of our reports dated February 21, 2025, with respect to the financial statements of The RealReal, Inc. and the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
San Francisco, California
February 21, 2025
Exhibit 31.1
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
RULES 13a-14(a) AND 15d-14(a) UNDER THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Rati Sahi Levesque certify that:
1. I have reviewed this Form-10K of The RealReal, Inc.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant's other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant's disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant's internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant's most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant's fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant's internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The registrant's other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant's auditors and the audit committee of the registrant's board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant's ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant's internal control over financial reporting.
| | | | | | | | |
| Date: February 21, 2025 | By: | /s/ Rati Sahi Levesque |
| | Rati Sahi Levesque |
| | Chief Executive Officer |
Exhibit 31.2
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
RULES 13a-14(a) AND 15d-14(a) UNDER THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Ajay Madan Gopal, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this Form-10K of The RealReal, Inc.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant's other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant's disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant's internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant's most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant's fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant's internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The registrant's other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant's auditors and the audit committee of the registrant's board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant's ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant's internal control over financial reporting.
| | | | | | | | |
| Date: February 21, 2025 | By: | /s/Ajay Madan Gopal |
| | Ajay Madan Gopal |
| | Chief Financial Officer |
Exhibit 32.1
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350, AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of The RealReal, Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the period ending December 31, 2024 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. § 1350, as adopted pursuant to § 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1) The Report fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2) The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and result of operations of the Company.
| | | | | | | | |
| Date: February 21, 2025 | By: | /s/ Rati Sahi Levesque |
| | Rati Sahi Levesque |
| | Chief Executive Officer |
Exhibit 32.2
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350, AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of The RealReal, Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the period ending December 31, 2024 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. § 1350, as adopted pursuant to § 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1)The Report fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2)The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and result of operations of the Company.
| | | | | | | | |
| Date: February 21, 2025 | By: | /s/ Ajay Madan Gopal |
| | Ajay Madan Gopal |
| | Chief Financial Officer |
v3.25.0.1
Cover Page - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Feb. 14, 2025 |
Jun. 28, 2024 |
| Cover [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Document Type |
10-K
|
|
|
| Document Annual Report |
true
|
|
|
| Document Period End Date |
Dec. 31, 2024
|
|
|
| Current Fiscal Year End Date |
--12-31
|
|
|
| Document Transition Report |
false
|
|
|
| Entity File Number |
001-38953
|
|
|
| Entity Incorporation, State or Country Code |
DE
|
|
|
| Entity Tax Identification Number |
45-1234222
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line One |
55 Francisco Street
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line Two |
Suite 150
|
|
|
| Entity Address, City or Town |
San Francisco
|
|
|
| Entity Address, State or Province |
CA
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Postal Zip Code |
94133
|
|
|
| City Area Code |
855
|
|
|
| Local Phone Number |
435-5893
|
|
|
| Title of 12(b) Security |
Common stock, $0.00001 par value
|
|
|
| Trading Symbol |
REAL
|
|
|
| Security Exchange Name |
NASDAQ
|
|
|
| Entity Well-known Seasoned Issuer |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Voluntary Filers |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Current Reporting Status |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Interactive Data Current |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Filer Category |
Accelerated Filer
|
|
|
| Entity Small Business |
true
|
|
|
| Entity Emerging Growth Company |
false
|
|
|
| Auditor Attestation Flag |
true
|
|
|
| Document Financial Statement Error Correction Flag |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Shell Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Public Float |
|
|
$ 314,689,544
|
| Entity Common Stock, Shares Outstanding |
|
111,246,608
|
|
| Documents Incorporated by Reference |
Part III incorporates information by reference from the definitive proxy statement for the registrant’s 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
|
|
|
| Entity Registrant Name |
TheRealReal, Inc.
|
|
|
| Entity Central Index Key |
0001573221
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Year Focus |
2024
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Period Focus |
FY
|
|
|
| Amendment Flag |
false
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.
| Name: |
dei_AmendmentFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnd date of current fiscal year in the format --MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_CurrentFiscalYearEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gMonthDayItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as an annual report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentAnnualReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates whether any of the financial statement period in the filing include a restatement due to error correction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection w
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFinStmtErrorCorrectionFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFiscal period values are FY, Q1, Q2, and Q3. 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarter 10-Q or 10-QT statements have value Q1, Q2, and Q3 respectively, with 10-K, 10-KT or other fiscal year statements having FY.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalPeriodFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fiscalPeriodItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis is focus fiscal year of the document report in YYYY format. For a 2006 annual report, which may also provide financial information from prior periods, fiscal 2006 should be given as the fiscal year focus. Example: 2006.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalYearFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gYearItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as a transition report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Forms 10-K, 10-Q, 20-F
-Number 240
-Section 13
-Subsection a-1
| Name: |
dei_DocumentTransitionReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:submissionTypeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDocuments incorporated by reference. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-23
| Name: |
dei_DocumentsIncorporatedByReferenceTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 1 such as Attn, Building Name, Street Name
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 2 such as Street or Suite number
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressCityOrTown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCode for the postal or zip code
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressPostalZipCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the state or province.
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressStateOrProvince |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:stateOrProvinceItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityCentralIndexKey |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:centralIndexKeyItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate number of shares or other units outstanding of each of registrant's classes of capital or common stock or other ownership interests, if and as stated on cover of related periodic report. Where multiple classes or units exist define each class/interest by adding class of stock items such as Common Class A [Member], Common Class B [Member] or Partnership Interest [Member] onto the Instrument [Domain] of the Entity Listings, Instrument.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' whether registrants (1) have filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that registrants were required to file such reports), and (2) have been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCurrentReportingStatus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate if registrant meets the emerging growth company criteria. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityEmergingGrowthCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommission file number. The field allows up to 17 characters. The prefix may contain 1-3 digits, the sequence number may contain 1-8 digits, the optional suffix may contain 1-4 characters, and the fields are separated with a hyphen.
| Name: |
dei_EntityFileNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fileNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate whether the registrant is one of the following: Large Accelerated Filer, Accelerated Filer, Non-accelerated Filer. Definitions of these categories are stated in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityFilerCategory |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:filerCategoryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTwo-character EDGAR code representing the state or country of incorporation.
| Name: |
dei_EntityIncorporationStateCountryCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarStateCountryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-T
-Number 232
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityInteractiveDataCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter.
| Name: |
dei_EntityPublicFloat |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityRegistrantName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant is a shell company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityShellCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates that the company is a Smaller Reporting Company (SRC). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntitySmallBusiness |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Tax Identification Number (TIN), also known as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), is a unique 9-digit value assigned by the IRS. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityTaxIdentificationNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:employerIdItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
| Name: |
dei_EntityVoluntaryFilers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Is used on Form Type: 10-K, 10-Q, 8-K, 20-F, 6-K, 10-K/A, 10-Q/A, 20-F/A, 6-K/A, N-CSR, N-Q, N-1A. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Securities Act
-Number 230
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityWellKnownSeasonedIssuer |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_IcfrAuditorAttestationFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLocal phone number for entity.
| Name: |
dei_LocalPhoneNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTitle of a 12(b) registered security. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b
| Name: |
dei_Security12bTitle |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:securityTitleItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the Exchange on which a security is registered. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection d1-1
| Name: |
dei_SecurityExchangeName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarExchangeCodeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTrading symbol of an instrument as listed on an exchange.
| Name: |
dei_TradingSymbol |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:tradingSymbolItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionPCAOB issued Audit Firm Identifier Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorFirmId |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:nonemptySequenceNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorLocation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Balance Sheets - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Current assets |
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ 172,212
|
$ 175,709
|
| Accounts receivable |
13,961
|
17,226
|
| Inventory, net |
23,583
|
22,246
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
22,913
|
20,766
|
| Total current assets |
232,669
|
235,947
|
| Property and equipment, net |
94,443
|
104,087
|
| Operating lease right-of-use assets |
75,714
|
86,348
|
| Restricted cash |
14,911
|
14,914
|
| Other assets |
5,358
|
5,627
|
| Total assets |
423,095
|
446,923
|
| Current liabilities |
|
|
| Accounts payable |
11,004
|
8,961
|
| Accrued consignor payable |
89,718
|
77,122
|
| Operating lease liabilities, current portion |
22,835
|
20,094
|
| Convertible senior notes, net, current portion |
26,653
|
0
|
| Other accrued and current liabilities |
98,466
|
82,685
|
| Total current liabilities |
248,676
|
188,862
|
| Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion |
85,790
|
104,856
|
| Convertible senior notes, net |
276,807
|
452,421
|
| Non-convertible notes, net |
134,470
|
0
|
| Warrant liability |
78,584
|
0
|
| Other noncurrent liabilities |
6,144
|
4,083
|
| Total liabilities |
830,471
|
750,222
|
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) |
|
|
| Stockholders’ deficit: |
|
|
| Common stock, $0.00001 par value; 500,000,000 shares authorized as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023; 111,242,479 and 104,670,500 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively |
1
|
1
|
| Additional paid-in capital |
846,450
|
816,325
|
| Accumulated deficit |
(1,253,827)
|
(1,119,625)
|
| Total stockholders’ deficit |
(407,376)
|
(303,299)
|
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit |
$ 423,095
|
$ 446,923
|
| X |
- DefinitionWarrant Liability, Noncurrent
| Name: |
real_WarrantLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableNetCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable, pertaining to costs that are statutory in nature, are incurred on contractual obligations, or accumulate over time and for which invoices have not yet been received or will not be rendered. Examples include taxes, interest, rent and utilities. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of excess of issue price over par or stated value of stock and from other transaction involving stock or stockholder. Includes, but is not limited to, additional paid-in capital (APIC) for common and preferred stock. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdditionalPaidInCapital |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset recognized for present right to economic benefit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(12))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Assets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset recognized for present right to economic benefit, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRepresents the caption on the face of the balance sheet to indicate that the entity has entered into (1) purchase or supply arrangements that will require expending a portion of its resources to meet the terms thereof, and (2) is exposed to potential losses or, less frequently, gains, arising from (a) possible claims against a company's resources due to future performance under contract terms, and (b) possible losses or likely gains from uncertainties that will ultimately be resolved when one or more future events that are deemed likely to occur do occur or fail to occur. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingencies |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable common stock (or common stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable common shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of the carrying value of long-term convertible debt as of the balance sheet date that is scheduled to be repaid within one year or in the normal operating cycle if longer. Convertible debt is a financial instrument which can be exchanged for a specified amount of another security, typically the entity's common stock, at the option of the issuer or the holder. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConvertibleDebtCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying amount of long-term convertible debt as of the balance sheet date, net of the amount due in the next twelve months or greater than the normal operating cycle, if longer. The debt is convertible into another form of financial instrument, typically the entity's common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConvertibleDebtNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after valuation and LIFO reserves of inventory expected to be sold, or consumed within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liability recognized for present obligation requiring transfer or otherwise providing economic benefit to others. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(26))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
| Name: |
us-gaap_Liabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities and equity items, including the portion of equity attributable to noncontrolling interests, if any. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(32))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesAndStockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal obligations incurred as part of normal operations that are expected to be paid during the following twelve months or within one business cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-5
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of notes payable (with maturities initially due after one year or beyond the operating cycle if longer), excluding current portion. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermNotesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncurrent assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due after one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset related to consideration paid in advance for costs that provide economic benefits in future periods, and amount of other assets that are expected to be realized or consumed within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PrepaidExpenseAndOtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478451/942-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash restricted as to withdrawal or usage, classified as noncurrent. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-SubTopic 210
-Topic 954
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477220/954-210-45-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCashNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Balance Sheets (Parenthetical) - $ / shares
|
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Statement of Financial Position [Abstract] |
|
|
| Common stock, par value (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.00001
|
$ 0.00001
|
| Common stock, shares authorized (in shares) |
500,000,000
|
500,000,000
|
| Common stock, shares issued (in shares) |
111,242,479
|
104,670,500
|
| Common stock, shares, outstanding (in shares) |
111,242,479
|
104,670,500
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfFinancialPositionAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Statements of Operations - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
$ 600,484
|
$ 549,304
|
$ 603,493
|
| Cost of revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
152,963
|
173,026
|
254,802
|
| Gross profit |
447,521
|
376,278
|
348,691
|
| Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
| Marketing |
55,256
|
58,275
|
62,988
|
| Operations and technology |
260,827
|
257,041
|
278,628
|
| Selling, general and administrative |
187,737
|
183,793
|
195,342
|
| Restructuring |
196
|
43,462
|
896
|
| Total operating expenses |
504,016
|
542,571
|
537,854
|
| Loss from operations |
(56,495)
|
(166,293)
|
(189,163)
|
| Change in fair value of warrant liability |
(68,167)
|
0
|
0
|
| Gain on extinguishment of debt |
4,177
|
0
|
0
|
| Interest income |
7,943
|
8,805
|
3,191
|
| Interest expense |
(21,384)
|
(10,701)
|
(10,472)
|
| Other income, net |
0
|
0
|
171
|
| Loss before provision for income taxes |
(133,926)
|
(168,189)
|
(196,273)
|
| Provision for income taxes |
276
|
283
|
172
|
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ (134,202)
|
$ (168,472)
|
$ (196,445)
|
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic (in dollars per share) |
$ (1.24)
|
$ (1.65)
|
$ (2.05)
|
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, diluted (in dollars per share) |
$ (1.24)
|
$ (1.65)
|
$ (2.05)
|
| Shares used to compute net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic (in shares) |
107,878,366
|
101,806,000
|
95,921,246
|
| Shares used to compute net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, diluted (in shares) |
107,878,366
|
101,806,000
|
95,921,246
|
| Consignment revenue |
|
|
|
| Revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
$ 473,396
|
$ 415,572
|
$ 384,979
|
| Cost of revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
53,801
|
58,120
|
56,963
|
| Direct revenue |
|
|
|
| Revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
64,580
|
79,160
|
158,726
|
| Cost of revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
55,809
|
74,343
|
141,661
|
| Shipping services revenue |
|
|
|
| Revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
62,508
|
54,572
|
59,788
|
| Cost of revenue: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
$ 43,353
|
$ 40,563
|
$ 56,178
|
| X |
- DefinitionOperations and technology expense.
| Name: |
real_OperationsAndTechnologyExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate cost of goods produced and sold and services rendered during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfRevenue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfRevenueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense (income) related to adjustment to fair value of warrant liability. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 13
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 480
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481766/480-10-25-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAdjustmentOfWarrants |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDifference between the fair value of payments made and the carrying amount of debt which is extinguished prior to maturity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainsLossesOnExtinguishmentOfDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate revenue less cost of goods and services sold or operating expenses directly attributable to the revenue generation activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 9: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
| Name: |
us-gaap_GrossProfit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest expense classified as nonoperating. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpenseNonoperating |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accretion (amortization) of purchase discount (premium) of interest income on nonoperating securities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(7)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentIncomeInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionExpenditures for planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services. Costs of public relations and corporate promotions are typically considered to be marketing costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_MarketingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of tax, noncontrolling interests, dividends on preferred stock and participating securities; of income (loss) available to common shareholders. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.B)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-5
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGenerally recurring costs associated with normal operations except for the portion of these expenses which can be clearly related to production and included in cost of sales or services. Includes selling, general and administrative expense.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpensesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of income (expense) related to nonoperating activities, classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNonoperatingIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4.b.1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482047/420-10-45-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenuesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total costs related to selling a firm's product and services, as well as all other general and administrative expenses. Direct selling expenses (for example, credit, warranty, and advertising) are expenses that can be directly linked to the sale of specific products. Indirect selling expenses are expenses that cannot be directly linked to the sale of specific products, for example telephone expenses, Internet, and postal charges. General and administrative expenses include salaries of non-sales personnel, rent, utilities, communication, etc. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ServiceMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ProductMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ShippingAndHandlingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Statements of Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Total |
Cumulative Effect, Period of Adoption, Adjustment |
Common Stock |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Additional Paid-in Capital
Cumulative Effect, Period of Adoption, Adjustment
|
Accumulated Deficit |
Accumulated Deficit
Cumulative Effect, Period of Adoption, Adjustment
|
| Beginning balance (in shares) at Dec. 31, 2021 |
|
|
92,960,066
|
|
|
|
|
| Beginning balance at Dec. 31, 2021 |
$ 73,128
|
$ (98,632)
|
$ 1
|
$ 841,255
|
$ (112,052)
|
$ (768,128)
|
$ 13,420
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options (in shares) |
|
|
1,929,265
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options |
2,906
|
|
|
2,906
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes (in shares) |
|
|
3,587,964
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes |
(216)
|
|
|
(216)
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP (in shares) |
|
|
610,877
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP |
1,400
|
|
|
1,400
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
47,767
|
|
|
47,767
|
|
|
|
| Net loss |
(196,445)
|
|
|
|
|
(196,445)
|
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Dec. 31, 2022 |
|
|
99,088,172
|
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Dec. 31, 2022 |
(170,092)
|
|
$ 1
|
781,060
|
|
(951,153)
|
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options (in shares) |
|
|
8,511
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options |
19
|
|
|
19
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes (in shares) |
|
|
4,708,141
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes |
(690)
|
|
|
(690)
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP (in shares) |
|
|
865,676
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP |
886
|
|
|
886
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
35,050
|
|
|
35,050
|
|
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (168,472)
|
|
|
|
|
(168,472)
|
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Dec. 31, 2023 |
104,670,500
|
|
104,670,500
|
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Dec. 31, 2023 |
$ (303,299)
|
|
$ 1
|
816,325
|
|
(1,119,625)
|
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Settlement of capped calls |
396
|
|
|
396
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options (in shares) |
|
|
136,658
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options |
376
|
|
|
376
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes (in shares) |
|
|
5,868,967
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld for employee taxes |
(1,646)
|
|
|
(1,646)
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP (in shares) |
|
|
566,354
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock for exercises under ESPP |
1,413
|
|
|
1,413
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
29,586
|
|
|
29,586
|
|
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (134,202)
|
|
|
|
|
(134,202)
|
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Dec. 31, 2024 |
111,242,479
|
|
111,242,479
|
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Dec. 31, 2024 |
$ (407,376)
|
|
$ 1
|
$ 846,450
|
|
$ (1,253,827)
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase to additional paid-in capital (APIC) for recognition of cost for award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-13
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToAdditionalPaidInCapitalSharebasedCompensationRequisiteServicePeriodRecognitionValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in additional paid in capital (APIC) resulting from the issuance of warrants. Includes allocation of proceeds of debt securities issued with detachable stock purchase warrants. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Section 25
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481284/470-20-25-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToAdditionalPaidInCapitalWarrantIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInStockholdersEquityRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued during the period as a result of an employee stock purchase plan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesEmployeeStockPurchasePlans |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued during the period related to Restricted Stock Awards, net of any shares forfeited. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesRestrictedStockAwardNetOfForfeitures |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of share options (or share units) exercised during the current period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate change in value for stock issued during the period as a result of employee stock purchase plan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueEmployeeStockPurchasePlan |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue of stock related to Restricted Stock Awards issued during the period, net of the stock value of such awards forfeited. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueRestrictedStockAwardNetOfForfeitures |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue of stock issued as a result of the exercise of stock options. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates amendment to accounting standards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476173/280-10-65-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476173/280-10-65-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-9
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-9
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-9
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-1
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479832/842-10-65-8
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 50
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477123/405-50-65-1
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482477/820-10-65-13
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482477/820-10-65-13
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-5
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-5
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-5
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 38: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 39: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479845/805-20-65-3
Reference 40: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479845/805-20-65-3
Reference 41: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479845/805-20-65-3
Reference 42: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 43: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 44: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 45: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 46: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 47: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 48: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 49: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 50: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 51: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 52: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 53: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 54: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 55: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 56: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 57: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 58: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 59: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 60: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 61: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (d)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-8
Reference 62: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 63: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 64: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 65: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 66: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 67: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 68: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 69: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 70: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 71: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 72: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 73: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 74: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 75: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 76: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 77: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 78: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476166/350-60-65-1
Reference 79: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476166/350-60-65-1
Reference 80: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingStandardsUpdateExtensibleList |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
enum2:enumerationSetItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfStockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Statements of Cash Flows - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
|
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (134,202)
|
$ (168,472)
|
$ (196,445)
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
|
|
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
33,100
|
31,695
|
27,669
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
29,082
|
34,273
|
46,138
|
| Reduction of operating lease right-of-use assets |
15,192
|
16,746
|
19,602
|
| Bad debt expense |
2,498
|
1,962
|
1,680
|
| Non-cash interest expense |
8,684
|
0
|
0
|
| Issuance costs allocated to liability classified warrants |
374
|
0
|
0
|
| Accretion of debt discounts and issuance costs |
2,127
|
2,573
|
2,368
|
| Property, plant, equipment, and right-of-use asset impairments |
0
|
39,739
|
0
|
| Provision for inventory write-downs and shrinkage |
2,590
|
9,783
|
4,077
|
| Gain on debt extinguishment |
(4,177)
|
0
|
0
|
| Change in fair value of warrant liability |
68,167
|
0
|
0
|
| Loss related to warehouse fire, net |
740
|
0
|
0
|
| Other adjustments |
(165)
|
(515)
|
702
|
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
| Accounts receivable |
767
|
(6,981)
|
(6,120)
|
| Inventory, net |
(3,677)
|
10,938
|
23,971
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
701
|
2,001
|
(2,952)
|
| Other assets |
76
|
(3,050)
|
(409)
|
| Operating lease liability |
(20,883)
|
(26,478)
|
(17,764)
|
| Accounts payable |
910
|
(425)
|
4,947
|
| Accrued consignor payable |
11,470
|
(4,421)
|
10,501
|
| Other accrued and current liabilities |
13,090
|
(464)
|
(9,823)
|
| Other noncurrent liabilities |
382
|
(172)
|
301
|
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
26,846
|
(61,268)
|
(91,557)
|
| Cash flow from investing activities: |
|
|
|
| Insurance proceeds related to warehouse fire |
461
|
0
|
0
|
| Capitalized proprietary software development costs |
(11,800)
|
(12,951)
|
(14,061)
|
| Purchases of property and equipment |
(14,248)
|
(29,177)
|
(22,861)
|
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(25,587)
|
(42,128)
|
(36,922)
|
| Cash flow from financing activities: |
|
|
|
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
376
|
19
|
2,906
|
| Proceeds from issuance of stock in connection with the Employee Stock Purchase Program |
1,413
|
886
|
1,400
|
| Taxes paid related to restricted stock vesting |
(1,646)
|
(679)
|
(205)
|
| Cash received from settlement of capped calls in conjunction with the 2024 Note Exchange |
396
|
0
|
0
|
| Issuance costs paid related to the 2024 Note Exchange |
(5,298)
|
0
|
0
|
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
(4,759)
|
226
|
4,101
|
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
(3,500)
|
(103,170)
|
(124,378)
|
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
|
|
|
| Beginning of period |
190,623
|
293,793
|
418,171
|
| End of period |
187,123
|
190,623
|
293,793
|
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information |
|
|
|
| Cash paid for interest |
10,680
|
8,127
|
8,104
|
| Cash paid for income taxes |
200
|
227
|
256
|
| Supplemental disclosures of non-cash investing and financing activities |
|
|
|
| Property and equipment additions not yet paid in cash |
1,818
|
1,757
|
13,860
|
| Capitalized proprietary software development costs not yet paid in cash |
654
|
1,122
|
1,590
|
| Stock-based compensation capitalized to proprietary software development costs |
504
|
777
|
1,629
|
| Liability classified warrants issued in connection with the 2024 Note Exchange |
10,417
|
0
|
0
|
| Net decrease in principal amount of debt due to the 2024 Note Exchange |
(17,232)
|
0
|
0
|
| Tax withholding liability for restricted stock |
$ 0
|
$ 11
|
$ 11
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccretion of debt discounts and issuance costs.
| Name: |
real_AccretionOfDebtDiscountsAndIssuanceCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPurchases of capitalized proprietary software development costs included in accounts payable and other accrued and current liabilities.
| Name: |
real_CapitalizedProprietarySoftwareDevelopmentCostsAdditionsNotYetPaidInCash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncrease (decrease) in accrued consignor payable.
| Name: |
real_IncreaseDecreaseInAccruedConsignorPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIssuance of Warrant Liability, Issuance Costs
| Name: |
real_IssuanceOfWarrantLiabilityIssuanceCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionReduction of operating lease right of use assets.
| Name: |
real_ReductionOfOperatingLeaseRightOfUseAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTax Withholding Liability For Restricted Stock
| Name: |
real_TaxWithholdingLiabilityForRestrictedStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToReconcileNetIncomeLossToCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of write-down of assets recognized in the income statement. Includes, but is not limited to, losses from tangible assets, intangible assets and goodwill. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetImpairmentCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFuture cash outflow to pay for purchases of fixed assets that have occurred. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_CapitalExpendituresIncurredButNotYetPaid |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage. Excludes amount for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsIncludingDisposalGroupAndDiscontinuedOperationsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; including effect from exchange rate change. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 230
-Topic 830
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477401/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsPeriodIncreaseDecreaseIncludingExchangeRateEffect |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashFlowNoncashInvestingAndFinancingActivitiesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe value of the financial instrument(s) that the original debt is being converted into in a noncash (or part noncash) transaction. "Part noncash" refers to that portion of the transaction not resulting in cash receipts or cash payments in the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtConversionConvertedInstrumentAmount1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of the original debt being converted in a noncash (or part noncash) transaction. "Part noncash" refers to that portion of the transaction not resulting in cash receipts or cash payments in the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtConversionOriginalDebtAmount1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense recognized in the current period that allocates the cost of tangible assets, intangible assets, or depleting assets to periods that benefit from use of the assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationDepletionAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost capitalized for award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationAllocationOfRecognizedPeriodCostsCapitalizedAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense (income) related to adjustment to fair value of warrant liability. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 13
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 480
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481766/480-10-25-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAdjustmentOfWarrants |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDifference between the fair value of payments made and the carrying amount of debt which is extinguished prior to maturity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainsLossesOnExtinguishmentOfDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate amount of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in amount due within one year (or one business cycle) from customers for the credit sale of goods and services. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsReceivable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate value of all inventory held by the reporting entity, associated with underlying transactions that are classified as operating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInInventories |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingCapitalAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in obligation for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in other expenses incurred but not yet paid. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOtherAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in current assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOtherCurrentAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in noncurrent operating liabilities classified as other.
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOtherNoncurrentLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in prepaid expenses, and assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInPrepaidDeferredExpenseAndOtherAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash paid for interest, excluding capitalized interest, classified as operating activity. Includes, but is not limited to, payment to settle zero-coupon bond for accreted interest of debt discount and debt instrument with insignificant coupon interest rate in relation to effective interest rate of borrowing attributable to accreted interest of debt discount. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestPaidNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of loss from reductions in inventory due to subsequent measurement adjustments, including, but not limited to, physical deterioration, obsolescence, or changes in price levels. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryWriteDown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe charge against earnings in the period for the uninsured portion of a loss from a fire, explosion, or natural disaster (hurricane, earthquake). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_LossFromCatastrophes |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from financing activities, including discontinued operations. Financing activity cash flows include obtaining resources from owners and providing them with a return on, and a return of, their investment; borrowing money and repaying amounts borrowed, or settling the obligation; and obtaining and paying for other resources obtained from creditors on long-term credit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from investing activities, including discontinued operations. Investing activity cash flows include making and collecting loans and acquiring and disposing of debt or equity instruments and property, plant, and equipment and other productive assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities, including discontinued operations. Operating activity cash flows include transactions, adjustments, and changes in value not defined as investing or financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of income (expense) included in net income that results in no cash inflow (outflow), classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNoncashIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionInterest paid other than in cash for example by issuing additional debt securities. As a noncash item, it is added to net income when calculating cash provided by or used in operations using the indirect method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaidInKindInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow associated with the development, modification or acquisition of software programs or applications for internal use (that is, not to be sold, leased or otherwise marketed to others) that qualify for capitalization. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForSoftware |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow paid to third parties in connection with debt origination, which will be amortized over the remaining maturity period of the associated long-term debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsOfDebtIssuanceCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow associated with the acquisition of long-lived, physical assets that are used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale; includes cash outflows to pay for construction of self-constructed assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquirePropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow provided by derivative instruments during the period, which are classified as financing activities, excluding those designated as hedging instruments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 23
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-23
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromDerivativeInstrumentFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow for proceeds from settlement of insurance claim, classified as investing activities. Excludes insurance settlement classified as operating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-12
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 21B
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-21B
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromInsuranceSettlementInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow from exercise of option under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2A
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow associated with the amount received from the stock plan during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromStockPlans |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense (reversal of expense) for expected credit loss on accounts receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479319/326-20-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProvisionForDoubtfulAccounts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncash expense for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Description of Business and Basis of Presentation
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Organization, Consolidation and Presentation of Financial Statements [Abstract] |
|
| Description of Business and Basis of Presentation |
Description of Business and Basis of Presentation Organization and Description of Business The RealReal, Inc. (the “Company”) is an online marketplace for authenticated, consigned luxury goods across multiple categories, including women’s fashion, men’s fashion, and jewelry and watches. The Company was incorporated in the state of Delaware on March 29, 2011 and is headquartered in San Francisco, California. Basis of Presentation The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and, in the opinion of management, reflect all adjustments necessary to state fairly the Company’s financial position, results of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the periods presented. For the years ended 2024, 2023, and 2022, comprehensive loss is equal to net loss as the Company has no other comprehensive income (loss) item in the periods presented. The Company’s functional and reporting currency is the U.S. dollar. The Company has made a presentation change to the Company's statements of operations to reclassify its legal settlements expense to selling, general, and administrative expenses. Additionally, the Company has made a presentation change to reclassify loss on disposal of property and equipment, impairment of capitalized proprietary software, and gain on lease termination to other adjustments within operating cash flows in the statements of cash flows. Changes to reclassify amounts in the prior periods have been made to conform to the current period presentation.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for the business description and basis of presentation concepts. Business description describes the nature and type of organization including but not limited to organizational structure as may be applicable to holding companies, parent and subsidiary relationships, business divisions, business units, business segments, affiliates and information about significant ownership of the reporting entity. Basis of presentation describes the underlying basis used to prepare the financial statements (for example, US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, Other Comprehensive Basis of Accounting, IFRS). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/235/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 275
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/275/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/205/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessDescriptionAndBasisOfPresentationTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies Use of Estimates The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period. Significant items subject to such estimates and assumptions include those related to revenue recognition, including the returns reserve, standalone selling price related to consignment revenue transactions, valuation of inventory, software development costs, stock-based compensation, fair value of warrant liability, initial fair value of non-convertible notes issued as part of the 2024 Note Exchange (see Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net), incremental borrowing rates related to lease liability, valuation of deferred taxes, and other contingencies. The Company evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors and adjusts those estimates and assumptions when facts and circumstances dictate. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Net Loss per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders The Company follows the two-class method when computing net loss per common share when shares are issued that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method determines net loss per common share for each class of common stock and participating securities according to dividends declared or accumulated and participation rights in undistributed earnings. The two-class method requires income (loss) available or attributable to common stockholders for the period to be allocated between common stock and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive dividends as if all income for the period had been distributed. The Company’s convertible senior notes are participating securities as they give the holders the right to receive dividends if dividends or distributions declared to the common stockholders is equal to or greater than the last reported sale price of the Company’s common stock on the trading day immediately preceding the ex-dividend date for such dividend or distribution as if the instruments had been converted into shares of common stock. No undistributed earnings were allocated to the participating securities as the contingent event is not satisfied as of the reporting date. For periods in which the Company reports net losses, diluted net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders is the same as basic net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders, because potentially dilutive common shares and assumed conversion of the convertible senior notes are not assumed to have been issued within the calculation, if their effect is anti-dilutive. Segments The Company has one operating segment and one reportable segment as its chief operating decision maker, who is its Chief Executive Officer, reviews financial information on a consolidated basis for purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance. All long-lived assets are located in the United States and substantially all revenue is attributed to consignors and buyers based in the United States. Revenue Recognition The Company generates revenue from the sale of pre-owned luxury goods through its online marketplace and retail stores. Revenue is recognized upon transfer of control of promised products or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for those products or services. The Company enters into contracts that include products and services that are capable of being distinct and accounted for as separate performance obligations as described below. The transaction price requires an allocation across consignment services, sales of Company-owned inventory, and shipping services. Estimation is required in the determination of the services' stand-alone selling price (“SSP”). Consignment Revenue The Company provides a service to sell pre-owned luxury goods on behalf of consignors to buyers through its online marketplace and retail stores. The Company retains a percentage of the proceeds received as payment for its consignment service, which the Company refers to as its take rate. SSP is estimated using observable stand-alone consignment sales which are conducted without shipping services. The Company reports consignment revenue on a net basis as an agent and not the gross amount collected from the buyer. Title to the consigned goods remains with the consignor until transferred to the buyer upon purchase of the consigned goods and expiration of the allotted return period. The Company does not take title of consigned goods at any time except in certain cases where returned goods become Company-owned inventory. The Company recognizes consignment revenue upon purchase of the consigned good by the buyer as its performance obligation of providing consignment services to the consignor is satisfied at that point. Consignment revenue is recognized net of estimated returns, cancellations, buyer incentives and adjustments. The Company recognizes a returns reserve based on historical experience, which is recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets (see Note 5). Sales tax assessed by governmental authorities is excluded from revenue. Certain transactions provide consignors with a material right resulting from the tiered consignor commission plan. Under this plan, the amount an individual consignor receives for future sales of consigned goods may be dependent on previous consignment sales for that consignor within his/her consignment period. Accordingly, in certain consignment transactions, a small portion of the Company’s consignment revenue is allocated to such material right using the portfolio method and recorded as deferred revenue, which is recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets. The impact of the deferral has not been material to the financial statements. The Company also generates subscription revenue from monthly memberships allowing buyers early access to shop for luxury goods. The buyers receive the early access and other benefits over the term of the subscription period, which represents a single stand-ready performance obligation. Therefore, the subscription fees paid by the buyer are recognized over the monthly subscription period. Subscription revenue was not material in 2024, 2023, and 2022. Direct Revenue The Company generates direct revenue from the sale of Company-owned inventory. The Company recognizes direct revenue on a gross basis upon shipment of the purchased good to the buyer as the Company acts as the principal in the transaction. SSP is estimated using observable stand-alone sales of Company-owned inventory which are conducted without shipping services, when available, or a market assessment approach. Direct revenue is recognized net of estimated returns, buyer incentives and adjustments. Sales tax assessed by governmental authorities is excluded from revenue. Cost of direct revenue is also recognized upon shipment to the buyer in an amount equal to that paid to the consignor from the original consignment sale, an amount equal to that paid as a direct purchase from a third party, or the lower of cost of the inventory purchased and its net realizable value. Shipping Services Revenue The Company provides a service to ship purchased items to buyers and a service to ship items from buyers back to the Company. The Company determines itself to be the principal in this arrangement. The Company charges a fee to buyers for this service and has elected to treat shipping and handling activities performed as a separate performance obligation. For shipping services revenue, the Company's SSP is estimated using a market approach considering external and internal data points on the stand-alone sales price of the shipping service. All outbound shipping and handling costs for buyers are accounted for as cost of shipping services and recognized as the shipping activity occurs. The Company also generates shipping services revenue from the shipping fees for consigned products returned by buyers to the Company within policy. The Company recognizes shipping revenue and associated costs over time as the shipping activity occurs, which is generally one to three days after shipment. Incentives Incentives, which include platform-wide discounts and buyer incentives, may periodically be offered to buyers. Platform-wide discounts are made available to all buyers on the online marketplace. Buyer incentives apply to specific buyers and consist of coupons or promotions that offer credits in connection with purchases on the Company’s platform, and do not impact the commissions paid to consignors. These are treated as a reduction of consignment revenue and direct revenue. Additionally, the Company periodically offers commission exceptions to the standard consignment rates to consignors to optimize its supply. These are treated as a reduction of consignment revenue at the time of sale. The Company may offer a certain type of buyer incentive in the form of site credits to buyers on current transactions to be applied towards future transactions, which are included in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets. Contract Liabilities The Company’s contractual liabilities primarily consist of deferred revenue for material rights primarily related to the tiered consignor commission plan, which are recognized as revenue using a portfolio approach based on the pattern of exercise, and certain buyer incentives. Contract liabilities are recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets and are generally expected to be recognized within one year. Contract liabilities were immaterial as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023. Cost of Revenue Cost of consignment revenue consists of credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and consignor inventory adjustments relating to lost or damaged products. Cost of direct revenue consists of the cost of goods sold, credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and inventory adjustments. Cost of shipping services revenue consists of the outbound shipping and handling costs to deliver purchased items to buyers, the shipping costs for consigned products returned by buyers to the Company within policy, and an allocation of the credit card fees associated with the shipping fee charged. Marketing Marketing expense is comprised of the cost of acquiring new consignors and buyers for our online platform and physical stores, including the cost of television, digital and direct mail advertising. Marketing expense also includes personnel-related costs, including stock-based compensation, of employees engaged in these activities. Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and were $42.9 million, $48.4 million, and $49.0 million in 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively. Operations and Technology Operations and technology expense is comprised of costs associated with the authentication, merchandising and fulfillment of goods sold through our online marketplace and retail stores, as well as general information technology expense. The principal component of operations and technology expense is personnel-related costs, including stock-based compensation, of employees engaged in these activities. Operations and technology expense also includes allocated facility and overhead costs, costs related to our retail stores, facility supplies, inbound consignment shipping costs, and depreciation of hardware and equipment, as well as research and development expense for technology associated with managing and improving our operations. In 2024, 2023, and 2022, the Company capitalized proprietary software developments costs of $11.8 million, $13.3 million, and $15.6 million, respectively. As such, operations and technology expense also includes amortization of capitalized technology development costs, which is taken on straight-line basis over three years once the technology is ready for its intended use. Selling, General and Administrative Selling, general and administrative expense is principally comprised of the personnel-related costs for employees involved in sales, finance and administration, and includes stock-based compensation expense. Selling, general and administrative expense also includes allocated facility and overhead costs and professional services, including accounting and legal advisors. Stock-based Compensation The Company incurs stock-based compensation expense from stock options, restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance based restricted stock units (“PSUs”) subject to performance or market conditions, and employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”) purchase rights. Stock-based compensation expense related to employees and nonemployees is measured based on the grant-date fair value of the awards. The Company estimates the fair value of stock options granted and the purchase rights issued under the ESPP using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The fair value of RSUs is estimated based on the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant, which is determined based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock. Compensation expense is recognized in the statements of operations over the period during which the employee is required to perform services in exchange for the award (the vesting period of the applicable award) using the straight-line method for awards with only a service condition. To determine the grant-date fair value of the Company's stock-based payment awards for PSUs subject to performance conditions, the quoted stock price on the date of grant is used. The stock-based compensation expense for PSUs with performance conditions is recognized based on the estimated number of shares that the Company expects will vest and is adjusted on a quarterly basis using the estimated achievement of financial performance targets. For PSUs subject to market conditions, the grant-date fair value is determined using the Monte Carlo simulation model which utilizes multiple input variables to estimate the probability that market conditions will be achieved. These variables include the Company's expected stock price volatility over the expected term of the award, the risk-free interest rate for the expected term of the award, and expected dividends. For PSUs with market conditions, the stock-based compensation expense is recognized on a tranche by tranche basis over the requisite service period using the fair value derived from the Monte Carlo simulation model. The compensation expense will be recognized regardless of whether the market condition is ever satisfied, provided the requisite service period is satisfied. For all awards, the Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur. Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less from the purchase date to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents primarily consist of investments in short-term money market funds. Restricted cash consists of cash deposited with a financial institution as collateral for the Company’s letters of credit for its facility leases and the Company’s credit cards. The Company had $14.9 million in restricted cash as of December 31, 2024 and 2023. The following table provides a reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash for the year ended December 31, 2024 that sum to the total of the same amounts shown in the statements of cash flows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | 175,709 | | | $ | 293,793 | | | Restricted cash | 14,911 | | | 14,914 | | | — | | | Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 187,123 | | | $ | 190,623 | | | $ | 293,793 | |
Accounts Receivable Accounts receivables are recorded at the amounts billed to buyers and do not bear interest. Accounts receivables result from credit card transactions, the majority of which are settled within two business days. Inventory, Net Inventory consists of finished goods arising from goods returned after the title has transferred from the buyer to the Company as well as finished goods from direct purchases from vendors and consignors. The cost of inventory is an amount equal to that paid to the consignor or vendors. Inventory is valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value using the specific identification method and the Company records provisions, as appropriate, to write down obsolete and excess inventory to estimated net realizable value. After the inventory value is reduced, adjustments are not made to increase it from the estimated net realizable value. Additionally, inventory is recorded net of an allowance for shrinkage which represents the risk of physical loss of inventory. Provisions for inventory shrinkage are estimated based on historical experience and are adjusted based upon physical inventory counts. Provisions to write down inventory to net realizable value and provisions for inventory shrinkage were $2.6 million and $9.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Return reserves, which reduce revenue and cost of sales, are estimated using historical experience. Liabilities for return allowances are included in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets and were $22.4 million and $22.2 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023. Included in inventory on the Company’s balance sheets are assets totaling $4.8 million and $5.2 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, for the rights to recover products from customers associated with its liabilities for return reserves. Property and Equipment, Net Property and equipment, net is recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. Repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. The estimated useful lives of our assets are as follows: | | | | | | | Proprietary software | 3 years | | Furniture and equipment | 3-5 years | | Vehicles | 5 years | | Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life |
Software Development Costs Proprietary software includes the costs of developing the Company’s internal proprietary business platform and automation projects. The Company capitalizes qualifying proprietary software development costs that are incurred during the application development stage. Capitalization of costs begins when two criteria are met: (1) the preliminary project stage is completed and (2) it is probable that the software will be completed and used for its intended function. Such costs are capitalized in the period incurred. Capitalization ceases and amortization begins when the software is substantially complete and ready for its intended use, including the completion of all significant testing. Costs related to preliminary project activities and post-implementation operating activities are expensed as incurred. Impairment of Long-lived Assets The carrying amounts of long-lived assets, including right-of-use assets, property and equipment, net and capitalized proprietary software, are periodically reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable or that the useful life is shorter than originally estimated. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by comparing the carrying amount of assets to future undiscounted net cash flows the assets are expected to generate over their remaining life. If the assets are considered to be impaired, the amount of any impairment is measured as the difference between the carrying value and the fair value of the impaired assets. If the useful life is shorter than originally estimated, the Company amortizes the remaining carrying value over the revised shorter useful life. Leases Contracts that have been determined to convey the right to use an identified asset are evaluated for classification as an operating or finance lease. For the Company’s operating leases, the Company records a lease liability based on the present value of the lease payments at lease inception, using the applicable incremental borrowing rate. The Company estimates the incremental borrowing rate by developing its own synthetic credit rating, corresponding yield curve, and the terms of each lease at the lease commencement date. The corresponding right-of-use asset is recorded based on the corresponding lease liability at lease inception, adjusted for payments made to the lessor at or before the commencement date, initial direct costs incurred and any tenant incentives allowed for under the lease. The Company does not include optional renewal terms or early termination provisions unless the Company is reasonably certain such options would be exercised at the inception of the lease. Operating lease right-of-use assets, current portion of operating lease liabilities, and operating lease liabilities, net of current portion are included on the Company’s balance sheet. The Company has elected the practical expedients that allows for the combination of lease components and non-lease components and to record short-term leases as lease expense on a straight-line basis on the statements of operations. Variable lease payments are recorded as expense as they are incurred. The Company has finance leases for vehicles and equipment, and the amounts of finance lease right-of-use assets and finance lease liabilities have been immaterial to date. Convertible Senior Notes, Net Prior to the adoption of ASU 2020-06 on January 1, 2022, convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash or other assets, or partially in cash, upon conversion, were separately accounted for as long-term debt and equity components (or conversion feature). The debt component represented the Company’s contractual obligation to pay principal and interest and the equity component represented the Company’s option to convert the debt security into equity of the Company or the equivalent amount of cash. Upon issuance, the Company allocated the debt component on the basis of the estimated fair value of a similar liability that does not have an associated convertible feature and the remaining proceeds are allocated to the equity component. The bifurcation of the debt and equity components resulted in a debt discount for the aforementioned notes. The Company uses the effective interest method to amortize the debt discount to interest expense over the amortization period which is the expected life of the debt. Following the adoption of ASU 2020-06, there is no bifurcation of the liability and equity components of the 3.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2025 (the “2025 Notes”) and the 1.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2028 (the “2028 Notes” and, together with the 2025 Notes, the “Notes”), and the entire principal of the Notes are accounted for as debt. Debt The Company initially recognizes incurred debt, net of any discounts, premiums and issuance costs related to the debt offering. All debt issuance costs are presented as a direct deduction from the related principal debt amounts on the balance sheet. Debt obligations due within 12 months are classified as current liabilities. Debt discounts, premiums and issuance costs are amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt using the effective interest method. When multiple instruments are issued in the same transaction, the Company allocates any issuance costs to the instruments on the same basis as the allocation of proceeds. Issuance costs allocated to instruments measured at fair value are expensed in the period incurred. Capped Call Transactions In June 2020 and March 2021, in connection with the issuance of its convertible senior notes, the Company entered into capped call transactions (see Note 7 - Convertible Senior Notes, Net). The capped call transactions are expected generally to reduce the potential dilution to the holders of the Company’s common stock upon any conversion of the convertible senior notes and/or offset any cash payments the Company is required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted convertible senior notes, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap based on the cap price. The Capped Calls (as defined below) are classified in stockholders’ equity as a reduction to additional paid-in capital and are not subsequently remeasured as long as the conditions for equity classification continue to be met. The Company monitors the conditions for equity classification, which continue to be met as of December 31, 2024. Debt Issuance Costs Debt issuance costs, which consist of direct incremental legal, consulting, banking and accounting fees related to the anticipated debt offering, are amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt based on the effective interest method. The Company presents debt issuance costs on the balance sheets as a direct deduction from the associated debt. The Company adopted ASU 2020-06 as of January 1, 2022 using the modified retrospective method. Prior to the adoption of ASU 2020-06 on January 1, 2022, a portion of debt issuance costs incurred in connection with the convertible senior notes issued in June 2020 and March 2021 was allocated to the equity component and was recorded as a reduction to additional paid in capital and was not amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt. Following the adoption of ASU 2020-06, the debt issuance costs previously allocated to the equity component of both series of Notes were reclassified to debt. As such, all of the debt issuance costs are recorded as a direct deduction from the related principal debt amounts on the balance sheet, and are all amortized to interest expense over the estimated remaining life of the related debt. Income Taxes Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in loss in the period of enactment. The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. Concentrations of Credit Risks Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and accounts receivable. At times, such amount may exceed federally-insured limits. The Company is closely monitoring ongoing events involving limited liquidity, defaults, non-performance or other adverse developments that affect financial institutions or other companies in the financial services industry or the financial services industry generally. The Company reduces credit risk by placing its cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and investments with major financial institutions with high credit ratings within the United States. The Company has not experienced any realized losses on cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash to date; however, no assurances can be provided. As of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there were no customers that represented 10% or more of the Company’s accounts receivable balance and there were no customers that individually exceeded 10% of the Company’s total revenue for each of the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022. Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures requires disclosures about significant segment expenses that are regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The Company adopted the standard during the year ended December 31, 2024 and applied it retrospectively to the periods presented. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company's financial statements. Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures. This new guidance is designed to enhance the transparency and decision usefulness of income tax disclosures. The amendments of this update are related to the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid, requiring (1) consistent categories and greater disaggregation of information in the rate reconciliation and (2) income taxes paid disaggregated by jurisdiction. ASU 2023-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements. In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-03, Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses, which requires companies to disclose in the notes to the financial statements the disaggregation of certain expense categories included within the income statement expense captions. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2027 on a prospective basis with optional retrospective application. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements. In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-04, Debt with Conversion and Other Options. This new guidance is designed to clarify requirements for determining whether certain settlements of convertible debt instruments should be accounted for as an induced conversion. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2025 and for interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for all significant accounting policies of the reporting entity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/235/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SignificantAccountingPoliciesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Cash and Cash Equivalents
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents [Abstract] |
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and Cash Equivalents The following tables summarize the estimated value of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents (in thousands) and do not include restricted cash. There are no unrealized gains or losses related to the restricted cash balance. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | Amortized Cost | | Unrealized Gain | | Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value | | Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | Cash | $ | 24,870 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 24,870 | | Money market funds | 147,342 | | | — | | | — | | | 147,342 | | | Total cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 172,212 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | Amortized Cost | | Unrealized Gain | | Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value | | Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | Cash | $ | 50,947 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 50,947 | | Money market funds | 124,762 | | | — | | | — | | | 124,762 | | | Total cash and cash equivalents | $ | 175,709 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 175,709 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure of the components of cash, cash equivalents, and short-term investments. Short-term investments may include current marketable securities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 320
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/320/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsAndShortTermInvestmentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Fair Value Measurement
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Fair Value Disclosures [Abstract] |
|
| Fair Value Measurement |
Fair Value Measurement Assets and liabilities recorded at fair value on a recurring basis on the balance sheets are categorized based upon the level of judgment associated with the inputs used to measure their fair values. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or an exit price that would be paid to transfer a liability in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The authoritative guidance on fair value measurements establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy for disclosure of fair value measurements as follows: Level 1—Observable inputs such as unadjusted, quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities at the measurement date. Level 2—Inputs (other than quoted prices included in Level 1) are either directly or indirectly observable for the asset or liability. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active. Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. There were no transfers between Level 1, Level 2 or Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy during the periods presented. Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis The following table sets forth the Company's financial instruments on the balance sheet that were measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the period indicated by level within the fair value hierarchy (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | | | | | | | | Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Money market funds | $ | 147,342 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 147,342 | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | 147,342 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 147,342 | | | | | | | | | | Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Warrants | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 78,584 | | | $ | 78,584 | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 78,584 | | | $ | 78,584 | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2023, the Company held $124.8 million in money market funds. Such amounts are considered Level 1 and the Company held no other assets or liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis. Fair Value Measurements of Other Financial Instruments The following table presents the carrying amounts and estimated fair values of the financial instruments that are not recorded at fair value on the balance sheets (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | Net Carrying Amount | | Estimated Fair Value | | Net Carrying Amount | | Estimated Fair Value | | 2025 Convertible senior notes | $ | 26,653 | | | $ | 26,493 | | | $ | 170,564 | | | $ | 128,219 | | | 2028 Convertible senior notes | $ | 276,807 | | | $ | 216,291 | | | $ | 281,857 | | | $ | 99,978 | | 2029 Non-convertible notes | $ | 134,470 | | | $ | 140,889 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
The principal amounts of the 2025 Notes, the 2028 Notes and the 2029 Notes are $26.7 million, $281.0 million, and $137.9 million, respectively. The difference between the principal amounts of such notes and their respective net carrying amounts are the unamortized debt issuance costs and debt premiums. As of December 31, 2024, the fair value of the 2025 Notes, the 2028 Notes and the 2029 Notes, which differs from their carrying value, is determined based on the quoted bid prices of such notes in an over-the counter market using the latest trading information of the reporting period. Fair Value Measurement of Warrants In connection with the 2024 Note Exchange (defined in Note 6 – Non-convertible Notes, Net), the Company issued warrants (the "Warrants") to acquire an aggregate of up to 7,894,737 shares (subject to adjustment in accordance with the terms of the Warrants) of the Company’s common stock to the holders of the Exchanged Notes at an exercise price of $1.71, subject to certain cashless exercise provisions and adjustment in accordance with the terms of the Warrants. The Warrants are exercisable from the date of issuance until they expire on March 1, 2029. The Warrants are accounted for as liabilities under ASC 480 since the warrants may be required to be settled in cash in case of a fundamental change, which could occur outside of the Company’s control. Changes in fair value are recognized within change in fair value of warrant liability on the Company’s statements of operations. Issuance costs allocated to the Warrants are included in selling, general and administrative on the Company’s statements of operations. The aggregate fair value of the Warrants upon issuance and as of December 31, 2024 was $10.4 million and $78.6 million, respectively, determined using a Black-Scholes Model with the following inputs: | | | | | | | | | | | | | On issuance | | December 31, 2024 | | Stock price | $1.77 | | $10.93 | | Exercise price | $1.71 | | $1.71 | Expected life in years | 5.00 | | 4.17 | Expected volatility | 94.84 | % | | 96.75 | % | Expected dividends | — | % | | — | % | Discount rate | 4.26 | % | | 4.38 | % |
The following table presents the activity related to the Warrants during the year ended December 31, 2024. | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | Opening balance | $ | — | | | Issuance of warrants | 10,417 | | | Change in fair value | 68,167 | | Balance as of December 31, 2024 | $ | 78,584 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueDisclosuresAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for the fair value of financial instruments (as defined), including financial assets and financial liabilities (collectively, as defined), and the measurements of those instruments as well as disclosures related to the fair value of non-financial assets and liabilities. Such disclosures about the financial instruments, assets, and liabilities would include: (1) the fair value of the required items together with their carrying amounts (as appropriate); (2) for items for which it is not practicable to estimate fair value, disclosure would include: (a) information pertinent to estimating fair value (including, carrying amount, effective interest rate, and maturity, and (b) the reasons why it is not practicable to estimate fair value; (3) significant concentrations of credit risk including: (a) information about the activity, region, or economic characteristics identifying a concentration, (b) the maximum amount of loss the entity is exposed to based on the gross fair value of the related item, (c) policy for requiring collateral or other security and information as to accessing such collateral or security, and (d) the nature and brief description of such collateral or security; (4) quantitative information about market risks and how such risks are managed; (5) for items measured on both a recurring and nonrecurring basis information regarding the inputs used to develop the fair value measurement; and (6) for items presented in the financial statement for which fair value measurement is elected: (a) information necessary to understand the reasons for the election, (b) discussion of the effect of fair value changes on earnings, (c) a description of [similar groups] items for which the election is made and the relation thereof to the balance sheet, the aggregate carrying value of items included in the balance sheet that are not eligible for the election; (7) all other required (as defined) and desired information. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 107
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-107
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-6A
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2E
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6A
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-6A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6A
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-6A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6A
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-6A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6A
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-6A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 940
-SubTopic 820
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478119/940-820-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueDisclosuresTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Balance Sheet Components
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Balance Sheet Related Disclosures [Abstract] |
|
| Balance Sheet Components |
Balance Sheet Components Property and Equipment, Net Property and equipment, net is recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. Property and equipment, net consists of the following (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 | Proprietary software | $ | 47,416 | | | $ | 44,964 | | Furniture and equipment | 51,959 | | | 47,389 | | Automobiles | 2,036 | | | 2,069 | | Leasehold improvements | 88,840 | | | 84,138 | | | Property and equipment, gross | 190,251 | | | 178,560 | | | Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (95,808) | | | (74,473) | | | Property and equipment, net | $ | 94,443 | | | $ | 104,087 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense on property and equipment was $32.7 million, $31.0 million, and $26.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company recorded $8.6 million of impairment of leasehold improvements and disposal of fixed assets related to the closures of several of its office and retail locations as part of the savings plan the Company implemented. The impairment charges are included in restructuring in the statements of operations. The Company did not record impairment of leasehold improvements or disposal of fixed assets related to the savings plan during the year ended December 31, 2024. Other Accrued and Current Liabilities Other accrued and current liabilities consist of the following (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 | | Returns reserve | $ | 22,409 | | | $ | 22,204 | | | Accrued compensation | 24,749 | | | 20,086 | | | Accrued sales tax and other taxes | 9,727 | | | 8,118 | | Site credit and gift card liability | 15,542 | | | 14,058 | | | Accrued marketing and outside services | 6,403 | | | 5,012 | | | Accrued shipping | 3,270 | | | 4,244 | | | Accrued interest | 4,996 | | | 1,166 | | | Deferred revenue | 2,441 | | | 2,214 | | | Other | 8,929 | | | 5,583 | | | Other accrued and current liabilities | $ | 98,466 | | | $ | 82,685 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for supplemental balance sheet disclosures, including descriptions and amounts for assets, liabilities, and equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/210/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SupplementalBalanceSheetDisclosuresTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Non-convertible Notes, Net
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Non-convertible Notes, Net |
Non-convertible Notes, Net 2024 Note Exchange On February 29, 2024 (the “Closing Date”), the Company entered into exchange agreements with certain holders (the “Exchange Holders”) of its 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes to exchange (i) $145.8 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2025 Notes and (ii) $6.5 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes (together, the “Exchanged Notes”) for $135.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the Company’s 4.25%/8.75% PIK/Cash Senior Secured Notes due 2029 (the “2029 Notes”), pursuant to an indenture (the “2024 Note Exchange”). The 2029 Notes bear interest at a rate of 13.00% per annum, consisting of cash interest at a rate of 8.75% per annum payable semi-annually in arrears and payment in-kind (“PIK”) interest at a rate of 4.25% per annum payable semi-annually. During the year ended December 31, 2024, $2.9 million was added to the principal amounts outstanding due to accrued PIK interest. The 2029 Notes will mature on the earlier of (a) March 1, 2029 and (b) any date, if any, on or after December 1, 2027 on which (a) the aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes then outstanding is greater than $20 million and (b) the difference between (i) the amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held by the Company and its subsidiaries (if any) as of such date of determination and (ii) the aggregate principal amount of 2028 Notes outstanding as of such date of determination is less than $75 million. In connection with the 2024 Note Exchange, the Company issued the Warrants (see Note 4 – Fair Value Measurement for further details on the terms of the Warrants). As a result of the 2024 Note Exchange, the Company’s principal debt balance decreased $17.2 million. As the terms of the 2029 Notes were deemed to have substantially different terms from the Exchanged Notes, the 2024 Note Exchange was accounted for as an extinguishment of the Exchanged Notes. In connection with debt extinguishment accounting, the Company recorded a gain of $4.2 million as the difference between the carrying amount of the Exchanged Notes and the fair value of the 2029 Notes. Included in the recorded gain are unamortized debt discounts and issuance costs related to the Exchanged Notes and the fair value of the Warrants as they represent fees paid to the Exchange Holders as part of the 2024 Note Exchange. The Company allocated issuance costs to the Warrants and the 2029 Notes based on relative fair value. The Company allocated $0.4 million of issuance costs to the Warrants with the balance being allocated to the 2029 Notes. Issuance costs related to the 2029 Notes are being amortized to interest expense through the expected maturity of the 2029 Notes at an effective interest rate of 13.35%. The indenture governing the 2029 Notes contains certain covenants, which include (i) a covenant by the Company not to permit liquidity (calculated as the sum of (a) unused commitments then available to be drawn under any revolving credit facility, delayed draw term loan facility or qualified securitization financing permitted thereunder (after giving effect to any borrowing base or similar limitations), plus (b) the amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held by the Company and its subsidiaries (if any)) to be less than $25 million as of the last day of any month, (ii) limitations on the Company’s and certain of its future subsidiaries’ (if any) ability to, among other things, (a) grant or incur liens securing indebtedness, (b) incur assume or guarantee additional indebtedness, (c) enter into transactions with affiliates, (d) sell or otherwise dispose of assets, including capital stock of subsidiaries, (e) make certain restricted payments or other investments, or (f) pay dividends or make other distributions (including loans and other advances and (iii) limitations, in the case of the Company and any future guarantor (if any), to consolidate, amalgamate or merge with or into, or sell all or substantially all of its assets to, another person. As of December 31, 2024 the Company was in compliance with all covenants. The indenture governing the 2029 Notes sets forth certain events of default after which the 2029 Notes may be declared immediately due and payable and sets forth certain types of bankruptcy or insolvency events of default involving the Company or its subsidiaries. The 2029 Notes are guaranteed by certain of the Company’s future wholly-owned domestic subsidiaries (if any) on a senior secured basis. The 2029 Notes and the guarantees (if any), together with any future indebtedness secured on a pari passu basis with the 2029 Notes and the guarantees (if any), are secured by a first priority lien on substantially all of the assets of the Company and the guarantors (if any), subject to certain exceptions. On or after March 1, 2025, the Company may redeem the 2029 Notes at its option, in whole at any time or in part from time to time, at the following redemption prices (expressed as percentages of principal amount) plus accrued and unpaid interest, to, but excluding, the applicable redemption date (subject to the right of holders of record of the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date), if redeemed during the following periods: March 1, 2025 to (but excluding) March 1, 2026 - 113.0%; March 1, 2026 to (but excluding) October 1, 2026 - 106.5%; and October 1, 2026 and thereafter - 100.0%. In addition, prior to March 1, 2025, the Company may redeem the 2029 Notes at its option, in whole at any time or in part from time to time, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 2029 Notes redeemed plus the applicable premium as of, and accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the applicable redemption date (subject to the right of holders of record of the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date). Notwithstanding the foregoing, at any time and from time to time on or prior to March 1, 2025, the Company may redeem in the aggregate up to 40% of the original aggregate principal amount of the 2029 Notes (calculated after giving effect to the issuance of any PIK payments) with the net proceeds of one or more equity offerings to the extent the net cash proceeds thereof are contributed to the common equity capital of the Company or are used to purchase capital stock (other than disqualified stock) of the Company, at a redemption price of 113.0%, plus accrued and unpaid interest, to, but excluding, the applicable redemption date (subject to the right of holders of record on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date), provided at least 60% of the original aggregate principal amount of the 2029 Notes (calculated after giving effect to any PIK payments) remains outstanding after each such redemption. A schedule of the Company's future maturities for the 2029 Notes with interest components included in principal, is as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | Amount | | Fiscal Year | | 2029 Notes | 2025 through 2028 | | $ | — | | 2029 | | 166,631 | | Total expected payments at maturity | | 166,631 | | Less unamortized debt issuance costs and debt premium, net | | (3,430) | | Less amounts related to PIK interest | | (28,730) | | Net carrying amount | | $ | 134,470 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for information about short-term and long-term debt arrangements, which includes amounts of borrowings under each line of credit, note payable, commercial paper issue, bonds indenture, debenture issue, own-share lending arrangements and any other contractual agreement to repay funds, and about the underlying arrangements, rationale for a classification as long-term, including repayment terms, interest rates, collateral provided, restrictions on use of assets and activities, whether or not in compliance with debt covenants, and other matters important to users of the financial statements, such as the effects of refinancing and noncompliance with debt covenants. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-6
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477092/405-40-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477092/405-40-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477092/405-40-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477092/405-40-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477092/405-40-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 10: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 470
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/470/tableOfContent
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Convertible Senior Notes, Net
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Convertible Senior Notes, Net |
Convertible Senior Notes, Net In June 2020, the Company issued an aggregate principal of $172.5 million of its 2025 Notes, pursuant to an indenture, in a private offering to qualified institutional buyers. The 2025 Notes will mature on June 15, 2025, unless earlier redeemed or repurchased by the Company or converted. In February 2024, certain of the 2025 Notes were extinguished in connection with the 2024 Note Exchange (see Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net). At issuance, the Company received net proceeds from the 2025 Notes offering of approximately $165.8 million, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and commission and offering expenses. The Company used approximately $22.5 million of the net proceeds from the 2025 Notes offering to fund the net cost of entering into the capped call transactions described below. The Company intends to use the remainder of the net proceeds for general corporate purposes. In March 2021, the Company issued an aggregate principal of $287.5 million of its 2028 Notes, pursuant to an indenture, in a private offering to qualified institutional buyers. The 2028 Notes will mature on March 1, 2028, unless earlier redeemed or repurchased by the Company or converted. In February 2024, certain of the 2028 Notes were extinguished in connection with the 2024 Note Exchange (see Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net). At issuance, the Company received net proceeds from the 2028 Notes offering of approximately $278.1 million, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and commission and offering expenses. The Company used approximately $33.7 million of the net proceeds from the 2028 Notes offering to fund the net cost of entering into the capped call transactions described below. The Company intends to use the remainder of the net proceeds for general corporate purposes. The 2025 Notes accrue interest at a rate of 3.00% per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning on December 15, 2020. The initial conversion rate applicable to the 2025 Notes is 56.2635 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of 2025 Notes (which is equivalent to an initial conversion price of approximately $17.77 per share of the Company’s common stock). The 2028 Notes accrue interest at a rate of 1.00% per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year, beginning on September 1, 2021. The initial conversion rate applicable to the 2028 Notes is 31.4465 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of 2028 Notes (which is equivalent to an initial conversion price of approximately $31.80 per share of the Company’s common stock). The conversion rate is subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of certain specified events but will not be adjusted for accrued and unpaid interest. In addition, upon the occurrence of a corporate event, the Company will, in certain circumstances, increase the conversion rate by a number of additional shares for a holder that elects to convert its 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes in connection with such corporate event. The 2025 Notes will be redeemable, in whole or in part, at the Company’s option at any time, and from time to time, on or after June 20, 2023, and the 2028 Notes will be redeemable, in whole or in part, at the Company's option at any time, and from time to time, on or after March 5, 2025, in each case if the last reported sale price per share of the Company’s common stock exceeds 130% of the conversion price then in effect for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive), including the trading day immediately preceding the date on which the Company provides notice of redemption, during any 30 consecutive trading day period ending on, and including, the trading day immediately before the date the Company sends the related redemption notice. In addition, calling any Note for redemption will constitute a make-whole fundamental change with respect to that Note, in which case the conversion rate applicable to the conversion of that Note will be increased in certain circumstances if it is converted after it is called for redemption. Prior to March 15, 2025, in the case of the 2025 Notes, and December 1, 2027, in the case of the 2028 Notes, the applicable Convertible Senior Notes will be convertible only under the following circumstances: •During any calendar quarter (and only during such calendar quarter), if, the last reported sale price per share of the Company’s common stock exceeds 130% of the applicable conversion price on each applicable trading day for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) in the period of the 30 consecutive trading day period ending on, and including, the last trading day of the immediately preceding calendar quarter; •During the five business day period after any five consecutive trading day period in which, for each day of that period, the trading price per $1,000 principal amount of 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes for such trading day was less than 98% of the product of the last reported sale price of the Company’s common stock and the applicable conversion rate on such trading day; •Upon the occurrence of specified corporate transactions; or •If the Company calls any 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes for redemption. On and after March 15, 2025, in the case of the 2025 Notes, and December 1, 2027, in the case of the 2028 Notes, until the close of business on the scheduled trading day immediately preceding the maturity date, holders may convert all or a portion of their 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes, in multiples of $1,000 principal amount, at any time, regardless of the foregoing circumstances. Upon conversion, the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes will be settled, at the Company’s election, in cash, shares of the Company’s common stock, or a combination of cash and shares of the Company’s common stock. It is the Company’s current intent to settle conversions of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes through combination settlement, which involves repayment of the principal portion in cash and any excess of the conversion value over the principal amount in shares of its common stock. The conditions allowing holders of either the 2025 Notes or the 2028 Notes to convert were not met as of December 31, 2024. The 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes are unsecured and unsubordinated obligations of the Company and will rank senior in right of payment to any of future indebtedness of the Company that is expressly subordinated in right of payment to the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes; rank equal in right of payment to any existing and future unsecured indebtedness of the Company that is not so subordinated; be effectively subordinated in right of payment to any secured indebtedness of the Company to the extent of the value of the assets securing such indebtedness; and be structurally subordinated to all existing and future indebtedness and other liabilities and obligations incurred by future subsidiaries of the Company. If bankruptcy, insolvency, or reorganization occurs with respect to the Company (and not solely with respect to a significant subsidiary of the Company), then the principal amount of, and all accrued and unpaid interest on, all of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes then outstanding will immediately become due and payable without any further action or notice by any person. If an event of default (other than bankruptcy, insolvency, or reorganization with respect to the Company and not solely with respect to a significant subsidiary of the Company) occurs and is continuing, then, with the exception of certain reporting events of default, the trustee, by notice to the Company, or noteholders of at least 25% of the aggregate principal amount of 2025 Notes or 2028 Notes, as applicable, then outstanding, by notice to us and the trustee, may declare the principal amount of, and all accrued and unpaid interest on, all of the 2025 Notes or 2028 Notes, as applicable, the outstanding to become due and payable immediately. The carrying amount of the 2025 Notes is $26.7 million as of December 31, 2024, with principal of $26.7 million, net of unamortized issuance costs of $0.1 million. The 2025 Notes were classified as short-term liabilities as of December 31, 2024. The issuance costs related to the 2025 Notes are being amortized to interest expense over the expected life of the 2025 Notes or approximately its five-year term at an effective interest rate of 3.74%. The carrying amount of the 2028 Notes is $276.8 million as of December 31, 2024, with principal of $281.0 million, net of unamortized issuance costs of $4.2 million. The 2028 Notes were classified as long term liabilities as of December 31, 2024. The issuance costs related to the 2028 Notes are being amortized to interest expense over the expected life of the 2028 Notes or approximately its seven-year term at an effective interest rate of 1.45%. The following table sets forth the amounts recorded in interest expense related to the 2025 Notes as of the dates indicated (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Contractual interest expense | $ | 1,531 | | | $ | 5,175 | | | $ | 5,175 | | | Amortization of debt issuance costs | 383 | | | 1,268 | | | 1,080 | | Total interest and amortization expense | $ | 1,914 | | | $ | 6,443 | | | $ | 6,255 | |
The following table sets forth the amounts recorded in interest expense related to the 2028 Notes as of the dates indicated (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Contractual interest expense | $ | 2,821 | | | $ | 2,875 | | | $ | 2,875 | | | Amortization of debt issuance costs | 1,308 | | | 1,305 | | | 1,288 | | Total interest and amortization expense | $ | 4,129 | | | $ | 4,180 | | | $ | 4,163 | |
A schedule of the Company's future maturities for the 2025 and 2028 Notes, is as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | Amount | | Fiscal Year | 2025 Notes | | 2028 Notes | 2025 | $ | 26,749 | | | $ | — | | 2026 | — | | | — | | 2027 | — | | | — | | 2028 | — | | | 281,019 | | Total principal payments | 26,749 | | | 281,019 | | Less unamortized debt issuance costs | (96) | | | (4,212) | | Net carrying amount | $ | 26,653 | | | $ | 276,807 | |
Capped Call Transactions with Respect to the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes In connection with the issuance of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes, including the initial purchasers’ exercise of the option to purchase additional Notes, the Company entered into capped call transactions with respect to its common stock with certain financial institutions (collectively, the “Counterparties”). The Company paid an aggregate amount of approximately $22.5 million to the Counterparties in connection with the 2025 capped call transactions (the “2025 Capped Calls”) and $33.7 million to the Counterparties in connection with the 2028 capped call transactions and (the “2028 Capped Calls” and, together with the 2025 Capped Calls, the “Capped Calls”). The 2025 Capped Calls and 2028 Capped Calls initially covered approximately 9,705,454 shares and 9,040,869 shares of the Company’s common stock at a strike price that corresponds to the initial conversion price of the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, respectively. The 2025 Capped Calls and the 2028 Capped Calls are subject to anti-dilution adjustments that are intended to be substantially identical to those in the 2025 Notes and the 2028 Notes, as applicable, and are exercisable upon conversion of the 2025 Notes or the 2028 Notes, as applicable. The Capped Calls are subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of specified extraordinary events affecting the Company, including merger events, tender offer and announcement events. In addition, the Capped Calls are subject to certain specified additional disruption events that may give rise to a termination of the Capped Calls, including nationalization, insolvency or delisting, changes in law, failures to deliver, insolvency filings and hedging disruptions. The 2025 Capped Calls settle in components commencing on April 16, 2025 with the last component scheduled to expire on June 12, 2025. The 2028 Capped Calls settle in components commencing on December 31, 2027 with the last component scheduled to expire on February 28, 2028. The cap price of the 2025 Capped Call is initially $27.88 per share, which represents a premium of 100.0% over the closing price of the Company’s common stock of $13.94 per share on June 10, 2020, and is subject to certain adjustments under the terms of the capped call transactions. The cap price of the 2028 Capped Call is initially $48.00 per share, which represents a premium of 100.0% over the closing price of the Company’s common stock of $24.00 per share on March 3, 2021, and is subject to certain adjustments under the terms of the capped call transactions. The Company expects to receive from the Counterparties a number of shares of the Company’s common stock or, at the Company’s election (subject to certain conditions), cash, with an aggregate market value (or, in the case of cash settlement, in an amount) approximately equal to the product of such excess times the number of shares of the Company’s common stock relating to the 2025 Capped Calls and 2028 Capped Calls being exercised. These Capped Call instruments meet the conditions outlined in ASC 815-40 to be classified in stockholders’ equity, are not accounted for as derivatives, and are not subsequently remeasured as long as the conditions for equity classification continue to be met. The Company recorded a reduction to additional paid-in capital of approximately $22.5 million and $33.7 million related to the premium payments for the 2025 Capped Call and 2028 Capped Call transactions. In connection with the 2024 Note Exchange, the Company received $0.4 million in cash in connection with settling certain Capped Calls. After giving effect to such settlements, the 2025 Capped Calls and 2028 Capped Calls outstanding cover approximately 1,504,992 and 8,837,095 shares of the Company's common stock, respectively. As the Capped Calls were equity classified, the proceeds from settlement of these Capped Calls were recorded to additional paid in capital.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for long-term debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 470
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/470/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Common Stock
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Common Stock [Abstract] |
|
| Common Stock |
Common Stock The Company had reserved shares of common stock for issuance, on an as-converted basis, as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 | | Options issued and outstanding | 917,370 | | | 1,119,676 | | | Outstanding restricted stock units | 14,305,562 | | | 12,695,176 | | | Shares available for grant under the 2019 equity incentive plan | 5,490,650 | | | 7,654,656 | | | Shares available for issuance under 2019 ESPP | 4,135,266 | | | 3,654,915 | | Warrants to purchase common stock | 7,894,737 | | | — | | Total | 32,743,585 | | | 25,124,423 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of common stock.
| Name: |
real_DisclosureOfCommonStockTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Share-based Compensation Plans
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| Share-based Compensation Plans |
Share-based Compensation Plans 2019 Equity Incentive Plan In connection with the Company’s initial public offering, the Company adopted the 2019 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2019 Plan”). The 2019 Plan allows the Company to grant stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units and performance awards to participants. Subject to the terms and conditions of the 2019 Plan, the initial number of shares authorized for grants under the 2019 Plan is 8,000,000. These available shares increase annually by an amount equal to the lesser of 8,000,000 shares, 5% of the number of shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31, or the number of shares determined by the Company’s board of directors. The Company’s board of directors approved an increase of shares available for grant under the 2019 Plan by 4,465,083 shares on May 5, 2021, by 4,648,003 shares on February 23, 2022, by 4,954,409 shares on February 13, 2023, and by 5,233,525 shares on February 20, 2024. Activity under the Company’s stock option plan is set forth below: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Number of
Options | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise
Price Per
Share | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(in thousands) | | Balances at December 31, 2023 | 1,119,676 | | | 7.79 | | | 4.2 | | $ | 15 | | | Options granted | — | | | — | | | | | | | Options exercised | (136,658) | | | 3.05 | | | | | | | Options cancelled | (65,648) | | | 8.53 | | | | | | | Balances at December 31, 2024 | 917,370 | | | 8.44 | | | 3.5 | | 3,445 | | | Options vested and exercisable— December 31, 2024 | 917,370 | | | 8.44 | | | 3.5 | | 3,445 | |
There were no stock options granted in 2024 and in 2023. The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $0.3 million, zero and $5.3 million, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised is the difference between the fair value of the underlying common stock on the date of exercise and the exercise price for in-the-money stock options. In February 2022, the Company granted PSUs with financial performance targets to certain employees of the Company. The number of shares of the Company's common stock issued upon settlement will depend on the achievement of financial metrics relative to the approved performance targets, and can range from 0% to 150% of the target amount. The PSUs are subject to continuous service with the Company and will vest after approximately three years. The PSUs are measured using the fair value at the date of grant. The compensation expense associated with PSUs is recognized based on the estimated number of shares that the Company expects will vest and may be adjusted based on interim estimates of performance against the performance condition. During the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company has not recognized stock-based compensation expense as attainment of financial performance targets is not considered probable. In March 2023, the Company granted PSUs under the 2019 Plan subject to the achievement of both market and service conditions to certain employees of the Company. The number of shares of the Company's common stock issued upon settlement will depend on the achievement of approved market conditions and continuous service with the Company. The PSUs are eligible to vest in three tranches over a five-year performance period. The PSUs are measured using the Monte Carlo simulation to obtain the fair value at the date of grant based on the probability that the market conditions will be met. The compensation expense associated with the PSUs is based on the fair value and is recognized over the requisite service period. The compensation expense will be recognized regardless of whether the market condition is ever satisfied, provided the requisite service period is satisfied. In March and October 2024, the Company granted PSUs with financial performance targets to certain employees of the Company. The number of shares of the Company's common stock issued upon settlement will depend on the achievement of financial metrics relative to the approved performance targets, and can range from 0% to 200% of the target amount. The PSUs are subject to continuous service with the Company and will vest after approximately three years from the grant date. The PSUs are measured using the fair value at the date of grant. The compensation expense associated with PSUs is recognized based on the estimated number of shares that the Company expects will vest and may be adjusted based on interim estimates of performance against the performance condition. Inducement Grants The Company granted stock-based awards outside of the 2019 Plan to the certain executives. These awards were granted as inducements material to their commencement of employment and entry into offer letters with the Company, in accordance with Nasdaq Listing Rule 5635(c)(4). The inducement pool consisted of a total of 5,625,000 shares of the Company's common stock, which includes (a) 2,050,000 shares of PSUs that are eligible to vest based on market and service conditions in four tranches over a five-year performance period and (b) 3,575,000 shares of RSUs generally subject to the same terms and conditions as grants that are made under the 2019 Plan. The unvested PSUs and RSUs held by the Company's former Chief Executive Officer John Koryl were forfeited upon his separation from the Company on October 28, 2024. The activity in the inducement pool is included in the summary of RSU activity table below. RSUs A summary of RSU activity for the year ended December 31, 2024 is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Number of
Shares | | Restricted Stock Units
Weighted-
Average Grant
Date Fair
Value | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value
(in thousands) | | Unvested December 31, 2023 | 12,695,176 | | | $ | 4.07 | | | $ | 25,517 | | | Granted | 13,109,475 | | | 3.33 | | | | | Vested | (6,312,012) | | | 4.56 | | | | | Forfeited | (5,187,077) | | | 3.23 | | | | | Unvested December 31, 2024 | 14,305,562 | | | $ | 3.48 | | | $ | 156,360 | |
Included in the table above for the year ended December 31, 2024 are 2,535,000 PSUs granted, 98,000 PSUs vested, and 1,979,678 PSUs forfeited. The weighted average grant date fair value per share of the PSUs granted, vested and forfeited in the year ended December 31, 2024 was $3.31, $1.63 and $2.53, respectively. The total fair value as of the respective vesting dates of RSUs that vested during the year ended December 31, 2024 was $21.7 million. Employee Stock Purchase Plan In connection with the Company’s initial public offering, the Company adopted the Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”). The Employee Stock Purchase Plan permits employees to purchase shares of common stock during six-month offering periods at a purchase price equal to the lesser of (1) 85% of the fair market value of a share of common stock on the first business day of such offering period and (2) 85% of the fair market value of a share of common stock on the last business day of such offering period. The initial number of shares of common stock that could be issued under the employee stock purchase plan was 1,750,000 shares. These available shares increase by an amount equal to the lesser of 1,750,000 shares, 1% of the number of shares of common stock outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31, or the number of shares determined by the Company’s board of directors. The Company's board of directors approved an increase in the shares available for grant under the ESPP by 893,016 shares on May 5, 2021, by 929,601 shares on February 23, 2022, by 990,882 shares on February 13, 2023, and by 1,046,705 shares on February 20, 2024. During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, employees purchased 566,354, 865,676, and 610,877 shares, respectively, at an average price of $2.49, $1.02 and $2.29, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, the Company had an immaterial amount of unrecognized stock-based compensation cost related to purchase rights under the employee stock purchase plan. Stock-based Compensation In determining the fair value of the stock-based awards, the Company uses the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and assumptions discussed below. Fair Value of Common Stock— The fair value of the shares of common stock has historically been determined by the Company’s board of directors as there was no public market for the common stock. Subsequent to our IPO, the fair value per share of common stock is the closing price of the Company’s common stock as reported on the applicable grant date. Expected Term —The expected term represents the period that the Company’s stock options are expected to be outstanding and is determined using the simplified method (based on the mid-point between the vesting date and the end of the contractual term) as the Company has concluded that its stock option exercise history does not provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term. Volatility —Because the Company was privately held and did not have an active trading market for its common stock for a sufficient period of time, the expected volatility was estimated based on the average volatility for comparable publicly-traded companies, over a period equal to the expected term of the stock option grants. Risk-free Rate —The risk-free rate assumption is based on the U.S. Treasury zero coupon issues in effect at the time of grant for periods corresponding with the expected term of the option. Dividends —The Company has never paid dividends on its common stock and does not anticipate paying dividends on common stock. Therefore, the Company uses an expected dividend yield of zero. The following assumptions were used to estimate the fair value of stock options granted in 2019, as there were no stock options granted in 2024, 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, 2019 | | Expected term (in years) | 5.0 – 6.1 | | Expected volatility | 44.2% – 47.8% | | Average risk-free rate | 1.9% – 2.6% | | Dividend yield | — |
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had approximately $43.3 million of unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to RSUs and PSUs, which the Company expects to recognize over the remaining weighted-average vesting period of approximately 2.2 years. As of December 31, 2024, the Company had no unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to options. Total stock-based compensation expense by function was as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Marketing | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,550 | | | $ | 2,209 | | | Operations and technology | 9,930 | | | 12,534 | | | 19,822 | | | Selling, general and administrative | 18,220 | | | 20,189 | | | 24,107 | | Total | $ | 29,082 | | | $ | 34,273 | | | $ | 46,138 | |
During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company recognized compensation expense of $1.0 million within selling, general and administrative associated with the modification of certain outstanding equity awards pursuant to the terms of the transition and separation agreement the Company entered into with its founder, Julie Wainwright, in connection with her resignation as Chief Executive Officer on June 6, 2022. During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company capitalized $0.5 million, $0.8 million, and $1.6 million of stock-based compensation expense to proprietary software, respectively.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/718/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisclosureOfCompensationRelatedCostsShareBasedPaymentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Leases
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| Leases |
Leases The Company leases its corporate offices, retail spaces and authentication centers under various noncancelable operating leases with terms ranging from one year to fifteen years. The Company recorded operating lease costs of $20.9 million, $22.8 million and $29.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company incurred $5.5 million, $5.2 million and $5.6 million of variable lease costs for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, which is comprised primarily of the Company’s proportionate share of operating expenses, property taxes and insurance. Due to the office and store closures in the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company reviewed its right-of-use assets for impairment. Impairment losses are measured and recorded for the excess of carrying value over its fair value, estimated based on expected future cash flows using discount rate and other quantitative and qualitative factors. As a result, the Company recorded $31.1 million related to the impairment of certain office and store right-of-use assets during the year ended December 31, 2023. No impairment charges were recorded during the year ended December 31, 2024. The impairment charges are included in restructuring in the statements of operations. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company entered into agreements to amend certain of its operating leases. The Company treated the lease termination amendments as lease modifications for accounting purposes as of the applicable effective dates of such terminations which resulted in a decrease of $7.7 million to the related lease liabilities, and a decrease of $1.4 million to the related right-of-use assets for the year ended December 31, 2023. The Company recorded a net gain on the lease terminations of $0.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The net gain on lease terminations is included in restructuring in the statements of operations. Maturities of operating lease liabilities by fiscal year for the Company’s operating leases are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | Fiscal Year | | Amount | | 2025 | | $ | 28,761 | | | 2026 | | 28,649 | | | 2027 | | 24,699 | | | 2028 | | 21,991 | | | 2029 | | 11,615 | | | Thereafter | | 8,822 | | | Total future minimum payments | | $ | 124,537 | | | Less: Imputed interest | | (15,912) | | | Present value of operating lease liabilities | | $ | 108,625 | |
Supplemental cash flow information related to the Company’s operating leases are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Operating cash flows used for operating leases | $ | 27,939 | | | $ | 34,118 | | | $ | 27,097 | | Operating lease assets obtained in exchange for operating lease liabilities (including remeasurement of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities due to lease modifications) | $ | 4,558 | | | $ | 6,272 | | | $ | 2,245 | |
The weighted average remaining lease term and discount rate for the Company’s operating leases are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | As of December 31, 2024 | | As of December 31, 2023 | | Weighted average remaining lease term | 4.6 years | | 5.5 years | | Weighted average discount rate | 6.2 | % | | 6.1 | % |
The Company has leases for certain vehicles and equipment that are classified as finance leases. The finance lease right-of-use asset and finance lease liabilities for these vehicle and equipment leases are immaterial as of December 31, 2024 and 2023.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for operating leases of lessee. Includes, but is not limited to, description of operating lease and maturity analysis of operating lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/842-20/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeasesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Restructuring
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Restructuring and Related Activities [Abstract] |
|
| Restructuring |
Restructuring In February 2023, the Company announced a savings plan to reduce its real estate presence and operating expenses through closure of certain retail and office locations and workforce reduction. For the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company recognized $43.5 million in restructuring which consisted of right-of-use asset impairment charge of $31.1 million, leasehold improvements impairment charge of $8.6 million, employee severance of $3.0 million, and other related charges of $1.5 million, partially offset by a $0.7 million gain on lease terminations. The Company recorded an immaterial amount of restructuring for the year ended December 31, 2024. The restructuring related charges were recorded on a separate line item in the Company's statements of operations.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for restructuring and related activities. Description of restructuring activities such as exit and disposal activities, include facts and circumstances leading to the plan, the expected plan completion date, the major types of costs associated with the plan activities, total expected costs, the accrual balance at the end of the period, and the periods over which the remaining accrual will be settled. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4.e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/420/tableOfContent
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringAndRelatedActivitiesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Commitments and Contingencies
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Commitments and Contingencies |
Commitments and Contingencies Fire at Secaucus, New Jersey Authentication Center In May 2024, the Company experienced a fire at one of its authentication centers in Secaucus, New Jersey. The damage was primarily limited to fixed assets, leasehold improvements, supplies, and consigned and owned inventories. The Company maintains property, cargo, general liability and business interruption insurance coverage. As of December 31, 2024, discussions with the insurance company are still ongoing. Based on the provisions of the Company’s insurance policies, the Company recorded insurance recoveries for fire related costs for which recovery was deemed probable. The Company recorded losses related to the fire, net of insurance recoveries, of $0.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2024 within Operations and Technology on the statements of operations. As of December 31, 2024, the Company recorded $2.5 million of insurance receivables within prepaid and other current assets on the balance sheet. The Company has received $3.9 million in payments from insurers towards its claims to cover immediate impacts of the fire. $3.4 million of the payments are included within net cash flows from operating activities and $0.5 million of the payments are included within net cash flows from investing activities in the statements of cash flows due to the nature of the advance insurance payments. Noncancelable Purchase Commitments Our contractual commitments primarily consist of software and other services in the ordinary course of business that are noncancellable with varying expiration dates through 2027. As of December 31, 2024, the future minimum payments under the Company’s noncancelable purchase commitments were as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | Year Ending December 31, | | Purchase
Commitments | | 2025 | | $ | 8,072 | | | 2026 | | 7,665 | | | 2027 | | 1,825 | | | 2028 | | — | | | 2029 | | — | | | Total future minimum payments | | $ | 17,562 | |
Contingencies From time to time, the Company is subject to, and it is presently involved in, litigation and other legal proceedings and from time to time, the Company receives inquiries from government agencies. Accounting for contingencies requires the Company to use judgment related to both the likelihood of a loss and the estimate of the amount or range of loss. The Company records a loss contingency when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company discloses material contingencies when a loss is not probable but reasonably possible.
On November 14, 2018, Chanel, Inc. sued the Company in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. The Complaint alleged federal and state law claims of trademark infringement, unfair competition, and false advertising. On February 1, 2019, Chanel, Inc. filed its First Amended Complaint that included substantially similar claims against the Company. On March 4, 2019, the Company filed a Motion to Dismiss the First Amended Complaint, which was granted in part and dismissed in part on March 30, 2020. The surviving claims against the Company include trademark infringement under 15 U.S.C. § 1114, false advertising under 15 U.S.C. § 1125, and unfair competition under New York common law. On May 29, 2020, the Company filed its Answer to the Amended Complaint. On November 3, 2020, the Company sought leave to amend its Answer to assert counterclaims against Chanel, Inc. for violations of the Sherman Act, 15 U.S.C. §§ 1 & 2, the Donnelly Act, N.Y. Gen. Bus. Law. § 340, and New York common law. The motion for leave to amend was granted on February 24, 2021. On February 25, 2021, the Company filed its First Amended Answer, Affirmative Defenses and Counterclaims against Chanel. The Company’s Counterclaims allege violations of the Sherman Act, 15 U.S.C. §§ 1 & 2, the Donnelly Act, N.Y. Gen. Bus. Law. § 340, and New York common law. On March 18, 2021, Chanel moved to dismiss the Company’s Counterclaims and moved to strike the Company’s unclean hands affirmative defense. Decisions on Chanel’s motion to dismiss and motion strike are pending. The parties agreed to a stay in April 2021 to engage in settlement discussions. After several mediation sessions, the parties were unable to reach a resolution, and the stay was lifted in November 2021. Chanel then sought a partial stay of discovery on the Company's counterclaims and unclean hands defense while Chanel's motion to dismiss and strike those claims are pending, and on March 10, 2022, the Court granted Chanel's request. The parties have continued to engage in fact discovery regarding Chanel's counterfeiting and false advertising claims against the Company. Fact discovery was scheduled to be completed by August 15, 2023. However, on July 19, 2023, the Court ordered a stay of the case at the parties’ request to enable the parties to attempt mediation again. The parties have continued to engage in settlement discussions facilitated by a mediator. The final outcome of this litigation, including our liability, if any, with respect to Chanel’s claims, is uncertain. An unfavorable outcome in this or similar litigation could adversely affect the Company’s business and could lead to other similar lawsuits. The Company is not able to predict or reasonably estimate the ultimate outcome or loss or range of possible losses relating to this claim.
Beginning on September 10, 2019, purported shareholder class action complaints were filed against the Company, its officers and directors and the underwriters of its IPO in the San Mateo Superior Court, Marin County Superior Court, and the United States District Court for the Northern District of California. On July 27, 2021, the Company reached an agreement in principle to settle the shareholder class action. On November 5, 2021, plaintiff filed the executed stipulation of settlement and motion for preliminary approval of the settlement with the federal court. On March 24, 2022, the court entered an order preliminarily approving the settlement. On July 28, 2022, the court entered an order finally approving the settlement and dismissing the case. The financial terms of the stipulation of settlement provide that the Company will pay $11.0 million within thirty (30) days of the later of preliminary approval of the settlement or plaintiff’s counsel providing payment instructions. The Company paid the settlement amount on March 29, 2022 with available resources and recorded approximately $11.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 under our Operating expenses as a Legal settlement. One of the plaintiffs in the Marin County case opted out of the federal settlement and is pursuing the claim in Marin County Superior Court. The stay of the state court case has been lifted, and the opt out plaintiff filed an amended complaint on October 31, 2022 alleging putative class claims under the Securities Act of 1933 (the “Securities Act”) on behalf of the two shareholders who opted out of the settlement and those who purchased stock from November 21, 2019 through March 9, 2020, based on purported new revelations. The claims are for alleged violations of Sections 11 and 15 of the Securities Act. On February 23, 2024, plaintiff filed a motion for class certification, which has been set for hearing on February 25, 2025. While the Company intends to defend vigorously against this litigation, there can be no assurance that the Company will be successful in its defense. For this reason, the Company cannot currently estimate the loss or range of possible losses it may experience in connection with this litigation. Indemnifications In the ordinary course of business, the Company may provide indemnifications of varying scope and terms to vendors, directors, officers and other parties with respect to certain matters including, but not limited to, losses arising out of the breach of such agreements, intellectual property infringement claims made by third parties and other liabilities relating to or arising from the Company's various services, or its acts or omissions. The Company has not incurred any material costs as a result of such indemnifications and have not accrued any liabilities related to such obligations in its financial statements.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for commitments and contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/405-30/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/450/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478522/954-440-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/440/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Income Taxes
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Income Taxes |
Income Taxes The components of the Company’s income tax provision consisted of (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Current: | | | | | | Federal | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | State | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | | | Total current tax expense | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | | | Deferred: | | | | | | Federal | — | | | — | | — | State | — | | | — | | — | | Total deferred tax expense | — | | | — | | | — | | | Total provision for income taxes | $ | 276 | | | $ | 283 | | | $ | 172 | |
The reconciliation of the Federal statutory income tax provision for the Company’s effective income tax provision (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | Tax at federal statutory rate | $ | (28,144) | | | $ | (35,290) | | | $ | (41,209) | | State taxes, net of federal effect | (7,627) | | | (9,554) | | | (11,257) | | | Stock-based compensation | 3,192 | | | 8,956 | | | 419 | | Non-deductible items | 1,988 | | | 504 | | | 524 | | | Tax credits | (169) | | | (531) | | | (563) | | | | | | | | Warrant liability fair value adjustment | 18,333 | | | — | | | — | | | Adoption of ASU 2020-06 | — | | | — | | | (28,045) | | Provision to return adjustments | (1,927) | | | 9,259 | | | — | | Valuation allowance | 14,651 | | | 26,501 | | | 80,254 | | | Other | (21) | | | 438 | | | 49 | | | Provision for income taxes | $ | 276 | | | $ | 283 | | | $ | 172 | |
The Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Deferred tax assets: | | | | Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 230,303 | | | $ | 232,259 | | Fixed assets and intangibles | 10,461 | | | 6,364 | | Capitalized research and development (1) | 18,679 | | | 13,835 | | Accruals and reserves | 18,685 | | | 12,477 | | | Stock options | 1,536 | | | 840 | | Operating lease liabilities | 29,424 | | | 33,683 | | | Capped calls | 15,011 | | | 15,065 | | | Convertible debt | — | | | 2,329 | | | Tax credits | 2,738 | | | 2,569 | | Other | 4,621 | | | — | | | Gross deferred tax assets | 331,458 | | | 319,421 | | Less: valuation allowance | (306,948) | | | (292,297) | | | Total deferred tax assets | 24,510 | | | 27,124 | | | Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | Operating lease right-of-use assets | (21,641) | | | (24,416) | | | | | | Other | (2,869) | | | (2,708) | | | Gross deferred tax liabilities | (24,510) | | | (27,124) | | | Net deferred tax assets | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
(1) Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, research and development costs are no longer fully deductible when incurred and are required to be capitalized and amortized for U.S. tax purposes effective January 1, 2022. The mandatory capitalization requirement increases our gross deferred tax assets, which are fully offset by the valuation allowance. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, the Company evaluates all available positive and negative evidence by considering whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be recognized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon future taxable income, future reversals of existing taxable temporary difference, taxable income in carryback years and tax-planning strategies. The Company believes it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets in the U.S. will not be realized; accordingly, a valuation allowance has been established against the Company's U.S. deferred tax assets. The net change in the valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023 was an increase of $14.7 million and an increase of $26.5 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company has a net operating loss carryforward of $861.8 million and $871.3 million for federal tax purposes, respectively, and $818.6 million and $817.5 million for state tax purposes, respectively. If not utilized, these losses will expire beginning in 2025 for state tax purposes. However, beginning in tax year 2018 and forward, the Federal law has changed such that net operating losses generated after December 31, 2017 may be carried forward indefinitely. Accordingly, $157.6 million of the federal net operating losses will begin to expire in 2033. However, $704.2 million of the federal net operating losses will not expire. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company has a credit carryforward of $4.7 million and $4.3 million for federal tax purposes, respectively, and $1.0 million for state tax purposes. If not utilized, these credits will expire beginning in 2041 for federal tax purposes and do not expire for state tax purposes. The Tax Reform Act of 1986 limits the use of net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards in certain situations where changes occur in the stock ownership of a company. During 2019, the Company analyzed whether any of the reported net operating losses would be limited because of these rules. Based on the analysis the Company believes $3.3 million of the Federal and $2.1 million of California net operating losses will not be available to offset future taxable income because of the limitation. The reported net operating losses have been adjusted based on this analysis. The Company files tax returns as prescribed by the tax laws of the jurisdictions in which it operates. In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by federal, state and local, jurisdictions, where applicable. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, all years generally remain open to examination. Additionally, net operating loss carryforwards are subject to examination by the Internal Revenue Service and the California Franchise Tax Board for up to three and four years, respectively, after utilization. Uncertain Income Tax Positions The following table reflects the changes to the Company's unrecognized tax benefits (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | Unrecognized tax benefits beginning balance | $ | 2,678 | | | $ | 1,525 | | Increases related to current year tax positions | 169 | | | 531 | | Increases related to prior year tax positions | — | | | 622 | | Unrecognized tax benefits ending balance | $ | 2,847 | | | $ | 2,678 | |
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company had unrecognized tax benefits of $2.8 million and $2.7 million, respectively, none of which, if recognized, would favorably impact the Company’s effective tax rate. The unrecognized tax benefits relate to federal and state research and development credits. The Company's policy is to include interest and penalties as a component to the statements of operations, however there were no associated interest and penalties during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023. The Company estimates that there will be no material changes in its uncertain tax positions in the next 12 months.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for income tax. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 231
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-231
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 270
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477891/740-270-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.5.Q1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-13
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/740/tableOfContent
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-14
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-21
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.C)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482603/740-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Earnings Per Share [Abstract] |
|
| Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders |
Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders A reconciliation of the numerator and denominator used in the calculation of the basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is as follows (in thousands, except share and per share data): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Numerator | | | | | | Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | | | Denominator | | | | | | Weighted-average common shares outstanding used to calculate net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | 107,878,366 | | | 101,806,000 | | | 95,921,246 | | Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (1.24) | | | $ | (1.65) | | | $ | (2.05) | |
The following securities were excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders for the periods presented, because including them would have been anti-dilutive (on an as-converted basis): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Options to purchase common stock | 917,370 | | | 1,119,676 | | | 1,754,776 | | | Restricted stock units | 14,305,562 | | | 12,695,176 | | | 11,369,021 | | | Estimated shares issuable under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 248,523 | | | 367,074 | | | 695,782 | | Assumed conversion of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes | 10,342,056 | | | 18,746,323 | | | 18,746,323 | | Warrants to purchase common stock | 7,894,737 | | | — | | | — | | Total | 33,708,248 | | | 32,928,249 | | | 32,565,902 | |
The 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes issued in June 2020 and in March 2021, respectively, are convertible, based on the applicable conversion rate, into cash, shares of the Company’s common stock or a combination thereof, at the Company’s election. The impact of the assumed conversion to diluted net loss per share is computed on an as-converted basis.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for earnings per share. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/260/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Retirement Plan
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Retirement Benefits [Abstract] |
|
| Retirement Plan |
Retirement Plan The Company has a defined-contribution 401(k) retirement plan covering substantially all of its employees. Eligible employees are permitted to contribute up to an amount not to exceed an annual statutory maximum. The Company matches employee contributions at a rate of 25% of vested contributions, up to a maximum of $2,000 per participant per year. The Company’s contributions to the 401(k) plan were $1.4 million, $0.8 million, and $1.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CompensationAndRetirementDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for retirement benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 70
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480794/715-70-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480482/715-20-55-17
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (q)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/715/tableOfContent
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (o)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (p)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (r)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (r)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480126/715-20-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480266/715-60-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_PensionAndOtherPostretirementBenefitsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Segment Information
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Segment Reporting [Abstract] |
|
| Segment Information |
Segment Information The Company has one reportable segment as its chief operating decision maker (the "CODM"), who is its Chief Executive Officer, reviews financial information on a consolidated basis. The Company generates revenue from the sale of pre-owned luxury goods through its online marketplace and retail stores. Revenue is comprised of consignment revenue, direct revenue, and shipping services revenue. The Company does not have intra-entity sales or transfers. The chief operating decision maker assesses performance and allocates resources based on net loss, as reported on the statements of operations. Net loss is used to monitor budget versus actual results. The CODM does not evaluate operating segments using asset or liability information.
The following table presents selected financial information with respect to the Company's single operating segment (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Total revenue | $ | 600,484 | | | $ | 549,304 | | | $ | 603,493 | | | Less: | | | | | | | Cost of consignment revenue | 53,801 | | | 58,120 | | | 56,963 | | | Cost of direct revenue | 55,809 | | | 74,343 | | | 141,661 | | | Cost of shipping services revenue | 43,353 | | | 40,563 | | | 56,178 | | | Total cost of revenue | 152,963 | | | 173,026 | | | 254,802 | | | Gross Profit | 447,521 | | | 376,278 | | | 348,691 | | | Less: | | | | | | People costs | 283,002 | | | 274,229 | | | 297,676 | | Software and purchased services | 108,866 | | | 104,454 | | | 103,695 | | | Occupancy expense | 37,295 | | | 37,718 | | | 44,911 | | Depreciation and amortization(1) | 32,764 | | | 31,695 | | | 27,669 | | | Stock-based compensation | 29,082 | | | 34,273 | | | 46,138 | | Administration and other segment expenses (2) | 12,811 | | | 16,740 | | | 16,869 | | Restructuring (3) | 196 | | | 43,462 | | | 896 | | | Total operating expenses | 504,016 | | | 542,571 | | | 537,854 | | | Change in fair value of warrant liability | (68,167) | | | — | | | — | | | Gain on extinguishment of debt | 4,177 | | | — | | | — | | | Interest income | 7,943 | | | 8,805 | | | 3,191 | | | Interest expense | (21,384) | | | (10,701) | | | (10,472) | | | Other income (expense), net | — | | | — | | | 171 | | Provision for income taxes | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | | | Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
(1) Expenses reported in operating expenses, excludes depreciation and amortization recorded in cost of revenue. (2) Administration and other segment expenses include insurance, supplies, and taxes. (3) Restructuring expenses for the year ended December 31, 2024 and 2022 consist of employee severance charges. For the year ended December 31, 2023 it consists of impairment of right-of-use assets and property and equipment, employee severance charges, gain on lease terminations, and other charges.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for reporting segments including data and tables. Reportable segments include those that meet any of the following quantitative thresholds a) it's reported revenue, including sales to external customers and intersegment sales or transfers is 10 percent or more of the combined revenue, internal and external, of all operating segments b) the absolute amount of its reported profit or loss is 10 percent or more of the greater, in absolute amount of 1) the combined reported profit of all operating segments that did not report a loss or 2) the combined reported loss of all operating segments that did report a loss c) its assets are 10 percent or more of the combined assets of all operating segments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 54
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-54
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 54
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-54
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 54
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-54
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 34
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-34
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 26C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-26C
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 26B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-26B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-15
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/280/tableOfContent
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 26
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-26
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-21
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-21
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Subsequent Events
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Subsequent Events [Abstract] |
|
| Subsequent Events |
Subsequent Events On February 10, 2025, the Company entered into an exchange agreement with certain holders of its 2028 Notes to exchange $183.3 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Notes for $146.7 million in aggregate principal amount of new convertible senior notes due 2031 (“2031 Notes”), issued pursuant to an Indenture, dated February 10, 2025. The exchange was consummated, and the 2031 Notes were issued in a private placement, on February 10, 2025. The 2031 Notes bear cash interest at a rate of 4.00% per annum payable semi-annually in arrears on February 15 and August 15 of each year, beginning on August 15, 2025 (with additional interest being paid solely on the first interest payment date of the 2031 Notes in consideration for the accrued and unpaid interest on the 2028 Notes exchanged for the 2031 Notes) and will mature on February 15, 2031. The 2031 Notes are convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Indenture. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this transaction on its financial statements.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for significant events or transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date through the date the financial statements were issued or the date the financial statements were available to be issued. Examples include: the sale of a capital stock issue, purchase of a business, settlement of litigation, catastrophic loss, significant foreign exchange rate changes, loans to insiders or affiliates, and transactions not in the ordinary course of business. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/855/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483399/855-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Pay vs Performance Disclosure - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Pay vs Performance Disclosure |
|
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (134,202)
|
$ (168,472)
|
$ (196,445)
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection v
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_PvpTable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph A
| Name: |
ecd_TradingArrByIndTable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16
-Subsection J
-Paragraph a
| Name: |
ecd_InsiderTradingPoliciesProcLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16
-Subsection J
-Paragraph a
| Name: |
ecd_InsiderTrdPoliciesProcAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Strategy Disclosure
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management, Strategy, and Governance [Line Items] |
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Processes for Assessing, Identifying, and Managing Threats [Text Block] |
We have developed processes for assessing, identifying and managing material risks from cybersecurity threats. We review our security plans and strategies as threats and conditions evolve. The following is a summary of our cybersecurity risk management and strategy processes:
Enterprise Risk Management: Our enterprise risk management program includes management of material risks from cybersecurity threats alongside other Company risks as part of our overall risk assessment process. In 2024, as part of our Enterprise Risk Management Program, our Internal Audit team identified and prioritized the most critical risks that could impact our ability to achieve our business priorities and make risk-informed strategic decisions. With management’s input, our Board and Internal Audit team have identified cybersecurity as one of the risks that merits the highest level of prioritization. Informed by this designation, our Internal Audit team tracks cybersecurity key indicators and engages in discussions on the status, priorities and impact of cybersecurity risk response plans; reports key information to management throughout the year to inform decision making; and reports to the Audit Committee on a quarterly basis and to the full Board on the results and progress of the risk mitigation process.
In addition, we employ a range of tools and services to inform our assessment, identification and management of material risks from cybersecurity threats, which include from time to time: •monitoring emerging data protection laws, including the California Consumer Privacy Act and the General Data Protection Regulation, and implementing responsive changes to our processes; •undertaking periodic reviews of our policies and statements related to cybersecurity; •conducting cybersecurity management and incident training for employees involved in our systems and processes that handle sensitive data; •conducting phishing email simulations for employees and contractors with access to corporate email systems; •requiring employees, as well as third-parties who provide services on our behalf, to treat information and data with care; and •conducting tabletop exercises to simulate a response to a cybersecurity incident and using the findings to improve our processes and technologies.
Incident Response Team and Outside Resources: We have formed an Incident Response Team that monitors and mitigates material risks from cybersecurity threats. This team is composed of members from the information security, engineering and legal teams. The Incident Response Team and our internal legal team work in tandem to estimate the severity and materiality of a cybersecurity incident, create a response plan and inform other stakeholders as appropriate, including the Audit Committee or the full Board. In addition, we engage several third party service providers to monitor cybersecurity threats in the market more broadly, including in relation to phishing, data leaks on the dark web, firewalls, code security and endpoint protection. To identify risks from cybersecurity threats associated with these third-party service providers, we conduct pre-contract screening and due diligence and post-contract monitoring.
Cybersecurity Task Force: We have formed a cross-functional Cybersecurity Task Force that focuses on long-term cybersecurity strategy. The Cybersecurity Task Force is composed of members from the information security, engineering and legal teams and reports to our Chief Technology and Product Officer. The Cybersecurity Task Force meets periodically to discuss developments and best practices in cybersecurity incident response. In addition, the Cybersecurity Task Force reviews the business impact and severity of potential cybersecurity incidents, as reported by our automated systems, utilization of the bug bounty program, and public reports on the threat landscape.
For a discussion of whether and how any risks from cybersecurity threats, including as a result of any previous cybersecurity incidents, have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect the Company, including our business strategy and results of operations, see “Risk Factors – Risks Related to Data Security, Privacy and Fraud,” which are incorporated by reference into this Item 1C. In the three most recently completed fiscal years, we have not experienced any material cybersecurity incidents and the expenses we have incurred from cybersecurity incidents were immaterial. This includes penalties and settlements, of which there were none.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Processes Integrated [Flag] |
true
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Processes Integrated [Text Block] |
We have developed processes for assessing, identifying and managing material risks from cybersecurity threats.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Third Party Engaged [Flag] |
true
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Third Party Oversight and Identification Processes [Flag] |
true
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Materially Affected or Reasonably Likely to Materially Affect Registrant [Flag] |
false
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Board of Directors Oversight [Text Block] |
Our Board of Directors provides oversight of risks from cybersecurity threats, in coordination with our Audit Committee and management team. The following is a summary of our governance processes related to cybersecurity risk management:
Board: Our full Board receives biannual updates on cybersecurity from our Chief Technology and Product Officer (the “CTPO”) or head of cybersecurity (the “CISO”) to, among other items, review cybersecurity incidents, review key metrics on our cybersecurity program and related risk management programs, and discuss our cybersecurity programs and goals. Our Board also regularly reviews cyber-related risks as part of our enterprise risk management program on a quarterly basis and receives updates from our Internal Audit team on the results of the risk monitoring and mitigation process, as described in more detail above.
Audit Committee: Our Audit Committee provides additional oversight of material risks from cybersecurity threats and engages with our CTPO or CISO regarding risk management of cybersecurity issues and to discuss potential updates to the Company’s cybersecurity risk management program, including as a result of any Cybersecurity Task Force findings. The Audit Committee receives a quarterly report from the Company’s cybersecurity team, which includes the CTPO, CISO, and members of the information security team, that summarizes progress on cyber-related key performance indicators, including product security, cloud security, risk and compliance, identity issues, and cyber defense. The Audit Committee updates the full Board on matters relating to material cybersecurity risks at least quarterly. Management: Our CTPO is responsible for assessing and managing the Company’s material risks from cybersecurity threats, and our CISO reports directly to our CTPO regarding such threats. Our CTPO is informed about and monitors the prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation or cybersecurity incidents through the management of and participation in the Company’s Internal Audit team, Incident Response Team and Cybersecurity Task Force, as described above. As discussed above, our CTPO or CISO reports biannually to the full Board and quarterly to the Audit Committee about risks from cybersecurity threats among other cybersecurity related matters. To the extent a material cybersecurity incident occurs, our CTPO and broader management team would inform the chair of our Audit Committee of the nature, scope and impact of the incident, and involve the other members of the Audit Committee or the full Board as necessary to evaluate the risks and determine next steps. Our CTPO and CISO have served in these roles since 2023. Our CTPO has more than 20 years of experience in various senior leadership roles involving managing cybersecurity and compliance teams, including as Head of Tech and Digital at Lovevery and as Chief Technology and Product Officer at Zulilly. O
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Board Committee or Subcommittee Responsible for Oversight [Text Block] |
Our Board of Directors provides oversight of risks from cybersecurity threats, in coordination with our Audit Committee and management team.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Process for Informing Board Committee or Subcommittee Responsible for Oversight [Text Block] |
Our full Board receives biannual updates on cybersecurity from our Chief Technology and Product Officer (the “CTPO”) or head of cybersecurity (the “CISO”) to, among other items, review cybersecurity incidents, review key metrics on our cybersecurity program and related risk management programs, and discuss our cybersecurity programs and goals. Our Board also regularly reviews cyber-related risks as part of our enterprise risk management program on a quarterly basis and receives updates from our Internal Audit team on the results of the risk monitoring and mitigation process, as described in more detail above.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Role of Management [Text Block] |
Our CTPO is responsible for assessing and managing the Company’s material risks from cybersecurity threats, and our CISO reports directly to our CTPO regarding such threats.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Positions or Committees Responsible [Flag] |
true
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Positions or Committees Responsible [Text Block] |
Our CTPO is responsible for assessing and managing the Company’s material risks from cybersecurity threats, and our CISO reports directly to our CTPO regarding such threats.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Expertise of Management Responsible [Text Block] |
Our CTPO and CISO have served in these roles since 2023. Our CTPO has more than 20 years of experience in various senior leadership roles involving managing cybersecurity and compliance teams, including as Head of Tech and Digital at Lovevery and as Chief Technology and Product Officer at Zulilly. Our CISO has more than 20 years of experience in leadership roles focused on cybersecurity, cloud engineering, infrastructure, and technical operations, including as CISO and Head of Cloud and Infrastructure Engineering at AutoZone and as Principal Executive Advisory Consultant at Amazon Web Services.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Process for Informing Management or Committees Responsible [Text Block] |
Our CTPO is informed about and monitors the prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation or cybersecurity incidents through the management of and participation in the Company’s Internal Audit team, Incident Response Team and Cybersecurity Task Force, as described above.
|
| Cybersecurity Risk Management Positions or Committees Responsible Report to Board [Flag] |
true
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskBoardCommitteeOrSubcommitteeResponsibleForOversightTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskBoardOfDirectorsOversightTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph i
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph i
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementExpertiseOfManagementResponsibleTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph i
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph i
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementPositionsOrCommitteesResponsibleFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
i:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph iii
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph iii
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementPositionsOrCommitteesResponsibleReportToBoardFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
i:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph i
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph i
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementPositionsOrCommitteesResponsibleTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementProcessesForAssessingIdentifyingAndManagingThreatsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph i
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph i
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementProcessesIntegratedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
i:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph i
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph i
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementProcessesIntegratedTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementStrategyAndGovernanceLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
i:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph ii
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskManagementThirdPartyEngagedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
i:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskMateriallyAffectedOrReasonablyLikelyToMateriallyAffectRegistrantFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
i:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskProcessForInformingBoardCommitteeOrSubcommitteeResponsibleForOversightTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskProcessForInformingManagementOrCommitteesResponsibleTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection c
-Paragraph 2
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskRoleOfManagementTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Section 106
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph iii
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Section 16K
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph iii
| Name: |
cyd_CybersecurityRiskThirdPartyOversightAndIdentificationProcessesFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cyd_ |
| Data Type: |
i:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Policies)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Basis of Presentation |
Basis of Presentation The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and, in the opinion of management, reflect all adjustments necessary to state fairly the Company’s financial position, results of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the periods presented. For the years ended 2024, 2023, and 2022, comprehensive loss is equal to net loss as the Company has no other comprehensive income (loss) item in the periods presented. The Company’s functional and reporting currency is the U.S. dollar.
|
| Presentation Change |
The Company has made a presentation change to the Company's statements of operations to reclassify its legal settlements expense to selling, general, and administrative expenses. Additionally, the Company has made a presentation change to reclassify loss on disposal of property and equipment, impairment of capitalized proprietary software, and gain on lease termination to other adjustments within operating cash flows in the statements of cash flows. Changes to reclassify amounts in the prior periods have been made to conform to the current period presentation.
|
| Use of Estimates |
Use of Estimates The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period. Significant items subject to such estimates and assumptions include those related to revenue recognition, including the returns reserve, standalone selling price related to consignment revenue transactions, valuation of inventory, software development costs, stock-based compensation, fair value of warrant liability, initial fair value of non-convertible notes issued as part of the 2024 Note Exchange (see Note 6 — Non-convertible Notes, Net), incremental borrowing rates related to lease liability, valuation of deferred taxes, and other contingencies. The Company evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors and adjusts those estimates and assumptions when facts and circumstances dictate. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
|
| Net Loss per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders |
Net Loss per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders The Company follows the two-class method when computing net loss per common share when shares are issued that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method determines net loss per common share for each class of common stock and participating securities according to dividends declared or accumulated and participation rights in undistributed earnings. The two-class method requires income (loss) available or attributable to common stockholders for the period to be allocated between common stock and participating securities based upon their respective rights to receive dividends as if all income for the period had been distributed. The Company’s convertible senior notes are participating securities as they give the holders the right to receive dividends if dividends or distributions declared to the common stockholders is equal to or greater than the last reported sale price of the Company’s common stock on the trading day immediately preceding the ex-dividend date for such dividend or distribution as if the instruments had been converted into shares of common stock. No undistributed earnings were allocated to the participating securities as the contingent event is not satisfied as of the reporting date. For periods in which the Company reports net losses, diluted net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders is the same as basic net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders, because potentially dilutive common shares and assumed conversion of the convertible senior notes are not assumed to have been issued within the calculation, if their effect is anti-dilutive.
|
| Segments |
Segments The Company has one operating segment and one reportable segment as its chief operating decision maker, who is its Chief Executive Officer, reviews financial information on a consolidated basis for purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance. All long-lived assets are located in the United States and substantially all revenue is attributed to consignors and buyers based in the United States.
|
| Revenue Recognition |
Revenue Recognition The Company generates revenue from the sale of pre-owned luxury goods through its online marketplace and retail stores. Revenue is recognized upon transfer of control of promised products or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for those products or services. The Company enters into contracts that include products and services that are capable of being distinct and accounted for as separate performance obligations as described below. The transaction price requires an allocation across consignment services, sales of Company-owned inventory, and shipping services. Estimation is required in the determination of the services' stand-alone selling price (“SSP”). Consignment Revenue The Company provides a service to sell pre-owned luxury goods on behalf of consignors to buyers through its online marketplace and retail stores. The Company retains a percentage of the proceeds received as payment for its consignment service, which the Company refers to as its take rate. SSP is estimated using observable stand-alone consignment sales which are conducted without shipping services. The Company reports consignment revenue on a net basis as an agent and not the gross amount collected from the buyer. Title to the consigned goods remains with the consignor until transferred to the buyer upon purchase of the consigned goods and expiration of the allotted return period. The Company does not take title of consigned goods at any time except in certain cases where returned goods become Company-owned inventory. The Company recognizes consignment revenue upon purchase of the consigned good by the buyer as its performance obligation of providing consignment services to the consignor is satisfied at that point. Consignment revenue is recognized net of estimated returns, cancellations, buyer incentives and adjustments. The Company recognizes a returns reserve based on historical experience, which is recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets (see Note 5). Sales tax assessed by governmental authorities is excluded from revenue. Certain transactions provide consignors with a material right resulting from the tiered consignor commission plan. Under this plan, the amount an individual consignor receives for future sales of consigned goods may be dependent on previous consignment sales for that consignor within his/her consignment period. Accordingly, in certain consignment transactions, a small portion of the Company’s consignment revenue is allocated to such material right using the portfolio method and recorded as deferred revenue, which is recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets. The impact of the deferral has not been material to the financial statements. The Company also generates subscription revenue from monthly memberships allowing buyers early access to shop for luxury goods. The buyers receive the early access and other benefits over the term of the subscription period, which represents a single stand-ready performance obligation. Therefore, the subscription fees paid by the buyer are recognized over the monthly subscription period. Subscription revenue was not material in 2024, 2023, and 2022. Direct Revenue The Company generates direct revenue from the sale of Company-owned inventory. The Company recognizes direct revenue on a gross basis upon shipment of the purchased good to the buyer as the Company acts as the principal in the transaction. SSP is estimated using observable stand-alone sales of Company-owned inventory which are conducted without shipping services, when available, or a market assessment approach. Direct revenue is recognized net of estimated returns, buyer incentives and adjustments. Sales tax assessed by governmental authorities is excluded from revenue. Cost of direct revenue is also recognized upon shipment to the buyer in an amount equal to that paid to the consignor from the original consignment sale, an amount equal to that paid as a direct purchase from a third party, or the lower of cost of the inventory purchased and its net realizable value. Shipping Services Revenue The Company provides a service to ship purchased items to buyers and a service to ship items from buyers back to the Company. The Company determines itself to be the principal in this arrangement. The Company charges a fee to buyers for this service and has elected to treat shipping and handling activities performed as a separate performance obligation. For shipping services revenue, the Company's SSP is estimated using a market approach considering external and internal data points on the stand-alone sales price of the shipping service. All outbound shipping and handling costs for buyers are accounted for as cost of shipping services and recognized as the shipping activity occurs. The Company also generates shipping services revenue from the shipping fees for consigned products returned by buyers to the Company within policy. The Company recognizes shipping revenue and associated costs over time as the shipping activity occurs, which is generally one to three days after shipment. Incentives Incentives, which include platform-wide discounts and buyer incentives, may periodically be offered to buyers. Platform-wide discounts are made available to all buyers on the online marketplace. Buyer incentives apply to specific buyers and consist of coupons or promotions that offer credits in connection with purchases on the Company’s platform, and do not impact the commissions paid to consignors. These are treated as a reduction of consignment revenue and direct revenue. Additionally, the Company periodically offers commission exceptions to the standard consignment rates to consignors to optimize its supply. These are treated as a reduction of consignment revenue at the time of sale. The Company may offer a certain type of buyer incentive in the form of site credits to buyers on current transactions to be applied towards future transactions, which are included in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets. Contract Liabilities The Company’s contractual liabilities primarily consist of deferred revenue for material rights primarily related to the tiered consignor commission plan, which are recognized as revenue using a portfolio approach based on the pattern of exercise, and certain buyer incentives. Contract liabilities are recorded in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets and are generally expected to be recognized within one year. Contract liabilities were immaterial as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
|
| Cost of Revenue |
Cost of Revenue Cost of consignment revenue consists of credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and consignor inventory adjustments relating to lost or damaged products. Cost of direct revenue consists of the cost of goods sold, credit card fees, packaging, customer service personnel-related costs, website hosting services, and inventory adjustments. Cost of shipping services revenue consists of the outbound shipping and handling costs to deliver purchased items to buyers, the shipping costs for consigned products returned by buyers to the Company within policy, and an allocation of the credit card fees associated with the shipping fee charged.
|
| Marketing |
Marketing Marketing expense is comprised of the cost of acquiring new consignors and buyers for our online platform and physical stores, including the cost of television, digital and direct mail advertising. Marketing expense also includes personnel-related costs, including stock-based compensation, of employees engaged in these activities. Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and were $42.9 million, $48.4 million, and $49.0 million in 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
|
| Operations and Technology |
Operations and Technology Operations and technology expense is comprised of costs associated with the authentication, merchandising and fulfillment of goods sold through our online marketplace and retail stores, as well as general information technology expense. The principal component of operations and technology expense is personnel-related costs, including stock-based compensation, of employees engaged in these activities. Operations and technology expense also includes allocated facility and overhead costs, costs related to our retail stores, facility supplies, inbound consignment shipping costs, and depreciation of hardware and equipment, as well as research and development expense for technology associated with managing and improving our operations. In 2024, 2023, and 2022, the Company capitalized proprietary software developments costs of $11.8 million, $13.3 million, and $15.6 million, respectively. As such, operations and technology expense also includes amortization of capitalized technology development costs, which is taken on straight-line basis over three years once the technology is ready for its intended use.
|
| Selling, General and Administrative |
Selling, General and Administrative Selling, general and administrative expense is principally comprised of the personnel-related costs for employees involved in sales, finance and administration, and includes stock-based compensation expense. Selling, general and administrative expense also includes allocated facility and overhead costs and professional services, including accounting and legal advisors.
|
| Stock-based Compensation |
Stock-based Compensation The Company incurs stock-based compensation expense from stock options, restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance based restricted stock units (“PSUs”) subject to performance or market conditions, and employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”) purchase rights. Stock-based compensation expense related to employees and nonemployees is measured based on the grant-date fair value of the awards. The Company estimates the fair value of stock options granted and the purchase rights issued under the ESPP using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The fair value of RSUs is estimated based on the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant, which is determined based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock. Compensation expense is recognized in the statements of operations over the period during which the employee is required to perform services in exchange for the award (the vesting period of the applicable award) using the straight-line method for awards with only a service condition. To determine the grant-date fair value of the Company's stock-based payment awards for PSUs subject to performance conditions, the quoted stock price on the date of grant is used. The stock-based compensation expense for PSUs with performance conditions is recognized based on the estimated number of shares that the Company expects will vest and is adjusted on a quarterly basis using the estimated achievement of financial performance targets. For PSUs subject to market conditions, the grant-date fair value is determined using the Monte Carlo simulation model which utilizes multiple input variables to estimate the probability that market conditions will be achieved. These variables include the Company's expected stock price volatility over the expected term of the award, the risk-free interest rate for the expected term of the award, and expected dividends. For PSUs with market conditions, the stock-based compensation expense is recognized on a tranche by tranche basis over the requisite service period using the fair value derived from the Monte Carlo simulation model. The compensation expense will be recognized regardless of whether the market condition is ever satisfied, provided the requisite service period is satisfied. For all awards, the Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur.
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less from the purchase date to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents primarily consist of investments in short-term money market funds.
|
| Restricted Cash |
Restricted cash consists of cash deposited with a financial institution as collateral for the Company’s letters of credit for its facility leases and the Company’s credit cards.
|
| Accounts Receivable |
Accounts Receivable Accounts receivables are recorded at the amounts billed to buyers and do not bear interest. Accounts receivables result from credit card transactions, the majority of which are settled within two business days.
|
| Inventory, Net |
Inventory, Net Inventory consists of finished goods arising from goods returned after the title has transferred from the buyer to the Company as well as finished goods from direct purchases from vendors and consignors. The cost of inventory is an amount equal to that paid to the consignor or vendors. Inventory is valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value using the specific identification method and the Company records provisions, as appropriate, to write down obsolete and excess inventory to estimated net realizable value. After the inventory value is reduced, adjustments are not made to increase it from the estimated net realizable value. Additionally, inventory is recorded net of an allowance for shrinkage which represents the risk of physical loss of inventory. Provisions for inventory shrinkage are estimated based on historical experience and are adjusted based upon physical inventory counts. Provisions to write down inventory to net realizable value and provisions for inventory shrinkage were $2.6 million and $9.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Return reserves, which reduce revenue and cost of sales, are estimated using historical experience. Liabilities for return allowances are included in other accrued and current liabilities on the balance sheets and were $22.4 million and $22.2 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023. Included in inventory on the Company’s balance sheets are assets totaling $4.8 million and $5.2 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, for the rights to recover products from customers associated with its liabilities for return reserves.
|
| Property and Equipment, Net |
Property and Equipment, Net Property and equipment, net is recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. Repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. The estimated useful lives of our assets are as follows: | | | | | | | Proprietary software | 3 years | | Furniture and equipment | 3-5 years | | Vehicles | 5 years | | Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life |
|
| Software Development Costs |
Software Development Costs Proprietary software includes the costs of developing the Company’s internal proprietary business platform and automation projects. The Company capitalizes qualifying proprietary software development costs that are incurred during the application development stage. Capitalization of costs begins when two criteria are met: (1) the preliminary project stage is completed and (2) it is probable that the software will be completed and used for its intended function. Such costs are capitalized in the period incurred. Capitalization ceases and amortization begins when the software is substantially complete and ready for its intended use, including the completion of all significant testing. Costs related to preliminary project activities and post-implementation operating activities are expensed as incurred.
|
| Impairment of Long-lived Assets |
Impairment of Long-lived Assets The carrying amounts of long-lived assets, including right-of-use assets, property and equipment, net and capitalized proprietary software, are periodically reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable or that the useful life is shorter than originally estimated. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by comparing the carrying amount of assets to future undiscounted net cash flows the assets are expected to generate over their remaining life. If the assets are considered to be impaired, the amount of any impairment is measured as the difference between the carrying value and the fair value of the impaired assets. If the useful life is shorter than originally estimated, the Company amortizes the remaining carrying value over the revised shorter useful life.
|
| Leases |
Leases Contracts that have been determined to convey the right to use an identified asset are evaluated for classification as an operating or finance lease. For the Company’s operating leases, the Company records a lease liability based on the present value of the lease payments at lease inception, using the applicable incremental borrowing rate. The Company estimates the incremental borrowing rate by developing its own synthetic credit rating, corresponding yield curve, and the terms of each lease at the lease commencement date. The corresponding right-of-use asset is recorded based on the corresponding lease liability at lease inception, adjusted for payments made to the lessor at or before the commencement date, initial direct costs incurred and any tenant incentives allowed for under the lease. The Company does not include optional renewal terms or early termination provisions unless the Company is reasonably certain such options would be exercised at the inception of the lease. Operating lease right-of-use assets, current portion of operating lease liabilities, and operating lease liabilities, net of current portion are included on the Company’s balance sheet. The Company has elected the practical expedients that allows for the combination of lease components and non-lease components and to record short-term leases as lease expense on a straight-line basis on the statements of operations. Variable lease payments are recorded as expense as they are incurred. The Company has finance leases for vehicles and equipment, and the amounts of finance lease right-of-use assets and finance lease liabilities have been immaterial to date.
|
| Convertible Senior Notes, net |
Convertible Senior Notes, Net Prior to the adoption of ASU 2020-06 on January 1, 2022, convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash or other assets, or partially in cash, upon conversion, were separately accounted for as long-term debt and equity components (or conversion feature). The debt component represented the Company’s contractual obligation to pay principal and interest and the equity component represented the Company’s option to convert the debt security into equity of the Company or the equivalent amount of cash. Upon issuance, the Company allocated the debt component on the basis of the estimated fair value of a similar liability that does not have an associated convertible feature and the remaining proceeds are allocated to the equity component. The bifurcation of the debt and equity components resulted in a debt discount for the aforementioned notes. The Company uses the effective interest method to amortize the debt discount to interest expense over the amortization period which is the expected life of the debt. Following the adoption of ASU 2020-06, there is no bifurcation of the liability and equity components of the 3.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2025 (the “2025 Notes”) and the 1.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2028 (the “2028 Notes” and, together with the 2025 Notes, the “Notes”), and the entire principal of the Notes are accounted for as debt.
|
| Debt and Debt Issuance Costs |
Debt The Company initially recognizes incurred debt, net of any discounts, premiums and issuance costs related to the debt offering. All debt issuance costs are presented as a direct deduction from the related principal debt amounts on the balance sheet. Debt obligations due within 12 months are classified as current liabilities. Debt discounts, premiums and issuance costs are amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt using the effective interest method. When multiple instruments are issued in the same transaction, the Company allocates any issuance costs to the instruments on the same basis as the allocation of proceeds. Issuance costs allocated to instruments measured at fair value are expensed in the period incurred. Debt Issuance Costs Debt issuance costs, which consist of direct incremental legal, consulting, banking and accounting fees related to the anticipated debt offering, are amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt based on the effective interest method. The Company presents debt issuance costs on the balance sheets as a direct deduction from the associated debt. The Company adopted ASU 2020-06 as of January 1, 2022 using the modified retrospective method. Prior to the adoption of ASU 2020-06 on January 1, 2022, a portion of debt issuance costs incurred in connection with the convertible senior notes issued in June 2020 and March 2021 was allocated to the equity component and was recorded as a reduction to additional paid in capital and was not amortized to interest expense over the estimated life of the related debt. Following the adoption of ASU 2020-06, the debt issuance costs previously allocated to the equity component of both series of Notes were reclassified to debt. As such, all of the debt issuance costs are recorded as a direct deduction from the related principal debt amounts on the balance sheet, and are all amortized to interest expense over the estimated remaining life of the related debt.
|
| Capped Call Transactions |
Capped Call Transactions In June 2020 and March 2021, in connection with the issuance of its convertible senior notes, the Company entered into capped call transactions (see Note 7 - Convertible Senior Notes, Net). The capped call transactions are expected generally to reduce the potential dilution to the holders of the Company’s common stock upon any conversion of the convertible senior notes and/or offset any cash payments the Company is required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted convertible senior notes, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap based on the cap price. The Capped Calls (as defined below) are classified in stockholders’ equity as a reduction to additional paid-in capital and are not subsequently remeasured as long as the conditions for equity classification continue to be met. The Company monitors the conditions for equity classification, which continue to be met as of December 31, 2024.
|
| Income Taxes |
Income Taxes Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in loss in the period of enactment. The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs.
|
| Concentrations of Credit Risks |
Concentrations of Credit Risks Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and accounts receivable. At times, such amount may exceed federally-insured limits. The Company is closely monitoring ongoing events involving limited liquidity, defaults, non-performance or other adverse developments that affect financial institutions or other companies in the financial services industry or the financial services industry generally. The Company reduces credit risk by placing its cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and investments with major financial institutions with high credit ratings within the United States. The Company has not experienced any realized losses on cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash to date; however, no assurances can be provided. As of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, there were no customers that represented 10% or more of the Company’s accounts receivable balance and there were no customers that individually exceeded 10% of the Company’s total revenue for each of the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
|
| Recently Adopted and Issued Accounting Pronouncements |
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures requires disclosures about significant segment expenses that are regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The Company adopted the standard during the year ended December 31, 2024 and applied it retrospectively to the periods presented. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company's financial statements. Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures. This new guidance is designed to enhance the transparency and decision usefulness of income tax disclosures. The amendments of this update are related to the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid, requiring (1) consistent categories and greater disaggregation of information in the rate reconciliation and (2) income taxes paid disaggregated by jurisdiction. ASU 2023-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements. In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-03, Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses, which requires companies to disclose in the notes to the financial statements the disaggregation of certain expense categories included within the income statement expense captions. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2027 on a prospective basis with optional retrospective application. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements. In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-04, Debt with Conversion and Other Options. This new guidance is designed to clarify requirements for determining whether certain settlements of convertible debt instruments should be accounted for as an induced conversion. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2025 and for interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adopting this new accounting standard will have on its financial statements.
|
| X |
- DefinitionCapped call transactions policy.
| Name: |
real_CappedCallTransactionsPolicyPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionConvertible senior notes.
| Name: |
real_ConvertibleSeniorNotesPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
real_CostOfRevenuePolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
real_MarketingPolicyPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionOperations and technology policy.
| Name: |
real_OperationsAndTechnologyPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSoftware development costs.
| Name: |
real_SoftwareDevelopmentCostsPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for basis of accounting, or basis of presentation, used to prepare the financial statements (for example, US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, Other Comprehensive Basis of Accounting, IFRS).
| Name: |
us-gaap_BasisOfAccountingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for cash and cash equivalents, including the policy for determining which items are treated as cash equivalents. Other information that may be disclosed includes (1) the nature of any restrictions on the entity's use of its cash and cash equivalents, (2) whether the entity's cash and cash equivalents are insured or expose the entity to credit risk, (3) the classification of any negative balance accounts (overdrafts), and (4) the carrying basis of cash equivalents (for example, at cost) and whether the carrying amount of cash equivalents approximates fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEntity's cash and cash equivalents accounting policy with respect to restricted balances. Restrictions may include legally restricted deposits held as compensating balances against short-term borrowing arrangements, contracts entered into with others, or company statements of intention with regard to particular deposits; however, time deposits and short-term certificates of deposit are not generally included in legally restricted deposits. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(1)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for reporting any exceptions to the comparability of prior year financial data with data shown for the most recent accounting period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483478/205-10-45-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComparabilityOfPriorYearFinancialData |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for salaries, bonuses, incentive awards, postretirement and postemployment benefits granted to employees, including equity-based arrangements; discloses methodologies for measurement, and the bases for recognizing related assets and liabilities and recognizing and reporting compensation expense. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CompensationRelatedCostsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for credit risk. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 825
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478898/942-825-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskCreditRisk |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy related to debt. Includes, but is not limited to, debt issuance costs, the effects of refinancings, method of amortizing debt issuance costs and original issue discount, and classifications of debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for computing basic and diluted earnings or loss per share for each class of common stock and participating security. Addresses all significant policy factors, including any antidilutive items that have been excluded from the computation and takes into account stock dividends, splits and reverse splits that occur after the balance sheet date of the latest reporting period but before the issuance of the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerSharePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for recognizing and measuring the impairment of long-lived assets. An entity also may disclose its accounting policy for long-lived assets to be sold. This policy excludes goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.CC)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480091/360-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 4
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482338/360-10-05-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOrDisposalOfLongLivedAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for income taxes, which may include its accounting policies for recognizing and measuring deferred tax assets and liabilities and related valuation allowances, recognizing investment tax credits, operating loss carryforwards, tax credit carryforwards, and other carryforwards, methodologies for determining its effective income tax rate and the characterization of interest and penalties in the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-20
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-19
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-25
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(h)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-28
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of inventory accounting policy for inventory classes, including, but not limited to, basis for determining inventory amounts, methods by which amounts are added and removed from inventory classes, loss recognition on impairment of inventories, and situations in which inventories are stated above cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483489/210-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478411/912-330-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/330/tableOfContent
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-4
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 270
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482989/270-10-45-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for leasing arrangement entered into by lessee. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeLeasesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy pertaining to new accounting pronouncements that may impact the entity's financial reporting. Includes, but is not limited to, quantification of the expected or actual impact.
| Name: |
us-gaap_NewAccountingPronouncementsPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477798/958-360-50-6
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477798/958-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for receivable. Includes, but is not limited to, accounts receivable and financing receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481569/310-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReceivablesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for revenue from contract with customer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-19
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 235
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for segment reporting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 54
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-54
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 36
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-36
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for inclusion of significant items in the selling, general and administrative (or similar) expense report caption. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 720
-SubTopic 35
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483406/720-35-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for the use of estimates in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-9
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-12
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_UseOfEstimates |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash |
The following table provides a reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash for the year ended December 31, 2024 that sum to the total of the same amounts shown in the statements of cash flows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | 175,709 | | | $ | 293,793 | | | Restricted cash | 14,911 | | | 14,914 | | | — | | | Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 187,123 | | | $ | 190,623 | | | $ | 293,793 | |
|
| Schedule of Restricted Cash |
The following table provides a reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash for the year ended December 31, 2024 that sum to the total of the same amounts shown in the statements of cash flows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | 175,709 | | | $ | 293,793 | | | Restricted cash | 14,911 | | | 14,914 | | | — | | | Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 187,123 | | | $ | 190,623 | | | $ | 293,793 | |
|
| Schedule of Property and Equipment, Net |
The estimated useful lives of our assets are as follows: | | | | | | | Proprietary software | 3 years | | Furniture and equipment | 3-5 years | | Vehicles | 5 years | | Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 | Proprietary software | $ | 47,416 | | | $ | 44,964 | | Furniture and equipment | 51,959 | | | 47,389 | | Automobiles | 2,036 | | | 2,069 | | Leasehold improvements | 88,840 | | | 84,138 | | | Property and equipment, gross | 190,251 | | | 178,560 | | | Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (95,808) | | | (74,473) | | | Property and equipment, net | $ | 94,443 | | | $ | 104,087 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, balances by class of assets, depreciation and depletion expense and method used, including composite depreciation, and accumulated deprecation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of cash and cash equivalents.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfCashAndCashEquivalentsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of cash and cash equivalents restricted as to withdrawal or usage. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(1)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfRestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Cash and Cash Equivalents (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Estimated Value of Cash and Cash Equivalents |
The following tables summarize the estimated value of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents (in thousands) and do not include restricted cash. There are no unrealized gains or losses related to the restricted cash balance. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | Amortized Cost | | Unrealized Gain | | Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value | | Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | Cash | $ | 24,870 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 24,870 | | Money market funds | 147,342 | | | — | | | — | | | 147,342 | | | Total cash and cash equivalents | $ | 172,212 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 172,212 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | Amortized Cost | | Unrealized Gain | | Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value | | Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | Cash | $ | 50,947 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 50,947 | | Money market funds | 124,762 | | | — | | | — | | | 124,762 | | | Total cash and cash equivalents | $ | 175,709 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 175,709 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of cash, cash equivalents, and investments.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfCashCashEquivalentsAndShortTermInvestmentsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Fair Value Measurement (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Fair Value Disclosures [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Financial Instruments Measured at Fair Value |
The following table sets forth the Company's financial instruments on the balance sheet that were measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the period indicated by level within the fair value hierarchy (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | | | | | | | | Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Money market funds | $ | 147,342 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 147,342 | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | 147,342 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 147,342 | | | | | | | | | | Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Warrants | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 78,584 | | | $ | 78,584 | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 78,584 | | | $ | 78,584 | | | | | | | | | |
|
| Schedule of Carrying Amounts and Estimated Fair Values |
The following table presents the carrying amounts and estimated fair values of the financial instruments that are not recorded at fair value on the balance sheets (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 | | Net Carrying Amount | | Estimated Fair Value | | Net Carrying Amount | | Estimated Fair Value | | 2025 Convertible senior notes | $ | 26,653 | | | $ | 26,493 | | | $ | 170,564 | | | $ | 128,219 | | | 2028 Convertible senior notes | $ | 276,807 | | | $ | 216,291 | | | $ | 281,857 | | | $ | 99,978 | | 2029 Non-convertible notes | $ | 134,470 | | | $ | 140,889 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
|
| Schedule of Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques |
The aggregate fair value of the Warrants upon issuance and as of December 31, 2024 was $10.4 million and $78.6 million, respectively, determined using a Black-Scholes Model with the following inputs: | | | | | | | | | | | | | On issuance | | December 31, 2024 | | Stock price | $1.77 | | $10.93 | | Exercise price | $1.71 | | $1.71 | Expected life in years | 5.00 | | 4.17 | Expected volatility | 94.84 | % | | 96.75 | % | Expected dividends | — | % | | — | % | Discount rate | 4.26 | % | | 4.38 | % |
|
| Schedule Of Warrants |
The following table presents the activity related to the Warrants during the year ended December 31, 2024. | | | | | | | December 31, 2024 | Opening balance | $ | — | | | Issuance of warrants | 10,417 | | | Change in fair value | 68,167 | | Balance as of December 31, 2024 | $ | 78,584 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule Of Warrant Liability
| Name: |
real_ScheduleOfWarrantLiabilityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of input and valuation technique used to measure fair value and change in valuation approach and technique for each separate class of asset and liability measured on recurring and nonrecurring basis. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 103
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-103
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringAndNonrecurringBasisValuationTechniquesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueDisclosuresAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of information pertaining to carrying amount and estimated fair value of short-term and long-term debt instruments or arrangements, including but not limited to, identification of terms, features, and collateral requirements.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfCarryingValuesAndEstimatedFairValuesOfDebtInstrumentsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of assets and liabilities, including [financial] instruments measured at fair value that are classified in stockholders' equity, if any, that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis. The disclosures contemplated herein include the fair value measurements at the reporting date by the level within the fair value hierarchy in which the fair value measurements in their entirety fall, segregating fair value measurements using quoted prices in active markets for identical assets (Level 1), significant other observable inputs (Level 2), and significant unobservable inputs (Level 3). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfFairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringBasisTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Balance Sheet Components (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Balance Sheet Related Disclosures [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Property and Equipment, Net |
The estimated useful lives of our assets are as follows: | | | | | | | Proprietary software | 3 years | | Furniture and equipment | 3-5 years | | Vehicles | 5 years | | Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 | Proprietary software | $ | 47,416 | | | $ | 44,964 | | Furniture and equipment | 51,959 | | | 47,389 | | Automobiles | 2,036 | | | 2,069 | | Leasehold improvements | 88,840 | | | 84,138 | | | Property and equipment, gross | 190,251 | | | 178,560 | | | Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (95,808) | | | (74,473) | | | Property and equipment, net | $ | 94,443 | | | $ | 104,087 | |
|
| Schedule of Other Accrued and Current Liabilities |
Other accrued and current liabilities consist of the following (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 | | Returns reserve | $ | 22,409 | | | $ | 22,204 | | | Accrued compensation | 24,749 | | | 20,086 | | | Accrued sales tax and other taxes | 9,727 | | | 8,118 | | Site credit and gift card liability | 15,542 | | | 14,058 | | | Accrued marketing and outside services | 6,403 | | | 5,012 | | | Accrued shipping | 3,270 | | | 4,244 | | | Accrued interest | 4,996 | | | 1,166 | | | Deferred revenue | 2,441 | | | 2,214 | | | Other | 8,929 | | | 5,583 | | | Other accrued and current liabilities | $ | 98,466 | | | $ | 82,685 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule of other accrued and current liabilities.
| Name: |
real_ScheduleOfOtherAccruedAndCurrentLiabilitiesTableTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, balances by class of assets, depreciation and depletion expense and method used, including composite depreciation, and accumulated deprecation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Non-convertible Notes, Net (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Future Minimum Payments Under Notes |
A schedule of the Company's future maturities for the 2029 Notes with interest components included in principal, is as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | Amount | | Fiscal Year | | 2029 Notes | 2025 through 2028 | | $ | — | | 2029 | | 166,631 | | Total expected payments at maturity | | 166,631 | | Less unamortized debt issuance costs and debt premium, net | | (3,430) | | Less amounts related to PIK interest | | (28,730) | | Net carrying amount | | $ | 134,470 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Amount | | Fiscal Year | 2025 Notes | | 2028 Notes | 2025 | $ | 26,749 | | | $ | — | | 2026 | — | | | — | | 2027 | — | | | — | | 2028 | — | | | 281,019 | | Total principal payments | 26,749 | | | 281,019 | | Less unamortized debt issuance costs | (96) | | | (4,212) | | Net carrying amount | $ | 26,653 | | | $ | 276,807 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of maturity and sinking fund requirement for long-term debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfMaturitiesOfLongTermDebtTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Convertible Senior Notes, Net (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Amounts Recorded in Interest Expense Related to Notes |
The following table sets forth the amounts recorded in interest expense related to the 2025 Notes as of the dates indicated (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Contractual interest expense | $ | 1,531 | | | $ | 5,175 | | | $ | 5,175 | | | Amortization of debt issuance costs | 383 | | | 1,268 | | | 1,080 | | Total interest and amortization expense | $ | 1,914 | | | $ | 6,443 | | | $ | 6,255 | |
The following table sets forth the amounts recorded in interest expense related to the 2028 Notes as of the dates indicated (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Contractual interest expense | $ | 2,821 | | | $ | 2,875 | | | $ | 2,875 | | | Amortization of debt issuance costs | 1,308 | | | 1,305 | | | 1,288 | | Total interest and amortization expense | $ | 4,129 | | | $ | 4,180 | | | $ | 4,163 | |
|
| Schedule of Future Minimum Payments Under Notes |
A schedule of the Company's future maturities for the 2029 Notes with interest components included in principal, is as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | Amount | | Fiscal Year | | 2029 Notes | 2025 through 2028 | | $ | — | | 2029 | | 166,631 | | Total expected payments at maturity | | 166,631 | | Less unamortized debt issuance costs and debt premium, net | | (3,430) | | Less amounts related to PIK interest | | (28,730) | | Net carrying amount | | $ | 134,470 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Amount | | Fiscal Year | 2025 Notes | | 2028 Notes | 2025 | $ | 26,749 | | | $ | — | | 2026 | — | | | — | | 2027 | — | | | — | | 2028 | — | | | 281,019 | | Total principal payments | 26,749 | | | 281,019 | | Less unamortized debt issuance costs | (96) | | | (4,212) | | Net carrying amount | $ | 26,653 | | | $ | 276,807 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of interest income and expense, including, but not limited to, interest income and expense from investments, loans, and securities.
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestIncomeAndInterestExpenseDisclosureTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of maturity and sinking fund requirement for long-term debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfMaturitiesOfLongTermDebtTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Common Stock (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Common Stock [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Reserved Shares of Common Stock for Issuance on Converted Basis |
The Company had reserved shares of common stock for issuance, on an as-converted basis, as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31,
2024 | | December 31,
2023 | | Options issued and outstanding | 917,370 | | | 1,119,676 | | | Outstanding restricted stock units | 14,305,562 | | | 12,695,176 | | | Shares available for grant under the 2019 equity incentive plan | 5,490,650 | | | 7,654,656 | | | Shares available for issuance under 2019 ESPP | 4,135,266 | | | 3,654,915 | | Warrants to purchase common stock | 7,894,737 | | | — | | Total | 32,743,585 | | | 25,124,423 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommon stock capital shares reserved for future issuance.
| Name: |
real_CommonStockCapitalSharesReservedForFutureIssuanceTableTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Share-based Compensation Plans (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Stock Option Plan Activity |
Activity under the Company’s stock option plan is set forth below: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Number of
Options | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise
Price Per
Share | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(in thousands) | | Balances at December 31, 2023 | 1,119,676 | | | 7.79 | | | 4.2 | | $ | 15 | | | Options granted | — | | | — | | | | | | | Options exercised | (136,658) | | | 3.05 | | | | | | | Options cancelled | (65,648) | | | 8.53 | | | | | | | Balances at December 31, 2024 | 917,370 | | | 8.44 | | | 3.5 | | 3,445 | | | Options vested and exercisable— December 31, 2024 | 917,370 | | | 8.44 | | | 3.5 | | 3,445 | |
|
| Schedule of RSUs Activity |
A summary of RSU activity for the year ended December 31, 2024 is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Number of
Shares | | Restricted Stock Units
Weighted-
Average Grant
Date Fair
Value | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value
(in thousands) | | Unvested December 31, 2023 | 12,695,176 | | | $ | 4.07 | | | $ | 25,517 | | | Granted | 13,109,475 | | | 3.33 | | | | | Vested | (6,312,012) | | | 4.56 | | | | | Forfeited | (5,187,077) | | | 3.23 | | | | | Unvested December 31, 2024 | 14,305,562 | | | $ | 3.48 | | | $ | 156,360 | |
|
| Schedule of Assumptions to Estimate Fair Value of Stock Options |
The following assumptions were used to estimate the fair value of stock options granted in 2019, as there were no stock options granted in 2024, 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, 2019 | | Expected term (in years) | 5.0 – 6.1 | | Expected volatility | 44.2% – 47.8% | | Average risk-free rate | 1.9% – 2.6% | | Dividend yield | — |
|
| Schedule of Total Stock-based Compensation Expense |
Total stock-based compensation expense by function was as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Marketing | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,550 | | | $ | 2,209 | | | Operations and technology | 9,930 | | | 12,534 | | | 19,822 | | | Selling, general and administrative | 18,220 | | | 20,189 | | | 24,107 | | Total | $ | 29,082 | | | $ | 34,273 | | | $ | 46,138 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of allocation of amount expensed and capitalized for award under share-based payment arrangement to statement of income or comprehensive income and statement of financial position. Includes, but is not limited to, corresponding line item in financial statement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationAllocationOfRecognizedPeriodCostsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the number and weighted-average grant date fair value for restricted stock units that were outstanding at the beginning and end of the year, and the number of restricted stock units that were granted, vested, or forfeited during the year. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedCompensationRestrictedStockUnitsAwardActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure for stock option plans. Includes, but is not limited to, outstanding awards at beginning and end of year, grants, exercises, forfeitures, and weighted-average grant date fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedCompensationStockOptionsActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the significant assumptions used during the year to estimate the fair value of stock options, including, but not limited to: (a) expected term of share options and similar instruments, (b) expected volatility of the entity's shares, (c) expected dividends, (d) risk-free rate(s), and (e) discount for post-vesting restrictions. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedPaymentAwardStockOptionsValuationAssumptionsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Leases (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Maturities of Operating Lease Liabilities |
Maturities of operating lease liabilities by fiscal year for the Company’s operating leases are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | Fiscal Year | | Amount | | 2025 | | $ | 28,761 | | | 2026 | | 28,649 | | | 2027 | | 24,699 | | | 2028 | | 21,991 | | | 2029 | | 11,615 | | | Thereafter | | 8,822 | | | Total future minimum payments | | $ | 124,537 | | | Less: Imputed interest | | (15,912) | | | Present value of operating lease liabilities | | $ | 108,625 | |
|
| Schedule of Supplemental Cash Flow Information Related to Operating Leases |
Supplemental cash flow information related to the Company’s operating leases are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Operating cash flows used for operating leases | $ | 27,939 | | | $ | 34,118 | | | $ | 27,097 | | Operating lease assets obtained in exchange for operating lease liabilities (including remeasurement of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities due to lease modifications) | $ | 4,558 | | | $ | 6,272 | | | $ | 2,245 | |
|
| Schedule of Weighted Average Remaining Lease Term and Discount Rate for Operating Leases |
The weighted average remaining lease term and discount rate for the Company’s operating leases are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | As of December 31, 2024 | | As of December 31, 2023 | | Weighted average remaining lease term | 4.6 years | | 5.5 years | | Weighted average discount rate | 6.2 | % | | 6.1 | % |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule of cash flow supplemental information related to operating leases.
| Name: |
real_ScheduleOfCashFlowSupplementalInformationRelatedToOperatingLeasesTableTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule of weighted average remaining lease term and discount rate for operating leases.
| Name: |
real_ScheduleOfWeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTermAndDiscountRateForOperatingLeasesTableTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of undiscounted cash flows of lessee's operating lease liability. Includes, but is not limited to, reconciliation of undiscounted cash flows to operating lease liability recognized in statement of financial position. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityMaturityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of contractual obligation by timing of payment due. Includes, but is not limited to, long-term debt obligation, lease obligation, and purchase obligation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Regulation S-X (SX)
-Number 210
-Section 12
-Subsection 04
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher SEC
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
| Name: |
srt_ContractualObligationFiscalYearMaturityScheduleTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
srt_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Income Taxes (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Components of Company's Tax Provision |
The components of the Company’s income tax provision consisted of (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Current: | | | | | | Federal | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | State | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | | | Total current tax expense | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | | | Deferred: | | | | | | Federal | — | | | — | | — | State | — | | | — | | — | | Total deferred tax expense | — | | | — | | | — | | | Total provision for income taxes | $ | 276 | | | $ | 283 | | | $ | 172 | |
|
| Schedule of Reconciliation of Company's Effective Tax Rate To Statutory Federal Rate |
The reconciliation of the Federal statutory income tax provision for the Company’s effective income tax provision (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | Tax at federal statutory rate | $ | (28,144) | | | $ | (35,290) | | | $ | (41,209) | | State taxes, net of federal effect | (7,627) | | | (9,554) | | | (11,257) | | | Stock-based compensation | 3,192 | | | 8,956 | | | 419 | | Non-deductible items | 1,988 | | | 504 | | | 524 | | | Tax credits | (169) | | | (531) | | | (563) | | | | | | | | Warrant liability fair value adjustment | 18,333 | | | — | | | — | | | Adoption of ASU 2020-06 | — | | | — | | | (28,045) | | Provision to return adjustments | (1,927) | | | 9,259 | | | — | | Valuation allowance | 14,651 | | | 26,501 | | | 80,254 | | | Other | (21) | | | 438 | | | 49 | | | Provision for income taxes | $ | 276 | | | $ | 283 | | | $ | 172 | |
|
| Schedule of Components of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities |
The Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Deferred tax assets: | | | | Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 230,303 | | | $ | 232,259 | | Fixed assets and intangibles | 10,461 | | | 6,364 | | Capitalized research and development (1) | 18,679 | | | 13,835 | | Accruals and reserves | 18,685 | | | 12,477 | | | Stock options | 1,536 | | | 840 | | Operating lease liabilities | 29,424 | | | 33,683 | | | Capped calls | 15,011 | | | 15,065 | | | Convertible debt | — | | | 2,329 | | | Tax credits | 2,738 | | | 2,569 | | Other | 4,621 | | | — | | | Gross deferred tax assets | 331,458 | | | 319,421 | | Less: valuation allowance | (306,948) | | | (292,297) | | | Total deferred tax assets | 24,510 | | | 27,124 | | | Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | Operating lease right-of-use assets | (21,641) | | | (24,416) | | | | | | Other | (2,869) | | | (2,708) | | | Gross deferred tax liabilities | (24,510) | | | (27,124) | | | Net deferred tax assets | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
(1) Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, research and development costs are no longer fully deductible when incurred and are required to be capitalized and amortized for U.S. tax purposes effective January 1, 2022. The mandatory capitalization requirement increases our gross deferred tax assets, which are fully offset by the valuation allowance.
|
| Schedule of Unrecognized Tax Benefits |
The following table reflects the changes to the Company's unrecognized tax benefits (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | Unrecognized tax benefits beginning balance | $ | 2,678 | | | $ | 1,525 | | Increases related to current year tax positions | 169 | | | 531 | | Increases related to prior year tax positions | — | | | 622 | | Unrecognized tax benefits ending balance | $ | 2,847 | | | $ | 2,678 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for each year presented including, but not limited to: current tax expense (benefit), deferred tax expense (benefit), investment tax credits, government grants, the benefits of operating loss carryforwards, tax expense that results from allocating certain tax benefits either directly to contributed capital or to reduce goodwill or other noncurrent intangible assets of an acquired entity, adjustments of a deferred tax liability or asset for enacted changes in tax laws or rates or a change in the tax status of the entity, and adjustments of the beginning-of-the-year balances of a valuation allowance because of a change in circumstances that causes a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset in future years. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfComponentsOfIncomeTaxExpenseBenefitTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of net deferred tax asset or liability recognized in an entity's statement of financial position, including the following: the total of all deferred tax liabilities, the total of all deferred tax assets, the total valuation allowance recognized for deferred tax assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDeferredTaxAssetsAndLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the reconciliation using percentage or dollar amounts of the reported amount of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for the year to the amount of income tax expense that would result from applying domestic federal statutory tax rates to pretax income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 231
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-231
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEffectiveIncomeTaxRateReconciliationTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the change in unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfUnrecognizedTaxBenefitsRollForwardTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Earnings Per Share [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Reconciliation of Numerator and Denominator Used in Calculation of Basic and Diluted Net Loss Per Share |
A reconciliation of the numerator and denominator used in the calculation of the basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is as follows (in thousands, except share and per share data): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Numerator | | | | | | Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | | | Denominator | | | | | | Weighted-average common shares outstanding used to calculate net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | 107,878,366 | | | 101,806,000 | | | 95,921,246 | | Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (1.24) | | | $ | (1.65) | | | $ | (2.05) | |
|
| Schedule of Anti-dilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Diluted Net Loss Per Share |
The following securities were excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders for the periods presented, because including them would have been anti-dilutive (on an as-converted basis): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Options to purchase common stock | 917,370 | | | 1,119,676 | | | 1,754,776 | | | Restricted stock units | 14,305,562 | | | 12,695,176 | | | 11,369,021 | | | Estimated shares issuable under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 248,523 | | | 367,074 | | | 695,782 | | Assumed conversion of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes | 10,342,056 | | | 18,746,323 | | | 18,746,323 | | Warrants to purchase common stock | 7,894,737 | | | — | | | — | | Total | 33,708,248 | | | 32,928,249 | | | 32,565,902 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of securities (including those issuable pursuant to contingent stock agreements) that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share (EPS) in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS because to do so would increase EPS amounts or decrease loss per share amounts for the period presented, by antidilutive securities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfAntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of an entity's basic and diluted earnings per share calculations, including a reconciliation of numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted per-share computations for income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEarningsPerShareBasicAndDilutedTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Segment Information (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Segment Reporting [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Segment Information |
The following table presents selected financial information with respect to the Company's single operating segment (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Total revenue | $ | 600,484 | | | $ | 549,304 | | | $ | 603,493 | | | Less: | | | | | | | Cost of consignment revenue | 53,801 | | | 58,120 | | | 56,963 | | | Cost of direct revenue | 55,809 | | | 74,343 | | | 141,661 | | | Cost of shipping services revenue | 43,353 | | | 40,563 | | | 56,178 | | | Total cost of revenue | 152,963 | | | 173,026 | | | 254,802 | | | Gross Profit | 447,521 | | | 376,278 | | | 348,691 | | | Less: | | | | | | People costs | 283,002 | | | 274,229 | | | 297,676 | | Software and purchased services | 108,866 | | | 104,454 | | | 103,695 | | | Occupancy expense | 37,295 | | | 37,718 | | | 44,911 | | Depreciation and amortization(1) | 32,764 | | | 31,695 | | | 27,669 | | | Stock-based compensation | 29,082 | | | 34,273 | | | 46,138 | | Administration and other segment expenses (2) | 12,811 | | | 16,740 | | | 16,869 | | Restructuring (3) | 196 | | | 43,462 | | | 896 | | | Total operating expenses | 504,016 | | | 542,571 | | | 537,854 | | | Change in fair value of warrant liability | (68,167) | | | — | | | — | | | Gain on extinguishment of debt | 4,177 | | | — | | | — | | | Interest income | 7,943 | | | 8,805 | | | 3,191 | | | Interest expense | (21,384) | | | (10,701) | | | (10,472) | | | Other income (expense), net | — | | | — | | | 171 | | Provision for income taxes | 276 | | | 283 | | | 172 | | | Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (134,202) | | | $ | (168,472) | | | $ | (196,445) | |
(1) Expenses reported in operating expenses, excludes depreciation and amortization recorded in cost of revenue. (2) Administration and other segment expenses include insurance, supplies, and taxes. (3) Restructuring expenses for the year ended December 31, 2024 and 2022 consist of employee severance charges. For the year ended December 31, 2023 it consists of impairment of right-of-use assets and property and equipment, employee severance charges, gain on lease terminations, and other charges.
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the profit or loss and total assets for each reportable segment. An entity discloses certain information on each reportable segment if the amounts (a) are included in the measure of segment profit or loss reviewed by the chief operating decision maker or (b) are otherwise regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker, even if not included in that measure of segment profit or loss. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-25
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfSegmentReportingInformationBySegmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies - Additional Information (Details)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
|
Dec. 31, 2024
USD ($)
segment
|
Dec. 31, 2023
USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2022
USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2021 |
Jun. 30, 2020 |
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Undistributed earnings allocated to participating securities |
$ 0
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of operating segment | segment |
1
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of reportable segment | segment |
1
|
|
|
|
|
| Advertising expense |
$ 42,900,000
|
$ 48,400,000
|
$ 49,000,000.0
|
|
|
| Restricted cash |
14,911,000
|
14,914,000
|
0
|
|
|
| Provision for inventory write-downs and shrinkage |
2,590,000
|
9,783,000
|
4,077,000
|
|
|
| Rights to recover products from customers |
$ 4,800,000
|
5,200,000
|
|
|
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes interest rate (in percent) |
3.00%
|
|
|
|
3.00%
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes interest rate (in percent) |
1.00%
|
|
|
1.00%
|
|
| Other Accrued and Current Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Inventory return reserves allowances |
$ 22,400,000
|
22,200,000
|
|
|
|
| Proprietary software |
|
|
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Research and development expense |
$ 11,800,000
|
$ 13,300,000
|
$ 15,600,000
|
|
|
| Property and equipment, useful life (in years) |
3 years
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionInventory return reserves allowances.
| Name: |
real_InventoryReturnReservesAllowances |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRights to recover products from customers.
| Name: |
real_RightsToRecoverProductsFromCustomers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSummary of significant accounting policies.
| Name: |
real_SummaryOfSignificantAccountingPoliciesLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount charged to advertising expense for the period, which are expenses incurred with the objective of increasing revenue for a specified brand, product or product line. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 720
-SubTopic 35
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483385/720-35-55-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 720
-SubTopic 35
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483406/720-35-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdvertisingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContractual interest rate for funds borrowed, under the debt agreement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateStatedPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of loss from reductions in inventory due to subsequent measurement adjustments, including, but not limited to, physical deterioration, obsolescence, or changes in price levels. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryWriteDown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of operating segments. An operating segment is a component of an enterprise: (a) that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses (including revenues and expenses relating to transactions with other components of the same enterprise), (b) whose operating results are regularly reviewed by the enterprise's chief operating decision maker to make decisions about resources to be allocated to the segment and assess its performance, and (c) for which discrete financial information is available. An operating segment may engage in business activities for which it has yet to earn revenues, for example, start-up operations may be operating segments before earning revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_NumberOfOperatingSegments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of segments reported by the entity. A reportable segment is a component of an entity for which there is an accounting requirement to report separate financial information on that component in the entity's financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 54
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-54
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_NumberOfReportableSegments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of long lived, physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Examples include, but not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, furniture and fixtures, and computer equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for research and development. Includes, but is not limited to, cost for computer software product to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed and writeoff of research and development assets acquired in transaction other than business combination or joint venture formation or both. Excludes write-down of intangible asset acquired in business combination or from joint venture formation or both, used in research and development activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482916/730-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 730
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479532/912-730-25-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash restricted as to withdrawal or usage. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(1)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of undistributed earnings (loss) allocated to participating securities for the basic earnings (loss) per share or per unit calculation under the two-class method. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 65
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-65
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 66
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-66
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UndistributedEarningsLossAllocatedToParticipatingSecuritiesBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=real_OtherAccruedAndCurrentLiabilitiesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_SoftwareDevelopmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies - Schedule of Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
Dec. 31, 2021 |
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ 172,212
|
$ 175,709
|
$ 293,793
|
|
| Restricted cash |
14,911
|
14,914
|
0
|
|
| Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
$ 187,123
|
$ 190,623
|
$ 293,793
|
$ 418,171
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage. Excludes amount for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash restricted as to withdrawal or usage. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(1)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.25.0.1
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies - Schedule of Property and Equipment, Net (Details)
|
Dec. 31, 2024 |
| Proprietary software |
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
| Property and equipment, useful life (in years) |
3 years
|
| Furniture and equipment | Minimum |
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
| Property and equipment, useful life (in years) |
3 years
|
| Furniture and equipment | Maximum |
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
| Property and equipment, useful life (in years) |
5 years
|
| Vehicles |
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
| Property and equipment, useful life (in years) |
5 years
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of long lived, physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Examples include, but not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, furniture and fixtures, and computer equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_SoftwareDevelopmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_FurnitureAndFixturesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_VehiclesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Cash and Cash Equivalents (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Cash and Cash Equivalents [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ 172,212
|
$ 175,709
|
$ 293,793
|
| Money market funds |
172,212
|
175,709
|
|
| Restricted Cash |
|
|
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Unrealized gain |
0
|
|
|
| Unrealized loss |
0
|
|
|
| Cash |
|
|
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
24,870
|
50,947
|
|
| Money market funds |
24,870
|
50,947
|
|
| Money market funds |
|
|
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
147,342
|
124,762
|
|
| Money market funds |
$ 147,342
|
$ 124,762
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionCash And Cash Equivalents Unrealized Gain
| Name: |
real_CashAndCashEquivalentsUnrealizedGain |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCash And Cash Equivalents Unrealized Loss
| Name: |
real_CashAndCashEquivalentsUnrealizedLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsCashAndCashEquivalentsAxis=real_RestrictedCashMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentTypeAxis=us-gaap_CashMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentTypeAxis=us-gaap_MoneyMarketFundsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Fair Value Measurement - Schedule of Financial Instruments Measured at Fair Value (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Feb. 29, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Money market funds |
$ 172,212
|
|
$ 175,709
|
| Financial liabilities: |
|
|
|
| Warrants |
78,584
|
$ 10,400
|
0
|
| Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Total |
147,342
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities: |
|
|
|
| Warrants |
78,584
|
|
|
| Total |
78,584
|
|
|
| Level 1 | Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Total |
147,342
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities: |
|
|
|
| Warrants |
0
|
|
|
| Total |
0
|
|
|
| Level 2 | Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Total |
0
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities: |
|
|
|
| Warrants |
0
|
|
|
| Total |
0
|
|
|
| Level 3 | Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Total |
0
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities: |
|
|
|
| Warrants |
78,584
|
|
|
| Total |
78,584
|
|
|
| Money market funds | Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Money market funds |
147,342
|
|
$ 124,800
|
| Money market funds | Level 1 | Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Money market funds |
147,342
|
|
|
| Money market funds | Level 2 | Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Money market funds |
0
|
|
|
| Money market funds | Level 3 | Recurring |
|
|
|
| Financial assets: |
|
|
|
| Money market funds |
$ 0
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionWarrant Liability, Noncurrent
| Name: |
real_WarrantLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of asset recognized for present right to economic benefit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsFairValueDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value of financial and nonfinancial obligations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesFairValueDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByMeasurementFrequencyAxis=us-gaap_FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByAssetClassAxis=us-gaap_MoneyMarketFundsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Fair Value Measurement - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, $ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Feb. 29, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Money market funds |
$ 172,212
|
|
$ 175,709
|
| Aggregate number of shares that can be acquired via the warrants issued (in shares) |
|
7,894,737
|
|
| Exercise price (in dollars per share) |
|
$ 1.71
|
|
| Warrant liability |
78,584
|
$ 10,400
|
0
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
26,700
|
|
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
281,000
|
|
|
| 2029 Non-convertible notes |
|
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
137,900
|
|
|
| Recurring |
|
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Warrant liability |
78,584
|
|
|
| Recurring | Money market funds |
|
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Money market funds |
$ 147,342
|
|
$ 124,800
|
| X |
- DefinitionWarrant Liability, Noncurrent
| Name: |
real_WarrantLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionExercise price per share or per unit of warrants or rights outstanding. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightExercisePriceOfWarrantsOrRights1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of securities into which the class of warrant or right may be converted. For example, but not limited to, 500,000 warrants may be converted into 1,000,000 shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightNumberOfSecuritiesCalledByWarrantsOrRights |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace (par) amount of debt instrument at time of issuance. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentFaceAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringAndNonrecurringBasisLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=real_A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=real_A2029ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByMeasurementFrequencyAxis=us-gaap_FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByAssetClassAxis=us-gaap_MoneyMarketFundsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Fair Value Measurement- Schedule of Carrying Amounts and Estimated Fair Values (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| 2025 Convertible senior notes | Net Carrying Amount |
|
|
| Fair Value, Balance Sheet Grouping, Financial Statement Captions [Line Items] |
|
|
| Convertible notes payable |
$ 26,653
|
$ 170,564
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes | Estimated Fair Value |
|
|
| Fair Value, Balance Sheet Grouping, Financial Statement Captions [Line Items] |
|
|
| Notes payable, fair value disclosure |
26,493
|
128,219
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | Net Carrying Amount |
|
|
| Fair Value, Balance Sheet Grouping, Financial Statement Captions [Line Items] |
|
|
| Convertible notes payable |
276,807
|
281,857
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | Estimated Fair Value |
|
|
| Fair Value, Balance Sheet Grouping, Financial Statement Captions [Line Items] |
|
|
| Notes payable, fair value disclosure |
216,291
|
99,978
|
| 2029 Non-convertible notes | Net Carrying Amount |
|
|
| Fair Value, Balance Sheet Grouping, Financial Statement Captions [Line Items] |
|
|
| Convertible notes payable |
134,470
|
0
|
| 2029 Non-convertible notes | Estimated Fair Value |
|
|
| Fair Value, Balance Sheet Grouping, Financial Statement Captions [Line Items] |
|
|
| Notes payable, fair value disclosure |
$ 140,889
|
$ 0
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncluding the current and noncurrent portions, carrying value as of the balance sheet date of a written promise to pay a note, initially due after one year or beyond the operating cycle if longer, which can be exchanged for a specified amount of one or more securities (typically common stock), at the option of the issuer or the holder. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConvertibleNotesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueBalanceSheetGroupingFinancialStatementCaptionsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of notes payable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2E
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NotesPayableFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=real_A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByMeasurementBasisAxis=us-gaap_CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByMeasurementBasisAxis=us-gaap_EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=real_A2029ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Fair Value Measurement - Schedule of Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques (Details)
|
Dec. 31, 2024
$ / shares
yr
|
Feb. 29, 2024
$ / shares
yr
|
| Stock price |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrant liability measurement input (in usd per share, years, percent) |
10.93
|
1.77
|
| Exercise price |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrant liability measurement input (in usd per share, years, percent) |
1.71
|
1.71
|
| Expected life in years |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrant liability measurement input (in usd per share, years, percent) | yr |
4.17
|
5.00
|
| Expected volatility |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrant liability measurement input (in usd per share, years, percent) |
0.9675
|
0.9484
|
| Expected dividends |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrant liability measurement input (in usd per share, years, percent) |
0
|
0
|
| Discount rate |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrant liability measurement input (in usd per share, years, percent) |
0.0438
|
0.0426
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 103
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-103
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringAndNonrecurringBasisValuationTechniquesLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionWarrant Liability, Gain (Loss)
| Name: |
real_WarrantLiabilityGainLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWarrant Liability, Issuances
| Name: |
real_WarrantLiabilityIssuances |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWarrant Liability, Noncurrent
| Name: |
real_WarrantLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueDisclosuresAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Balance Sheet Components - Schedule of Property and Equipment, Net (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 190,251
|
$ 178,560
|
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(95,808)
|
(74,473)
|
| Property and equipment, net |
94,443
|
104,087
|
| Proprietary software |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
47,416
|
44,964
|
| Furniture and equipment |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
51,959
|
47,389
|
| Automobiles |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
2,036
|
2,069
|
| Leasehold improvements |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 88,840
|
$ 84,138
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization for physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedDepreciationDepletionAndAmortizationPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(13))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478451/942-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=real_ProprietarySoftwareMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=real_FurnitureAndEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_AutomobilesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_LeaseholdImprovementsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionThe current period expense charged against earnings on long-lived, physical assets not used in production, and which are not intended for resale, to allocate or recognize the cost of such assets over their useful lives; or to record the reduction in book value of an intangible asset over the benefit period of such asset; or to reflect consumption during the period of an asset that is not used in production. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe adjustment to reduce the value of existing agreements that specify the lessee's rights to use the leased property. This expense is charged when the estimates of future profits generated by the leased property are reduced. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLeasehold |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Balance Sheet Components - Schedule of Other Accrued and Current Liabilities (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Balance Sheet Related Disclosures [Abstract] |
|
|
| Returns reserve |
$ 22,409
|
$ 22,204
|
| Accrued compensation |
24,749
|
20,086
|
| Accrued sales tax and other taxes |
9,727
|
8,118
|
| Site credit and gift card liability |
15,542
|
14,058
|
| Accrued marketing and outside services |
6,403
|
5,012
|
| Accrued shipping |
3,270
|
4,244
|
| Accrued interest |
4,996
|
1,166
|
| Deferred revenue |
2,441
|
2,214
|
| Other |
8,929
|
5,583
|
| Other accrued and current liabilities |
$ 98,466
|
$ 82,685
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccrued returns reserve current.
| Name: |
real_AccruedReturnsReserveCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
real_SiteCreditAndGiftCardLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred through that date and payable for the marketing, trade and selling of the entity's goods and services. Marketing costs would include expenditures for planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services; costs of public relations and corporate promotions; and obligations incurred and payable for sales discounts, rebates, price protection programs, etc. offered to customers and under government programs. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer).
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedMarketingCostsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of the obligations incurred through that date and payable for employees' services provided. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedSalariesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of [accrued] interest payable on all forms of debt, including trade payables, that has been incurred and is unpaid. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionObligations not otherwise itemized or categorized in the footnotes to the financial statements that are due within one year or operating cycle, if longer, from the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481573/470-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherSundryLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable for statutory income, sales, use, payroll, excise, real, property and other taxes. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxesPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.25.0.1
Non-convertible Notes, Net - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
|
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Feb. 29, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
Mar. 31, 2021 |
Jun. 30, 2020 |
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gain on extinguishment of debt |
|
$ 4,177,000
|
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
|
|
| Issuance costs allocated to liability classified warrants |
$ 400,000
|
374,000
|
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
|
|
| Senior Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Decrease in debt balance |
17,200,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gain on extinguishment of debt |
4,200,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
|
$ 26,700,000
|
|
|
|
$ 172,500,000
|
| Notes interest rate (in percent) |
|
3.00%
|
|
|
|
3.00%
|
| Effective interest rate (in percent) |
|
3.74%
|
|
|
|
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes | Senior Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Aggregate principal amount exchanged |
145,800,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
|
$ 281,000,000
|
|
|
$ 287,500,000
|
|
| Notes interest rate (in percent) |
|
1.00%
|
|
|
1.00%
|
|
| Effective interest rate (in percent) |
|
1.45%
|
|
|
|
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | Senior Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Aggregate principal amount exchanged |
6,500,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | Minimum | Senior Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Maturity threshold of debt outstanding |
20,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | Maximum | Senior Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Maturity threshold of debt outstanding |
75,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2029 Convertible Senior Notes | Senior Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
$ 135,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Payable-in-kind interest (in percent) |
4.25%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash interest rate (percent) |
8.75%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes interest rate (in percent) |
13.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Paid-in-kind interest added to debt principal |
|
$ 2,900,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Effective interest rate (in percent) |
13.35%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Liquidity threshold |
$ 25,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2029 Convertible Senior Notes | Senior Notes | March 1, 2025 to (but excluding) March 1, 2026 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt redemption price (percent) |
113.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2029 Convertible Senior Notes | Senior Notes | March 1, 2026 to (but excluding) October 1, 2026 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt redemption price (percent) |
106.50%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2029 Convertible Senior Notes | Senior Notes | October 1, 2026 and thereafter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt redemption price (percent) |
100.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2029 Convertible Senior Notes | Senior Notes | prior to March 1, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentage of debt principal that can be redeemed (percent) |
100.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2029 Convertible Senior Notes | Senior Notes | any time and from time to time on or prior to March 1, 2025 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt redemption price (percent) |
113.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentage of debt principal that can be redeemed (percent) |
40.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentage of aggregate principal to remain outstanding (percent) |
60.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Accrued Paid-In-Kind Interest, Capitalized
| Name: |
real_DebtInstrumentAccruedPaidInKindInterestCapitalized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Covenant, Debt Outstanding Maturity Threshold
| Name: |
real_DebtInstrumentCovenantDebtOutstandingMaturityThreshold |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Covenant, Liquidity Threshold, Amount
| Name: |
real_DebtInstrumentCovenantLiquidityThresholdAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Covenant, Redemption Price, Percentage Threshold Of Aggregate Principal Outstanding
| Name: |
real_DebtInstrumentCovenantRedemptionPricePercentageThresholdOfAggregatePrincipalOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Payable-In-Cash, Interest Percentage
| Name: |
real_DebtInstrumentPayableInCashInterestPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Payable-In-Kind, Interest Percentage
| Name: |
real_DebtInstrumentPayableInKindInterestPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIssuance of Warrant Liability, Issuance Costs
| Name: |
real_IssuanceOfWarrantLiabilityIssuanceCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace (par) amount of debt instrument at time of issuance. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentFaceAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNet increase or decrease in the carrying amount of the debt instrument for the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentIncreaseDecreaseForPeriodNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEffective interest rate for the funds borrowed under the debt agreement considering interest compounding and original issue discount or premium. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateEffectivePercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContractual interest rate for funds borrowed, under the debt agreement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateStatedPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage price of original principal amount of debt at which debt can be redeemed by the issuer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 470
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477734/942-470-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPricePercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage of principal amount of debt redeemed.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPricePercentageOfPrincipalAmountRedeemed |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace (par) amount of the original debt instrument that was repurchased.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRepurchasedFaceAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDifference between the fair value of payments made and the carrying amount of debt which is extinguished prior to maturity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainsLossesOnExtinguishmentOfDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=us-gaap_SeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2029SeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodAxis=us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodAxis=us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodAxis=us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodAxis=us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodAxis=us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFiveMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAccrued Paid-in-Kind Interest
| Name: |
real_AccruedPaidInKindInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLong-Term Debt, Maturity, Including Interest
| Name: |
real_LongTermDebtMaturityIncludingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unamortized debt discount (premium) and debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentUnamortizedDiscountPremiumAndDebtIssuanceCostsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of unamortized premium (discount) and debt issuance cost, of long-term debt. Excludes lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2029SeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Convertible Senior Notes, Net - Additional Information (Details)
|
|
1 Months Ended |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
|
Feb. 29, 2024
USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2021
USD ($)
$ / shares
|
Jun. 30, 2020
USD ($)
$ / shares
|
Dec. 31, 2024
USD ($)
d
shares
|
Dec. 31, 2023
USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2022
USD ($)
|
Mar. 03, 2021
$ / shares
|
Jun. 10, 2020
$ / shares
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash received from settlement of capped calls in conjunction with the 2024 Note Exchange |
|
|
|
$ 396,000
|
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
|
|
| Purchased Calls |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash received from settlement of capped calls in conjunction with the 2024 Note Exchange |
$ 400,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
|
|
$ 172,500,000
|
$ 26,700,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Net proceeds from the notes offering |
|
|
165,800,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Proceeds to fund net cost of entering into capped calls |
|
|
$ 22,500,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes interest rate (in percent) |
|
|
3.00%
|
3.00%
|
|
|
|
|
| Initial conversion rate |
|
|
5.62635%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Initial conversion price (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
$ 17.77
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold percentage of stock price trigger (in percent) |
|
|
|
130.00%
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold trading days | d |
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold consecutive trading days | d |
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentage on aggregate principal amount of notes to be payable upon the event of default (in percent) |
|
|
|
25.00%
|
|
|
|
|
| Long-term debt |
|
|
|
$ 26,700,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Unamortized issuance costs |
|
|
|
$ 100,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Amortization period (in years) |
|
|
|
5 years
|
|
|
|
|
| Effective interest rate (in percent) |
|
|
|
3.74%
|
|
|
|
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes | Purchased Calls |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Payment to counterparties for purchased calls |
|
|
$ 22,500,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Common stock subject to adjustment and exercisable upon conversion of initial notes (in shares) | shares |
|
|
|
9,705,454
|
|
|
|
|
| Capped call, initial strike price (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ 27.88
|
| Capped call, premium over closing stock price |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100.00%
|
| Closing price of common stock per share (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ 13.94
|
| Reduction to additional paid premium payments for capped call transactions |
|
|
$ 22,500,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Common stock outstanding included in the capped call transaction (in shares) | shares |
|
|
|
1,504,992
|
|
|
|
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes | Conversion Option One |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold percentage of stock price trigger (in percent) |
|
|
|
130.00%
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold trading days | d |
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold consecutive trading days | d |
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
|
|
| 2025 Convertible senior notes | Conversion Option Two |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold percentage of stock price trigger (in percent) |
|
|
|
98.00%
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold trading days | d |
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes, threshold consecutive trading days | d |
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
|
$ 287,500,000
|
|
$ 281,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Net proceeds from the notes offering |
|
278,100,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Proceeds to fund net cost of entering into capped calls |
|
$ 33,700,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes interest rate (in percent) |
|
1.00%
|
|
1.00%
|
|
|
|
|
| Initial conversion rate |
|
3.14465%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Initial conversion price (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
$ 31.80
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long-term debt |
|
|
|
$ 276,800,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Unamortized issuance costs |
|
|
|
$ 4,200,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Amortization period (in years) |
|
|
|
7 years
|
|
|
|
|
| Effective interest rate (in percent) |
|
|
|
1.45%
|
|
|
|
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | Purchased Calls |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Payment to counterparties for purchased calls |
|
$ 33,700,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Common stock subject to adjustment and exercisable upon conversion of initial notes (in shares) | shares |
|
|
|
9,040,869
|
|
|
|
|
| Capped call, initial strike price (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ 48.00
|
|
| Capped call, premium over closing stock price |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100.00%
|
|
| Closing price of common stock per share (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ 24.00
|
|
| Reduction to additional paid premium payments for capped call transactions |
|
$ 33,700,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Common stock outstanding included in the capped call transaction (in shares) | shares |
|
|
|
8,837,095
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAdjustments to additional paid premium payments for capped call transactions.
| Name: |
real_AdjustmentsToAdditionalPaidPremiumPaymentsForCappedCallTransactions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCapped Call, Initial Strike Price
| Name: |
real_CappedCallInitialStrikePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCapped Call, Premium Over Closing Stock Price
| Name: |
real_CappedCallPremiumOverClosingStockPrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommon Stock Subject To Adjustment And Exercisable Upon Conversion Of Initial Notes
| Name: |
real_CommonStockSubjectToAdjustmentAndExercisableUponConversionOfInitialNotes |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPayment to counterparties for purchased calls.
| Name: |
real_PaymentToCounterpartiesForPurchasedCalls |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage on aggregate principal amount of notes to be payable upon the event of default.
| Name: |
real_PercentageOnAggregatePrincipalAmountOfNotesToBePayableUponEventOfDefault |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPurchase of capped calls.
| Name: |
real_PurchaseOfCappedCalls |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDividend or interest rate associated with the financial instrument issued in exchange for the original debt being converted in a noncash or part noncash transaction. Noncash are transactions that affect recognized assets or liabilities but that do not result in cash receipts or cash payments. Part noncash refers to that portion of the transaction not resulting in cash receipts or cash payments. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtConversionConvertedInstrumentRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe price per share of the conversion feature embedded in the debt instrument. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentConvertibleConversionPrice1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThreshold period of specified consecutive trading days within which common stock price to conversion price of convertible debt instrument must exceed threshold percentage for specified number of trading days to trigger conversion feature.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentConvertibleThresholdConsecutiveTradingDays1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionMinimum percentage of common stock price to conversion price of convertible debt instruments to determine eligibility of conversion.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentConvertibleThresholdPercentageOfStockPriceTrigger |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThreshold number of specified trading days that common stock price to conversion price of convertible debt instruments must exceed threshold percentage within a specified consecutive trading period to trigger conversion feature.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentConvertibleThresholdTradingDays |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace (par) amount of debt instrument at time of issuance. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentFaceAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEffective interest rate for the funds borrowed under the debt agreement considering interest compounding and original issue discount or premium. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateEffectivePercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContractual interest rate for funds borrowed, under the debt agreement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateStatedPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod of time between issuance and maturity of debt instrument, in PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of underlying investment in derivative. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 320
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-13(Column A)(Footnote 3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477271/946-320-S99-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 320
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5C
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-13C(Column A)(Footnote 3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477271/946-320-S99-5C
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 320
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5C
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-13C(Column B)(Footnote 3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477271/946-320-S99-5C
| Name: |
us-gaap_DerivativeUnderlyingInvestmentShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of unamortized premium (discount) and debt issuance cost, of long-term debt. Excludes lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow from the issuance of a long-term debt instrument which can be exchanged for a specified amount of another security, typically the entity's common stock, at the option of the issuer or the holder. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromConvertibleDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow provided by derivative instruments during the period, which are classified as financing activities, excluding those designated as hedging instruments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 23
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-23
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromDerivativeInstrumentFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPrice of a single share of a number of saleable stocks of a company.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe remaining balance of debt issuance expenses that were capitalized and are being amortized against income over the lives of the respective bond issues. This does not include the amounts capitalized as part of the cost of the utility plant or asset.
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnamortizedDebtIssuanceExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OptionIndexedToIssuersEquityEquityAxis=real_CappedCallTransactionsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodAxis=real_ConversionOptionOneMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodAxis=real_ConversionOptionTwoMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Convertible Senior Notes, Net - Schedule of Amounts Recorded in Interest Expense Related to Notes (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| 2025 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Contractual interest expense |
$ 1,531
|
$ 5,175
|
$ 5,175
|
| Amortization of debt issuance costs |
383
|
1,268
|
1,080
|
| Total interest and amortization expense |
1,914
|
6,443
|
6,255
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Contractual interest expense |
2,821
|
2,875
|
2,875
|
| Amortization of debt issuance costs |
1,308
|
1,305
|
1,288
|
| Total interest and amortization expense |
$ 4,129
|
$ 4,180
|
$ 4,163
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense attributable to debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfFinancingCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of the cost of borrowed funds accounted for as interest expense for debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpenseDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRepresents the portion of interest incurred in the period on debt arrangements that was charged against earnings, excluding amortization of debt discount (premium) and financing costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpenseDebtExcludingAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionLong-Term Debt, Maturity, Including Interest
| Name: |
real_LongTermDebtMaturityIncludingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before unamortized (discount) premium and debt issuance costs, of long-term debt. Includes, but is not limited to, notes payable, bonds payable, commercial loans, mortgage loans, convertible debt, subordinated debt and other types of debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentCarryingAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unamortized debt discount (premium) and debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentUnamortizedDiscountPremiumAndDebtIssuanceCostsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Common Stock (Details) - shares
|
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common stock reserved for future issuance (in shares) |
32,743,585
|
25,124,423
|
| Warrants To Purchase Common Stock |
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common stock reserved for future issuance (in shares) |
7,894,737
|
0
|
| 2019 Equity Incentive Plan |
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common stock reserved for future issuance (in shares) |
5,490,650
|
7,654,656
|
| 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common stock reserved for future issuance (in shares) |
4,135,266
|
3,654,915
|
| Outstanding Restricted Stock Units |
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common stock reserved for future issuance (in shares) |
14,305,562
|
12,695,176
|
| Options Issued and Outstanding |
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common stock reserved for future issuance (in shares) |
917,370
|
1,119,676
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/recommendedDisclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483014/272-10-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482987/272-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(27)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfStockLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate number of common shares reserved for future issuance. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockCapitalSharesReservedForFutureIssuance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightAxis=real_WarrantsToPurchaseCommonStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=real_TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=real_TwoThousandNineteenEmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=real_OptionsIssuedAndOutstandingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Share-based Compensation Plans - Additional Information (Details)
|
1 Months Ended |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
Oct. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023
tranche
|
Feb. 28, 2022 |
Dec. 31, 2024
USD ($)
tranche
$ / shares
shares
|
Dec. 31, 2023
USD ($)
$ / shares
shares
|
Dec. 31, 2022
USD ($)
$ / shares
shares
|
Feb. 20, 2024
shares
|
Feb. 13, 2023
shares
|
Feb. 23, 2022
shares
|
May 05, 2021
shares
|
Dec. 31, 2019
shares
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised | $ |
|
|
|
|
$ 300,000
|
$ 0
|
$ 5,300,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based payment arrangement, expense | $ |
|
|
|
|
29,082,000
|
34,273,000
|
46,138,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation capitalized to proprietary software development costs | $ |
|
|
|
|
$ 504,000
|
$ 777,000
|
1,629,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based payment arrangement, expense | $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ 1,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Estimated shares issuable under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of authorized (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
1,750,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annual increase in available number of authorized (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
1,750,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annual increase in number of shares, percentage of shares of outstanding common stock (in percent) |
|
|
|
|
1.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Increase in available for grant (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,046,705
|
990,882
|
929,601
|
893,016
|
|
| Options granted as percentage on fair value of stock (in percent) |
|
|
|
|
85.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of purchased (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
566,354
|
865,676
|
610,877
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average price of purchased (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
$ 2.49
|
$ 1.02
|
$ 2.29
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Unrecognized compensation costs | $ |
|
|
|
|
$ 0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Performance Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period (in years) |
3 years
|
3 years
|
|
3 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based payment arrangement, expense | $ |
|
|
|
|
$ 0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
2,535,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vested (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
98,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Forfeited (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
1,979,678
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Granted (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
$ 3.31
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vested (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
1.63
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Forfeited (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
$ 2.53
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Outstanding Restricted Stock Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nonvested, number of shares (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
14,305,562
|
12,695,176
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
13,109,475
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vested (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
6,312,012
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Forfeited (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
5,187,077
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Granted (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
$ 3.33
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vested (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
4.56
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Forfeited (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
|
|
$ 3.23
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vested in period, fair value | $ |
|
|
|
|
$ 21,700,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| RSUs and PSUs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Unrecognized compensation costs | $ |
|
|
|
|
$ 43,300,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Weighted average period expect to recognized |
|
|
|
|
2 years 2 months 12 days
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Options to purchase common stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Unrecognized compensation costs | $ |
|
|
|
|
$ 0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Minimum | Performance Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Performance target, percentage (in percent) |
0.00%
|
0.00%
|
|
0.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Maximum | Performance Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Performance target, percentage (in percent) |
200.00%
|
200.00%
|
|
150.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2019 Equity Incentive Plan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of authorized (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,000,000
|
| Annual increase in available number of authorized (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,000,000
|
| Annual increase in number of shares, percentage of shares of outstanding common stock (in percent) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.00%
|
| Increase in available for grant (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,233,525
|
4,954,409
|
4,648,003
|
4,465,083
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2019 Equity Incentive Plan | Performance Shares | Share-Based Payment Arrangement, Employee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period (in years) |
|
|
5 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of tranche | tranche |
|
|
3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Inducement Grants | Share-Based Payment Arrangement, Employee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nonvested, number of shares (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
5,625,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Inducement Grants | Performance Shares | Share-Based Payment Arrangement, Employee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period (in years) |
|
|
|
|
5 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of tranche | tranche |
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nonvested, number of shares (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
2,050,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Inducement Grants | Outstanding Restricted Stock Units | Share-Based Payment Arrangement, Employee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nonvested, number of shares (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
3,575,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate Intrinsic Value of Options Exercised
| Name: |
real_AggregateIntrinsicValueOfOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare based compensation arrangement by share based payment award increase in number of shares available for grant.
| Name: |
real_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardIncreaseInNumberOfSharesAvailableForGrant |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare based compensation arrangement by share based payment award number of shares authorized annual increase percent of shares outstanding.
| Name: |
real_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAuthorizedAnnualIncreasePercentOfSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare based compensation arrangement by share based payment award number of shares authorized annual increase shares.
| Name: |
real_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAuthorizedAnnualIncreaseShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-Based Compensation Arrangement by Share-Based Payment Award, Vesting, Number of Tranche
| Name: |
real_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardVestingNumberOfTranche |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost capitalized for award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationAllocationOfRecognizedPeriodCostsCapitalizedAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost not yet recognized for nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted-average period over which cost not yet recognized is expected to be recognized for award under share-based payment arrangement, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognizedPeriodForRecognition1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod over which grantee's right to exercise award under share-based payment arrangement is no longer contingent on satisfaction of service or performance condition, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, combination of market, performance or service condition. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardAwardVestingPeriod1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that were forfeited during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeitedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average fair value as of the grant date of equity-based award plans other than stock (unit) option plans that were not exercised or put into effect as a result of the occurrence of a terminating event. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeituresWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of grants made during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value at grant date for nonvested equity-based awards issued during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of non-vested equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that validly exist and are outstanding as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that vested during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value of share-based awards for which the grantee gained the right by satisfying service and performance requirements, to receive or retain shares or units, other instruments, or cash. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriodTotalFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value as of grant date pertaining to an equity-based award plan other than a stock (or unit) option plan for which the grantee gained the right during the reporting period, by satisfying service and performance requirements, to receive or retain shares or units, other instruments, or cash in accordance with the terms of the arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares authorized for issuance under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGross number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPer share weighted-average price paid for shares purchased on open market for issuance under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardPerShareWeightedAveragePriceOfSharesPurchased |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares purchased for issuance under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardSharesPurchasedForAward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPurchase price of common stock expressed as a percentage of its fair value.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardPurchasePriceOfCommonStockPercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=srt_ChiefExecutiveOfficerMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsidiarySaleOfStockAxis=us-gaap_EmployeeStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_EmployeeStockOptionMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=real_TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GranteeStatusAxis=us-gaap_ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=real_InducementGrantsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Share-based Compensation Plans - Schedule of Stock Option Plan Activity (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Number of Options |
|
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
0
|
| 2019 Equity Incentive Plan |
|
|
|
| Number of Options |
|
|
|
| Number of options , beginning balance (in shares) |
1,119,676
|
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
0
|
|
|
| Exercised (in shares) |
(136,658)
|
|
|
| Cancelled (in shares) |
(65,648)
|
|
|
| Number of options, ending balance (in shares) |
917,370
|
1,119,676
|
|
| Options vested and exercisable (in shares) |
917,370
|
|
|
| Weighted- Average Exercise Price Per Share |
|
|
|
| Beginning balance (in dollars per share) |
$ 7.79
|
|
|
| Granted (in dollars per share) |
0
|
|
|
| Exercised (in dollars per share) |
3.05
|
|
|
| Cancelled (in dollars per share) |
8.53
|
|
|
| Ending balance (in dollars per share) |
8.44
|
$ 7.79
|
|
| Options vested and exercisable (in dollars per share) |
$ 8.44
|
|
|
| Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life (years) |
|
|
|
| Weighted average remaining contractual term (in years) |
3 years 6 months
|
4 years 2 months 12 days
|
|
| Options vested and exercisable (in years) |
3 years 6 months
|
|
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value, beginning balance |
$ 15
|
|
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value, ending balance |
3,445
|
$ 15
|
|
| Options vested and exercisable |
$ 3,445
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNonOptionEquityInstrumentsOutstandingRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares under options that were cancelled during the reporting period as a result of occurrence of a terminating event specified in contractual agreements pertaining to the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGross number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which the current fair value of the underlying stock exceeds the exercise price of options outstanding. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options outstanding, including both vested and non-vested options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePriceRollforward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which current fair value of underlying stock exceeds exercise price of fully vested and expected to vest exercisable or convertible options. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestExercisableAggregateIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of fully vested and expected to vest exercisable options that may be converted into shares under option plan. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestExercisableNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted-average exercise price, at which grantee can acquire shares reserved for issuance, for fully vested and expected to vest exercisable or convertible options. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestExercisableWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which option holders acquired shares when converting their stock options into shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisesInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees could have acquired the underlying shares with respect to stock options that were terminated. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average per share amount at which grantees can acquire shares of common stock by exercise of options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for option awards outstanding, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for fully vested and expected to vest exercisable or convertible options, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestExercisableWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of share options (or share units) exercised during the current period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=real_TwoThousandNineteenEquityIncentivePlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Share-based Compensation Plans - Schedule of RSUs Activity (Details) - Restricted stock units
$ / shares in Units, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
Dec. 31, 2024
USD ($)
$ / shares
shares
|
|---|
| Number of Shares |
|
| Unvested, beginning balance (in shares) | shares |
12,695,176
|
| Granted (in shares) | shares |
13,109,475
|
| Vested (in shares) | shares |
6,312,012
|
| Forfeited (in shares) | shares |
(5,187,077)
|
| Unvested, ending balance (in shares) | shares |
14,305,562
|
| Restricted Stock Units Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|
| Weighted-average grant date fair value (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
$ 4.07
|
| Granted (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
3.33
|
| Vested (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
4.56
|
| Forfeited (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
3.23
|
| Weighted-average grant date fair value (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
$ 3.48
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value, unvested, beginning balance | $ |
$ 25,517
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value, unvested, Ending balance | $ |
$ 156,360
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that were forfeited during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeitedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average fair value as of the grant date of equity-based award plans other than stock (unit) option plans that were not exercised or put into effect as a result of the occurrence of a terminating event. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeituresWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of grants made during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value at grant date for nonvested equity-based awards issued during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of non-vested equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that validly exist and are outstanding as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPer share or unit weighted-average fair value of nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes share and unit options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValueRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that vested during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value as of grant date pertaining to an equity-based award plan other than a stock (or unit) option plan for which the grantee gained the right during the reporting period, by satisfying service and performance requirements, to receive or retain shares or units, other instruments, or cash in accordance with the terms of the arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIntrinsic value of nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes share and unit options.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsAggregateIntrinsicValueNonvested |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated dividend rate (a percentage of the share price) to be paid (expected dividends) to holders of the underlying shares over the option's term. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedDividendRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated measure of the maximum percentage by which a share price is expected to fluctuate during a period. Volatility also may be defined as a probability-weighted measure of the dispersion of returns about the mean. The volatility of a share price is the standard deviation of the continuously compounded rates of return on the share over a specified period. That is the same as the standard deviation of the differences in the natural logarithms of the stock prices plus dividends, if any, over the period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedVolatilityRateMaximum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated measure of the minimum percentage by which a share price is expected to fluctuate during a period. Volatility also may be defined as a probability-weighted measure of the dispersion of returns about the mean. The volatility of a share price is the standard deviation of the continuously compounded rates of return on the share over a specified period. That is the same as the standard deviation of the differences in the natural logarithms of the stock prices plus dividends, if any, over the period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedVolatilityRateMinimum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum risk-free interest rate assumption that is used in valuing an option on its own shares.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsRiskFreeInterestRateMaximum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe minimum risk-free interest rate assumption that is used in valuing an option on its own shares.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsRiskFreeInterestRateMinimum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionExpected term of award under share-based payment arrangement, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Share-based Compensation Plans - Schedule of Total Stock-based Compensation Expense (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Share-based payment arrangement, expense |
$ 29,082
|
$ 34,273
|
$ 46,138
|
| Marketing |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Share-based payment arrangement, expense |
932
|
1,550
|
2,209
|
| Operations and technology |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Share-based payment arrangement, expense |
9,930
|
12,534
|
19,822
|
| Selling, general and administrative |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Share-based payment arrangement, expense |
$ 18,220
|
$ 20,189
|
$ 24,107
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=real_MarketingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=real_OperationsAndTechnologyMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Leases - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Leases [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Operating lease costs |
$ 20,900
|
$ 22,800
|
$ 29,000
|
| Variable lease costs |
5,500
|
5,200
|
5,600
|
| Right-of-use asset impairment charge |
0
|
31,100
|
|
| Lease liability adjustment |
$ 20,883
|
26,478
|
$ 17,764
|
| Gain on debt extinguishment |
|
700
|
|
| Austin, TX, Atlanta, GA, and Miami, FL |
|
|
|
| Leases [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Lease liability adjustment |
|
7,700
|
|
| Right of use asset adjustment |
|
$ 1,400
|
|
| Minimum |
|
|
|
| Leases [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Operating lease term (in years) |
1 year
|
|
|
| Maximum |
|
|
|
| Leases [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Operating lease term (in years) |
15 years
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on termination of lease before expiration of lease term. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 40
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479092/842-20-40-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnTerminationOfLease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in obligation for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTerm of lessee's operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseTermOfContract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of single lease cost, calculated by allocation of remaining cost of lease over remaining lease term. Includes, but is not limited to, single lease cost, after impairment of right-of-use asset, calculated by amortization of remaining right-of-use asset and accretion of lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of loss from impairment of right-of-use asset from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479365/842-20-25-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseImpairmentLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of periodic reduction over lease term of carrying amount of right-of-use asset from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAssetAmortizationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of variable lease cost, excluded from lease liability, recognized when obligation for payment is incurred for finance and operating leases. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_VariableLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=real_AustinTXAtlantaGAAndMiamiFLMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Leases - Schedule of Maturities of Operating Lease Liabilities (Details)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024
USD ($)
|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| 2025 |
$ 28,761
|
| 2026 |
28,649
|
| 2027 |
24,699
|
| 2028 |
21,991
|
| 2029 |
11,615
|
| Thereafter |
8,822
|
| Total future minimum payments |
124,537
|
| Less: Imputed interest |
(15,912)
|
| Present value of operating lease liabilities |
$ 108,625
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease due after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments in excess of discounted obligation for lease payments for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityUndiscountedExcessAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionCash paid for amounts included in measurement of lease liabilities.
| Name: |
real_CashPaidForAmountsIncludedInMeasurementOfLeaseLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRight-of-Use Asset Obtained in Exchange for Operating Lease Liability, Including Re-Measurement Of Right-Of-Use Asset and Lease Liabilities
| Name: |
real_RightOfUseAssetObtainedInExchangeForOperatingLeaseLiabilityIncludingReMeasurementOfRightOfUseAssetAndLeaseLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average discount rate for operating lease calculated at point in time. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRatePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining lease term for operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on termination of lease before expiration of lease term. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 40
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479092/842-20-40-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnTerminationOfLease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe adjustment to reduce the value of existing agreements that specify the lessee's rights to use the leased property. This expense is charged when the estimates of future profits generated by the leased property are reduced. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLeasehold |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of loss from impairment of right-of-use asset from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479365/842-20-25-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseImpairmentLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of other expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses associated with a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherRestructuringCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4.b.1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482047/420-10-45-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses for special or contractual termination benefits provided to current employees involuntarily terminated under a benefit arrangement associated exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to one-time termination benefits, a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_SeveranceCosts1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Commitments and Contingencies - Additional Information (Details)
$ in Thousands |
|
|
12 Months Ended |
|
Oct. 31, 2022
plaintiff
|
Jul. 28, 2022
USD ($)
plaintiff
|
Dec. 31, 2024
USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2023
USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2022
USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2021
USD ($)
|
| Other Commitments [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Loss related to the fire |
|
|
$ 740
|
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
|
| Proceeds included within net cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
461
|
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
|
| Class action complaints filed in San Mateo County, California |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Commitments [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Litigation settlement, amount awarded to other party |
|
$ 11,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Payment period for amount awarded to other party |
|
30 days
|
|
|
|
|
| Legal settlement |
|
|
|
|
|
$ 11,000
|
| Number of plaintiffs that opted out | plaintiff |
|
1
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of plaintiffs that opted out or purchased stock | plaintiff |
2
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fire at Secaucus, New Jersey Authentication Center |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other Commitments [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Loss related to the fire |
|
|
700
|
|
|
|
| Insurance receivable |
|
|
2,500
|
|
|
|
| Aggregate advance payments received |
|
|
3,900
|
|
|
|
| Proceeds from insurers included in net cash from operating activities |
|
|
3,400
|
|
|
|
| Proceeds included within net cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
$ 500
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionLitigation Settlement, Payment Period For Amount Awarded To Other Party
| Name: |
real_LitigationSettlementPaymentPeriodForAmountAwardedToOtherParty |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLoss Contingency, Number Of Plaintiffs Opting Out
| Name: |
real_LossContingencyNumberOfPlaintiffsOptingOut |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLoss Contingency, Number Of Plaintiffs Opting Out Or Purchased Stock
| Name: |
real_LossContingencyNumberOfPlaintiffsOptingOutOrPurchasedStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount due in settlement of a claim for reimbursement from an insurance company when the Company has suffered a loss covered under an insurance policy.
| Name: |
us-gaap_InsuranceSettlementsReceivable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount awarded to other party in judgment or settlement of litigation.
| Name: |
us-gaap_LitigationSettlementAmountAwardedToOtherParty |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of litigation expense, including but not limited to legal, forensic, accounting, and investigative fees. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(6))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 220
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_LitigationSettlementExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe charge against earnings in the period for the uninsured portion of a loss from a fire, explosion, or natural disaster (hurricane, earthquake). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_LossFromCatastrophes |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherCommitmentsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow for proceeds from settlement of insurance claim, classified as investing activities. Excludes insurance settlement classified as operating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-12
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 21B
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-21B
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromInsuranceSettlementInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow for proceeds from settlement of insurance claim, classified as operating activities. Excludes insurance settlement classified as investing activities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Subparagraph (c)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-16
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 21B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-21B
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromInsuranceSettlementOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of insurance proceeds for an event or transaction that is unusual in nature or infrequent in occurrence, or both. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483613/220-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnusualOrInfrequentItemInsuranceProceeds |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_LitigationCaseAxis=real_ClassActionsComplaintFiledInSanMateoCountyCaliforniaMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LossContingenciesByNatureOfContingencyAxis=real_FireAtSecaucusNewJerseyAuthenticationCenterMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionMinimum amount of purchase arrangement in which the entity has agreed to expend funds to procure goods or services from a supplier.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PurchaseObligation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of purchase arrangement to be paid in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Includes, but is not limited to, recorded and unrecorded purchase obligations, long-term purchase commitment, and short-term purchase commitment. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach).
| Name: |
us-gaap_PurchaseObligationDueInFifthYear |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of purchase arrangement to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Includes, but is not limited to, recorded and unrecorded purchase obligations, long-term purchase commitment, and short-term purchase commitment. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach).
| Name: |
us-gaap_PurchaseObligationDueInFourthYear |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of purchase arrangement to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Includes, but is not limited to, recorded and unrecorded purchase obligations, long-term purchase commitment, and short-term purchase commitment. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach).
| Name: |
us-gaap_PurchaseObligationDueInNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of purchase arrangement to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Includes, but is not limited to, recorded and unrecorded purchase obligations, long-term purchase commitment, and short-term purchase commitment. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach).
| Name: |
us-gaap_PurchaseObligationDueInSecondYear |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of purchase arrangement to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Includes, but is not limited to, recorded and unrecorded purchase obligations, long-term purchase commitment, and short-term purchase commitment. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach).
| Name: |
us-gaap_PurchaseObligationDueInThirdYear |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current federal tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current national tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentFederalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current state and local tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current regional, territorial, and provincial tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentStateAndLocalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Income Taxes - Schedule of Reconciliation of Company's Effective Tax Rate To Statutory Federal Rate (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Tax at federal statutory rate |
$ (28,144)
|
$ (35,290)
|
$ (41,209)
|
| State taxes, net of federal effect |
(7,627)
|
(9,554)
|
(11,257)
|
| Stock-based compensation |
3,192
|
8,956
|
419
|
| Non-deductible items |
1,988
|
504
|
524
|
| Tax credits |
(169)
|
(531)
|
(563)
|
| Warrant liability fair value adjustment |
18,333
|
0
|
0
|
| Adoption of ASU 2020-06 |
0
|
0
|
(28,045)
|
| Provision to return adjustments |
(1,927)
|
9,259
|
0
|
| Valuation allowance |
14,651
|
26,501
|
80,254
|
| Other |
(21)
|
438
|
49
|
| Total provision for income taxes |
$ 276
|
$ 283
|
$ 172
|
v3.25.0.1
Income Taxes - Schedule of Components of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Deferred tax assets: |
|
|
| Net operating loss carryforwards |
$ 230,303
|
$ 232,259
|
| Fixed assets and intangibles |
10,461
|
6,364
|
| Capitalized research and development |
18,679
|
13,835
|
| Accruals and reserves |
18,685
|
12,477
|
| Stock options |
1,536
|
840
|
| Operating lease liabilities |
29,424
|
33,683
|
| Capped calls |
15,011
|
15,065
|
| Convertible debt |
0
|
2,329
|
| Tax credits |
2,738
|
2,569
|
| Other |
4,621
|
0
|
| Gross deferred tax assets |
331,458
|
319,421
|
| Less: valuation allowance |
(306,948)
|
(292,297)
|
| Total deferred tax assets |
24,510
|
27,124
|
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
|
|
| Operating lease right-of-use assets |
(21,641)
|
(24,416)
|
| Other |
(2,869)
|
(2,708)
|
| Gross deferred tax liabilities |
(24,510)
|
(27,124)
|
| Net deferred tax assets |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Assets, Capped Calls
| Name: |
real_DeferredTaxAssetsCappedCalls |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Assets, Convertible Debt
| Name: |
real_DeferredTaxAssetsConvertibleDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred tax assets fixed assets and intangible assets.
| Name: |
real_DeferredTaxAssetsFixedAssetsAndIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred tax assets operating lease liabilities.
| Name: |
real_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLeaseLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComponentsOfDeferredTaxAssetsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComponentsOfDeferredTaxLiabilitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of valuation allowance, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary difference from in-process research and development cost acquired in business combination or from joint venture formation or both. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsInProcessResearchAndDevelopment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allocation of valuation allowances and deferred tax liability, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible differences and carryforwards, without jurisdictional netting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsLiabilitiesNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of valuation allowance, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences, classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of a valuation allowances, of deferred tax assets attributable to deductible tax credit carryforwards including, but not limited to, research, foreign, general business, alternative minimum tax, and other deductible tax credit carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxCreditCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from share-based compensation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseCompensationAndBenefitsShareBasedCompensationCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from reserves and accruals. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseReservesAndAccruals |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax liability attributable to taxable temporary differences from leasing arrangements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesLeasingArrangements |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax liability attributable to taxable temporary differences classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.25.0.1
Income Taxes - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2019 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Change in valuation allowance |
$ 14,700
|
$ 26,500
|
|
|
| Unrecognized tax benefits |
2,847
|
2,678
|
|
$ 1,525
|
| Federal Tax |
|
|
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Operating loss carryforward |
861,800
|
871,300
|
|
|
| Net operating losses, subject to expiration |
157,600
|
|
|
|
| Net operating losses, not subject to expiration |
704,200
|
|
|
|
| Tax credit carryforward |
4,700
|
4,300
|
|
|
| Net operating loss not available to offset future taxable income |
|
|
$ 3,300
|
|
| State Tax |
|
|
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Operating loss carryforward |
818,600
|
817,500
|
|
|
| Tax credit carryforward |
$ 1,000
|
$ 1,000
|
|
|
| Net operating loss not available to offset future taxable income |
|
|
$ 2,100
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionNet operating loss not available to offset future taxable income.
| Name: |
real_NetOperatingLossNotAvailableToOffsetFutureTaxableIncome |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards that are not subject to expiration dates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwardsNotSubjectToExpiration |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards that are subject to expiration dates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwardsSubjectToExpiration |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating loss carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwardsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of the tax credit carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxCreditCarryforwardAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-10B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefits |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in the valuation allowance for a specified deferred tax asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowanceDeferredTaxAssetChangeInAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReconciliationOfUnrecognizedTaxBenefitsExcludingAmountsPertainingToExaminedTaxReturnsRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-10B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefits |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from tax positions that have been or will be taken in current period tax return. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIncreasesResultingFromCurrentPeriodTaxPositions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from tax positions taken in prior period tax returns. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIncreasesResultingFromPriorPeriodTaxPositions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders - Schedule of Reconciliation of Numerator and Denominator Used in Calculation of Basic and Diluted Net Loss Per Share (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Numerator |
|
|
|
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ (134,202)
|
$ (168,472)
|
$ (196,445)
|
| Denominator |
|
|
|
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding used to calculate net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic (in shares) |
107,878,366
|
101,806,000
|
95,921,246
|
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding used to calculate net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, diluted (in shares) |
107,878,366
|
101,806,000
|
95,921,246
|
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic (in dollars per share) |
$ (1.24)
|
$ (1.65)
|
$ (2.05)
|
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, diluted (in dollars per share) |
$ (1.24)
|
$ (1.65)
|
$ (2.05)
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average number Of shares outstanding basic and diluted.
| Name: |
real_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasicAndDilutedAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of tax, noncontrolling interests, dividends on preferred stock and participating securities; of income (loss) available to common shareholders. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.B)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-5
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersBasicAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders - Schedule of Anti-dilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Diluted Net Loss Per Share (Details) - shares
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Antidilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Earnings Per Share [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive securities (in shares) |
33,708,248
|
32,928,249
|
32,565,902
|
| Options to purchase common stock |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Earnings Per Share [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive securities (in shares) |
917,370
|
1,119,676
|
1,754,776
|
| Restricted stock units |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Earnings Per Share [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive securities (in shares) |
14,305,562
|
12,695,176
|
11,369,021
|
| Estimated shares issuable under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Earnings Per Share [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive securities (in shares) |
248,523
|
367,074
|
695,782
|
| Assumed conversion of the 2025 Notes and 2028 Notes |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Earnings Per Share [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive securities (in shares) |
10,342,056
|
18,746,323
|
18,746,323
|
| Warrants to purchase common stock |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Earnings Per Share [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Antidilutive securities (in shares) |
7,894,737
|
0
|
0
|
| X |
- DefinitionSecurities (including those issuable pursuant to contingent stock agreements) that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share (EPS) or earnings per unit (EPU) in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS or EPU because to do so would increase EPS or EPU amounts or decrease loss per share or unit amounts for the period presented. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareByAntidilutiveSecuritiesAxis=us-gaap_EmployeeStockOptionMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareByAntidilutiveSecuritiesAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareByAntidilutiveSecuritiesAxis=us-gaap_EmployeeStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareByAntidilutiveSecuritiesAxis=real_ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareByAntidilutiveSecuritiesAxis=us-gaap_WarrantMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost for defined contribution plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 70
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480794/715-70-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanCostRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 70
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480794/715-70-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanDisclosureLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of discretionary contributions made by an employer to a defined contribution plan.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanEmployerDiscretionaryContributionAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage employer matches of the employee's percentage contribution matched.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanEmployerMatchingContributionPercentOfMatch |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of operating segments. An operating segment is a component of an enterprise: (a) that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses (including revenues and expenses relating to transactions with other components of the same enterprise), (b) whose operating results are regularly reviewed by the enterprise's chief operating decision maker to make decisions about resources to be allocated to the segment and assess its performance, and (c) for which discrete financial information is available. An operating segment may engage in business activities for which it has yet to earn revenues, for example, start-up operations may be operating segments before earning revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_NumberOfOperatingSegments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.25.0.1
Segment Information - Schedule of Segment Information (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
$ 600,484
|
$ 549,304
|
$ 603,493
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
152,963
|
173,026
|
254,802
|
| Gross profit |
447,521
|
376,278
|
348,691
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
33,100
|
31,695
|
27,669
|
| Stock-based compensation |
29,082
|
34,273
|
46,138
|
| Restructuring |
196
|
43,462
|
896
|
| Total operating expenses |
504,016
|
542,571
|
537,854
|
| Change in fair value of warrant liability |
(68,167)
|
0
|
0
|
| Gain on extinguishment of debt |
4,177
|
0
|
0
|
| Interest income |
7,943
|
8,805
|
3,191
|
| Interest expense |
(21,384)
|
(10,701)
|
(10,472)
|
| Other income (expense), net |
0
|
0
|
171
|
| Provision for income taxes |
276
|
283
|
172
|
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
(134,202)
|
(168,472)
|
(196,445)
|
| Consignment revenue |
|
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
473,396
|
415,572
|
384,979
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
53,801
|
58,120
|
56,963
|
| Direct revenue |
|
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
64,580
|
79,160
|
158,726
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
55,809
|
74,343
|
141,661
|
| Shipping services revenue |
|
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
62,508
|
54,572
|
59,788
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
43,353
|
40,563
|
56,178
|
| Reportable Segment |
|
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenue |
600,484
|
549,304
|
603,493
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
152,963
|
173,026
|
254,802
|
| Gross profit |
447,521
|
376,278
|
348,691
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| People costs |
283,002
|
274,229
|
297,676
|
| Software and purchased services |
108,866
|
104,454
|
103,695
|
| Occupancy expense |
37,295
|
37,718
|
44,911
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
32,764
|
31,695
|
27,669
|
| Stock-based compensation |
29,082
|
34,273
|
46,138
|
| Administration and other segment expense |
12,811
|
16,740
|
16,869
|
| Restructuring |
196
|
43,462
|
896
|
| Total operating expenses |
504,016
|
542,571
|
537,854
|
| Change in fair value of warrant liability |
(68,167)
|
0
|
0
|
| Gain on extinguishment of debt |
4,177
|
0
|
0
|
| Interest income |
7,943
|
8,805
|
3,191
|
| Interest expense |
(21,384)
|
(10,701)
|
(10,472)
|
| Other income (expense), net |
0
|
0
|
171
|
| Provision for income taxes |
276
|
283
|
172
|
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
(134,202)
|
(168,472)
|
(196,445)
|
| Reportable Segment | Consignment revenue |
|
|
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
53,801
|
58,120
|
56,963
|
| Reportable Segment | Direct revenue |
|
|
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
55,809
|
74,343
|
141,661
|
| Reportable Segment | Shipping services revenue |
|
|
|
| Less: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenue |
$ 43,353
|
$ 40,563
|
$ 56,178
|
| X |
- DefinitionAdministration And Other Segment Expense
| Name: |
real_AdministrationAndOtherSegmentExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSoftware And Purchased Services Expenses
| Name: |
real_SoftwareAndPurchasedServicesExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate cost of goods produced and sold and services rendered during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfRevenue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfRevenueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense recognized in the current period that allocates the cost of tangible assets, intangible assets, or depleting assets to periods that benefit from use of the assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationDepletionAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense (income) related to adjustment to fair value of warrant liability. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 13
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 480
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481766/480-10-25-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAdjustmentOfWarrants |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDifference between the fair value of payments made and the carrying amount of debt which is extinguished prior to maturity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 50
-Section 40
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481303/470-50-40-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainsLossesOnExtinguishmentOfDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate revenue less cost of goods and services sold or operating expenses directly attributable to the revenue generation activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 9: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
| Name: |
us-gaap_GrossProfit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest expense classified as nonoperating. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpenseNonoperating |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accretion (amortization) of purchase discount (premium) of interest income on nonoperating securities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(7)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentIncomeInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of tax, noncontrolling interests, dividends on preferred stock and participating securities; of income (loss) available to common shareholders. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.B)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-5
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of net occupancy expense that may include items, such as depreciation of facilities and equipment, lease expenses, property taxes and property and casualty insurance expense. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(14)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 840
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481161/840-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OccupancyNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGenerally recurring costs associated with normal operations except for the portion of these expenses which can be clearly related to production and included in cost of sales or services. Includes selling, general and administrative expense.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of income (expense) related to nonoperating activities, classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNonoperatingIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReconciliationFromSegmentTotalsToConsolidatedAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4.b.1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482047/420-10-45-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ServiceMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ProductMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ShippingAndHandlingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementBusinessSegmentsAxis=real_ReportableSegmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.25.0.1
Subsequent Events (Details) - USD ($)
|
Feb. 10, 2025 |
Dec. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2021 |
| 2028 Convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
| Subsequent Event [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
|
$ 281,000,000
|
$ 287,500,000
|
| 2028 Convertible senior notes | Subsequent Event | Convertible Debt |
|
|
|
| Subsequent Event [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Aggregate principal amount exchanged |
$ 183,300,000
|
|
|
| 2031 Senior Notes | Subsequent Event | Convertible Debt |
|
|
|
| Subsequent Event [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Debt principal amounts |
$ 146,700,000
|
|
|
| Cash interest rate (percent) |
4.00%
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Payable-In-Cash, Interest Percentage
| Name: |
real_DebtInstrumentPayableInCashInterestPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
real_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace (par) amount of debt instrument at time of issuance. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentFaceAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace (par) amount of the original debt instrument that was repurchased.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentRepurchasedFaceAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDetail information of subsequent event by type. User is expected to use existing line items from elsewhere in the taxonomy as the primary line items for this disclosure, which is further associated with dimension and member elements pertaining to a subsequent event. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483399/855-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2028ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventTypeAxis=us-gaap_SubsequentEventMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=us-gaap_ConvertibleDebtMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=real_A2031ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
RealReal (NASDAQ:REAL)
Historical Stock Chart
From Jan 2025 to Feb 2025
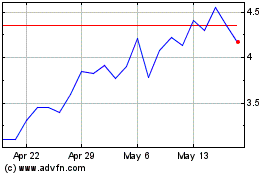
RealReal (NASDAQ:REAL)
Historical Stock Chart
From Feb 2024 to Feb 2025