Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada -- December 5, 2023 --
InvestorsHub NewsWire -- International Lithium Corp. (TSXV:
ILC) (OTCQB: ILHMF) (FSE: IAH) (the
"Company" or "ILC") is pleased to
announce a positive Preliminary Economic Assessment ("PEA") for a
proposed lithium mining operation to produce spodumene concentrate
at Raleigh Lake, 25 kilometres west of Ignace, Ontario. The PEA
relies on recent metallurgical test work (Phase 1) which indicates
that a spodumene concentrate containing 6% Li2O ("SC6")
can be produced using a simple crushing circuit and heavy liquid
separation techniques. In the Phase 1 tests lithium recoveries were
above 81% while iron oxide content remained within acceptable
limits. As originally foreshadowed, the very near proximity of
Raleigh Lake to existing service infrastructure along the
Trans-Canada Highway corridor affords significant logistical and
economic advantages to the project.
This PEA only considers spodumene concentrate, i.e. lithium, as
a revenue source. The Company continues to investigate the
potential value associated with the extraction of rubidium from the
microcline zone within the spodumene deposit.
PEA Highlights
Economics (discounted at 8% p.a., CAD$)
-
Pre-tax Cashflow = CAD$709.4 million, NPV = CAD$385.1 million,
IRR = 46.5% p.a.
-
After-tax Cashflow = CAD$634.0 million, NPV = CAD$342.9 million,
IRR = 44.3% p.a.
-
Price assumptions: CAD$3,139/tonne for 6% Li2O
concentrate (USD$2,325/tonne)
CAPEX/OPEX
-
Total pre-production capital costs: CAD$111.9 million
-
Total sustaining capital: CAD$17.5 million
-
Total life of mine ("LoM") operating costs: CAD$381 million
(including concentrate transport)
-
Average operating costs: CAD$94.38/tonne milled, CAD$993/tonne
SC6
Mining Method
-
Traditional open pit drilling and blasting followed by load and
haul
-
The plant feed production rate is proposed to be 540,000 tonnes
per year ("tpy")
-
This LoM mine plan is proposed to mine 57 million tonnes ("Mt")
of material over the mine life, which will be comprised of 4Mt of
mill feed and 53Mt of waste with an average strip ratio of
13.2:1
-
Life of mine is forecast at nine years; project duration is 11
years
Process Plant
-
The base case process plant is designed to crush 1,500 tonnes
per day ("tpd") and process 1,500 tpd in a dense media separation
("DMS") plant to produce a nominal 56,000 tpy of 6% Li2O
at 81% recovery
-
Process engineering and design were developed to a scoping level
based on the results of the SGS laboratory testing. The SGS lab
tests obtained 22.9 weight percentages of 6% Lithium Concentrate
and estimated 81% lithium recovery
-
A design factor of 10% is applied on nominal requirements to
ensure that the process equipment has enough capacity to take care
of the expected feed variation
-
Total production for LoM is 414,904 tonnes of 6% Li2O
spodumene concentrate ("SC6")
Raleigh Lake is 100% owned by ILC and there are no overriding
royalties. The Company's vision for Raleigh Lake is a low-risk,
low-impact, small-scale mining operation that can begin to provide
critical minerals necessary to fulfil Canada's Critical Mineral
Strategy in a shorter time frame than would be required for a much
larger scale, longer duration and more remotely located project.
Revenues from the mine production would continue to feed back into
exploration work to expand ILC's drive to become a significant
Critical Minerals supplier in North America.
Executive
Comment
John Wisbey, Chairman and CEO of
ILC commented:
"It is very pleasing for ILC to have delivered its first PEA at
Raleigh Lake, Ontario with highly respectable numbers of CAD$385.1
million pre-tax NPV and 46.5% IRR (post-tax CAD$342.9 million and
44.3% IRR) despite the significant fall in the lithium price this
year. This reflects, to a considerable extent, our good access to
infrastructure at Raleigh Lake, which has a very beneficial effect
on our projected costs. It should be noted that this PEA only
relates to the 600 hectare Zone 1 out of our 48,500 hectares of
claims at Raleigh Lake. It is also important to note that at this
stage these numbers only relate to the lithium at Raleigh Lake and
not to the separately declared rubidium resource. Given the high
market price of rubidium, this leaves appreciable upside.
This year's fall in the lithium price has of course depressed
these numbers versus what they would have been only a few months
ago. For example, a major Canadian lithium company produced a
feasibility report in August 2023, using a price assumption of USD$
4,699 (CAD$6,109) per tonne for 6% spodumene concentrate. Had we
applied this same number to the spreadsheet that ERM have used for
ILC's PEA, our own NPV would have been CAD$1,137 million pre-tax
and CAD$906 million post-tax. These numbers are more than 2.6 times
the NPV numbers that we are now reporting. Of course, what this
means is that, as for every mining company, there is a high level
of operational gearing in our business. It is also very important
that, when comparing different companies in the sector, investors
and analysts compare like price assumptions with like.
The omission of rubidium from this initial PEA reflects the fact
that we and our consultants need to do more work on the real size
of the rubidium market. Our measured and indicated contained tonnes
of rubidium at Raleigh Lake are 822 tonnes and the inferred 521
tonnes. The market price for >99% rubidium carbonate as at end
November 2023 was USD$ 1,159.38 per kg, meaning USD$ 1.16 million
per tonne. However, if world annual demand for rubidium is and
remains much smaller than our resource there, our ability in future
to sell at the rate we can produce would be affected, as could the
market price."
PEA Summary
Environmental Resource Management ("ERM") was retained by
International Lithium Corp. ("ILC" or the "Company") to prepare a
Preliminary Economic Assessment ("PEA") in accordance with National
Instrument 43-101 (NI 43-101) for the Raleigh Lake Project (the
"Project") located near Ignace, Ontario, Canada.
The Raleigh Lake Project is roughly 25 kilometres west of Ignace
and 235 kilometres west of Thunder Bay in the northwestern part of
Ontario within the Kenora Mining District. It is adjacent to the
Trans-Canada Highway (Hwy 17) with CN Rail, TC Energy natural gas
pipeline and Hydro One 235kV power lines transcending the Property.
It is owned 100% by International Lithium Canada Ltd., a 100% owned
subsidiary of ILC. There are no royalties or other encumbrances on
the Property.
ILC identified the opportunity at Raleigh Lake in 2016 but did
not begin actively pursuing work on the project until 2021 when an
initial test drilling campaign was conducted along with regional
lithogeochemical sampling. In 2022 the Company completed sufficient
drilling to define a maiden Mineral Resource Estimate ("MRE") with
resources reported in the measured, indicated, and inferred
categories (see below and Company press releases dated March 1 and
April 13, 2023). Upon analyzing the MRE the Company embarked upon
some initial metallurgical and economic studies that culminated in
the results presented here. It is the Company's opinion that the
results to date provide a good basis to pursue a mining operation
at Raleigh Lake and such an operation can be considered low impact
due to the existence of well-developed and utilized infrastructure
and the path to environmental permitting and eventual production
would be shorter than if the project were to be more remotely
located. The entire operation could be significantly more
sustainable than remote operations and have direct economic
benefits for the nearby and surrounding communities.
The proposed open pit mining operation would extract 57Mt of
material over the mine life, which will be comprised of 4Mt of mill
feed and 53Mt of waste with an average strip ratio of 13.2:1. The
proposed PEA level mine plan is based around work at a proposed
plant feed production rate of 540,000 tpy producing a total of
414,904 tonnes of SC6 concentrate over the mine life. The average
mill feed grade is 0.70% Li2O (Table 1).
Table 1: Summary of Base Case Cash Flow Modelling and Project
Financial Analysis.
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
Unit
|
|
Project Schedule
|
|
Overall project life
|
11
|
years
|
|
Mine life
|
9
|
years
|
|
Mining, Processing and Economic Parameters
|
|
Total mill feed
|
4.4
|
Mt
|
|
Average mill feed grade
|
0.70
|
% Li2O
|
|
Open pit mining rate
|
1,500
|
tpd
|
|
Process recovery
|
81.0
|
%
|
|
Total concentrate produced - 6% TG Li2O
|
414,904
|
T
|
|
Commodity price - 6% TG Li2O
|
$2,325
|
USD/t
|
|
Exchange Rate
|
1.35
|
CAD/USD
|
A summary of the base case capital and operating costs
calculated and used in the economic analysis exercise is shown in
Table 2 below. Total costs are based on unit cost rates per tonne
mill feed multiplied by the total tonnes of mill feed (4.37Mt).
Table 2: Summary of Base Case Capital and Operating Costs.
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
Unit
|
|
Unit Operating Costs -Production Phase
|
|
Mining
|
CAD$3.55
|
/t mined
|
|
Mining
|
CAD$40.98
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Milling
|
CAD$28.53
|
/t mill feed
|
|
G & A
|
CAD$17.74
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Concentrate transportation
|
CAD$7.13
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Total
|
CAD$94.38
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Project Operating and Sustaining Capital
Costs
|
|
Total operating costs
|
CAD$381.0 million
|
|
Total sustaining capital costs
|
CAD$17.5 million
|
|
All operating and capital costs
|
CAD$398.6 million
|
A summary of the base case revenues used in the economic
analysis exercise is shown in Table 3 and a summary of the pre- and
post-tax economic analysis results is shown in Table 4.
Table 3: Summary of Base Case Revenues.
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
|
Project Revenue, Profit and Pre/Post Tax Cash
Flows
|
|
Concentrate sales revenue
|
CAD$1,302.3 million
|
|
Concentrate transportation costs
|
CAD$31.1 million
|
|
Net operating revenue
|
CAD$1,271.2 million
|
|
Operating and sustaining capital costs
|
CAD$398.6 million
|
|
EBITDA
|
CAD$872.6 million
|
|
Payable taxes
|
CAD$75.5 million
|
|
Net profit after taxes (NPAT)
|
CAD$797.1 million
|
|
Total pre-production capital costs
|
CAD$163.1 million
|
Table 4: Summary of Pre- and Post-tax Economic Analysis
Results.
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
Unit
|
|
Economic Analysis Results
|
|
Discount Rate
|
8.0
|
% p.a.
|
|
Pre-Tax Cashflow
|
$709.5
|
CAD$ million
|
|
Pre-Tax NPV
|
$385.1
|
CAD$ million
|
|
Pre-Tax IRR
|
46.5
|
% p.a.
|
|
Post-Tax Cashflow
|
$634.0
|
CAD$ million
|
|
Post-Tax NPV
|
$342.9
|
CAD$ million
|
|
Post-Tax IRR
|
44.3
|
% p.a
|
Resource
Estimate
The MRE for the Raleigh Lake project that the current PEA study
was based on was produced by Nordmin Engineering Ltd. ("Nordmin"),
based in Thunder Bay, Ontario, who prepared an independent lithium
(spodumene-hosted) and rubidium (microcline-hosted) MRE for the
Project and Technical Report, "NI 43-101 TECHNICAL REPORT AND
MINERAL RESOURCE ESTIMATE FOR THE RALEIGH LAKE LITHIUM PROJECT,
IGNACE, ONTARIO" (the " MRE Report") consistent with the standards
and guidelines set out by the Canadian Institute of Mining,
Metallurgy and Petroleum ("CIM") and in accordance with National
Instrument 43-101 - Standards of Disclosure for Mineral
Projects.
In preparation of the MRE and MRE Report, Nordmin applied
processes that were appropriate for lithium pegmatite-style
deposits. The Report is available on SEDAR. The effective date for
the Report was April 13, 2023.
Detailed summaries of the MRE Report can be found in Company
news releases dated March 1 and April 13, 2023. A tabulated listing
of the MRE for both lithium in spodumene and rubidium in microcline
is given in Table 5 and Table 6 respectively.
Table 5: Lithium Open Pit and Underground MRE.
|
Area
|
Resource Category
|
Mass (kt)
|
Grade
|
Contained
Li (t)
|
|
Li (ppm)
|
Li2O
(%)
|
|
Open Pit
650ppm
Li Cut-off
|
Measured
|
80
|
3,887
|
0.84%
|
313
|
|
Indicated
|
2,021
|
2,919
|
0.63%
|
5,897
|
|
Measured + Indicated
|
2,101
|
2,956
|
0.64%
|
6,210
|
|
Inferred
|
3,247
|
2,595
|
0.56%
|
8,427
|
|
Underground
2,000ppm
Li Cut-off
|
Measured
|
3
|
2,560
|
0.55%
|
8
|
|
Indicated
|
189
|
3,203
|
0.69%
|
606
|
|
Measured + Indicated
|
192
|
3,192
|
0.69%
|
614
|
|
Inferred
|
655
|
3,162
|
0.68%
|
2,073
|
|
Total
|
Measured + Indicated
|
2,293
|
2,976
|
0.64%
|
6,824
|
|
Inferred
|
3,902
|
2,691
|
0.58%
|
10,499
|
Refer to notes on Mineral Resources below.
Table 6: Rubidium Open Pit and Underground MRE.
|
Area
|
Resource Category
|
Mass (kt)
|
Grade
|
Contained
Rb (t)
|
|
Rb (ppm)
|
Rb2O
(%)
|
|
Open Pit
4,000ppm
Rb Cut-off
|
Measured
|
5
|
5,412
|
0.59%
|
29
|
|
Indicated
|
90
|
6,073
|
0.66%
|
547
|
|
Measured + Indicated
|
95
|
6,036
|
0.66%
|
576
|
|
Inferred
|
18
|
3,005
|
0.33%
|
53
|
|
Underground
4,000ppm
Rb Cut-off
|
Measured
|
5
|
6,547
|
0.72%
|
35
|
|
Indicated
|
33
|
6,474
|
0.71%
|
211
|
|
Measured + Indicated
|
38
|
6,484
|
0.71%
|
246
|
|
Inferred
|
106
|
4,427
|
0.48%
|
468
|
|
Total
|
Measured + Indicated
|
133
|
6,163
|
0.67%
|
822
|
|
Inferred
|
123
|
4,224
|
0.46%
|
521
|
Refer to notes on Mineral Resources below.
Notes on Mineral Resources
-
The MRE was prepared by Christian Ballard, P.Geo., of Nordmin,
who is the Qualified Person ("QP") as defined by NI 43-101 and is
independent of ILC.
-
Mineral Resources, which are not Mineral Reserves, do not have
demonstrated economic viability. The above Inferred Mineral
Resources are subject to potential upgrade to Indicated and
Measured Mineral Resources with continued drilling. There is no
guarantee that any part of the Mineral Resources discussed herein
will be converted to another category or to a Mineral Reserve in
the future. The estimate of Mineral Resources may be materially
affected by environmental, permitting, legal, marketing, or other
relevant issues.
-
The Mineral Resources in this report were estimated using the
Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum standards on
Mineral Resources and reserves, definitions, and guidelines
prepared by the CIM standing committee on reserve definitions and
adopted by the CIM council (CIM 2014 and 2019).
-
The MRE is developed with data from diamond drill holes totaling
13,821 m.
-
The pit constrained mineral resources were defined using a
parented block model, within an optimized pit shell with average
pit slope angles of 45° in rock and 30° in overburden, a 9.8 strip
ratio (waste material: mineralized material) and a revenue factor
of 1.0. The pit optimization shells were created using
Deswik.AdvOPM software.
-
The lithium resource pit optimization parameters include: 5.5%
Li2O spodumene concentrate; US$1,800 Li2O
spodumene concentrate price; exchange rate of CAD$1.30/USD$1;
concentrate transportation and offsite charges of CAD$175/t, mining
cost of CAD$6/t, processing plus general and administration cost of
CAD$41/t; and a process recovery of 75%. Only lithium value was
used to generate the resource optimized pit shell.
-
Underground constrained mineral resources were defined within 5
x 5 x 5 m minable shape optimization wireframes. The mineable shape
optimization constraining wireframes were created using Deswik.SO
software.
-
The lithium resource underground minable shape optimization
parameters include: 5.5% Li2O spodumene concentrate;
US$1,800 Li2O spodumene concentrate price; exchange rate
of CAD 1.30/USD 1; concentrate transportation and offsite charges
of CAD$175/t, mining cost of CAD$80/t, processing plus general and
administration cost of CAD$50/t; and a process recovery of 75%.
-
The rubidium resource was constrained above market value due to
the current limited world market. A 4,000 ppm rubidium cut-off
grade was selected. The rubidium resource was excluded from (i.e.
neither taken into account nor used as a credit for) the
underground and open pit lithium resource.
-
A default density of 2.668 g/cm3 was used for the mineralized
zones.
-
All figures are rounded to reflect the relative accuracy of the
estimates; totals may not add correctly.
-
The effective date of the MRE was February 16, 2023. The
effective date for the MRE Report was April 13, 2023, and is
available on SEDAR.
Preliminary Economic
Assessment
The Project:
-
Is 100% owned by ILC and is not subject to any off-take
agreements, partnerships, or royalties.
-
Consists of 48,500 hectares (485 square kilometres) of adjoining
mineral claims.
-
Is located approximately 25 kilometres west of the Township of
Ignace, Ontario.
-
Distinguishes itself from other lithium projects in Canada by
being very well situated near to major public infrastructure,
including:

Figure 1: Major public infrastructure relative to the Raleigh
Lake project.
-
The Trans-Canada Highway, with direct access to Thunder Bay on
Lake Superior, is less than six kilometers north of the
Project;
-
The Canadian Pacific Railway, natural gas pipelines, and Hydro
One power transmission lines (115 and 230 kV) are just a few
kilometres from the Project.
Mining Methods
The mining method selected for this project will use traditional
open pit drilling and blasting followed by load and haul. The
primary mining production will be executed using hydraulic
excavators, front shovels, and/or wheel loaders as appropriate to
the terrain and depending on the major production equipment
available for the project. The material will be hauled from the
bench to the crusher, ROM stockpiles or waste dump depending on the
material type. Furthermore, ancillary equipment, such as
bulldozers, graders, and a range of vehicles, is employed to
perform functions related to maintenance, support, services, and
utilities.
The proposed PEA level mine plan is based around work at a
proposed plant feed production rate of 540,000 tpy.
This LoM mine plan is proposed to mine 57Mt of material over the
mine life, which will be comprised of 4Mt of mill feed and 53Mt of
waste with an average strip ratio of 13.2:1 (Table 7).
The open pit created for the Raleigh Lake deposit covers about
800 metres in length and 450 metres in width at the surface (Figure
2). The pit's lowest point extends to a depth of 330 metres above
sea level, while the entrance to the pit is positioned at 475
metres above sea level. The pit incorporates two entrance ramps,
with the first granting access to the southern section of the pit
and the second facilitating entry to the northern part.
The approach selected for the storage of tailings generated at
the concentrator and the waste rock from the mine will be
co-disposal. This co-disposal method involves containing filtered
tailings within designated waste rock cells. This approach offers
the benefit of enhancing overall stockpile stability and the
efficiency of water drainage. The primary goal is to guarantee
long-term physical and geochemical stability.
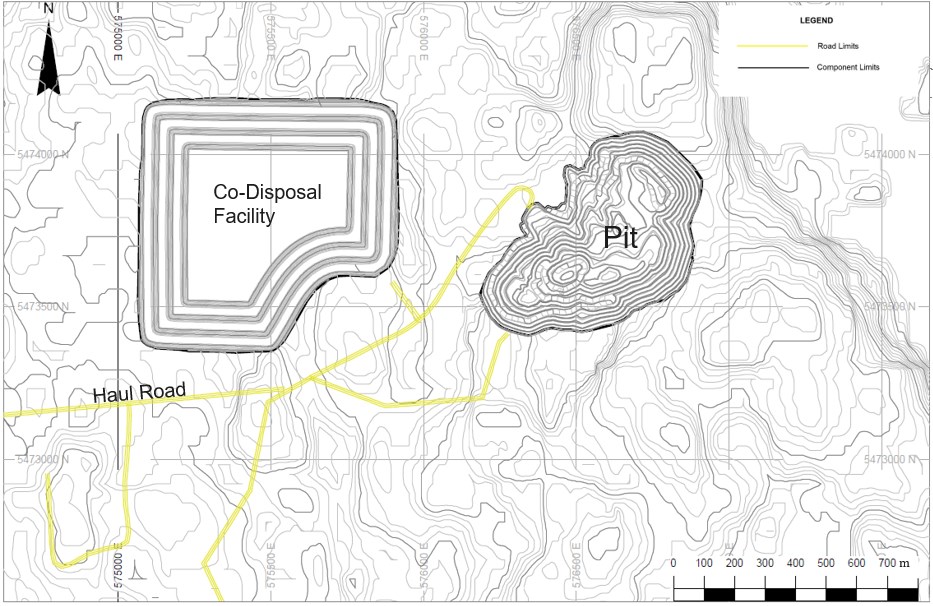
Figure 2: General arrangement of the mine site layout for
Raleigh Lake showing the final open pit (right) and co-disposal
facility (left).
Table 7: Proposed mine production schedule for Raleigh Lake.
|
Project Year
|
-1
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
Total
|
|
Mill Feed (tonnes)
|
54,037
|
324,183
|
539,881
|
540,107
|
539,899
|
539,895
|
540,305
|
539,713
|
540,312
|
208,721
|
4,367,053
|
|
Measured (tonnes)
|
0
|
0
|
5,566
|
0
|
6,338
|
27,854
|
0
|
8,927
|
23,584
|
2,725
|
74,994
|
|
Indicated (tonnes)
|
20,659
|
112,928
|
365,731
|
298,367
|
265,030
|
250,939
|
41,048
|
152,832
|
278,257
|
115,990
|
1,901,781
|
|
Inferred (tonnes)
|
33,378
|
211,254
|
168,584
|
241,741
|
268,531
|
261,103
|
499,257
|
377,954
|
238,471
|
90,005
|
2,390,278
|
|
Grade Li2O (%)
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.71
|
0.94
|
0.83
|
0.79
|
0.49
|
0.54
|
0.68
|
0.65
|
0.70
|
|
Measured (Li2O%)
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
0.30
|
0.00
|
0.63
|
1.19
|
0.00
|
1.13
|
0.78
|
0.66
|
0.92
|
|
Indicated (Li2O%)
|
0.47
|
0.51
|
0.70
|
0.93
|
0.67
|
0.75
|
0.47
|
0.63
|
0.67
|
0.58
|
0.70
|
|
Inferred (Li2O%)
|
0.79
|
0.75
|
0.75
|
0.94
|
0.99
|
0.79
|
0.49
|
0.48
|
0.68
|
0.75
|
0.70
|
|
Waste (tonnes)
|
7,572,425
|
8,641,731
|
8,930,422
|
9,147,177
|
8,855,024
|
4,651,476
|
2,979,449
|
1,530,607
|
864,285
|
509,626
|
53,682,222
|
|
Concentrate (tonnes)
|
0
|
34,194
|
51,828
|
68,321
|
60,532
|
57,726
|
35,668
|
38,988
|
49,323
|
18,324
|
414,904
|
Mineral Processing
The Raleigh Lake Orebody contains two metallurgical domains, the
lithium spodumene domain and the rubidium microcline domain. These
two separate domains represent zones in the Raleigh Lake orebody
that require customized process flowsheets to be developed for each
zone. For the lithium domain, the objective is the recovery of
spodumene to 6% Li2O concentrate grade, while the
rubidium bearing microcline domain objective is to develop a
flowsheet for extraction of the rubidium from the microcline.
The current focus was to perform mineralogy and mineral
processing testing to develop the flowsheet for the lithium zone
(Li-Head) and do a literature review to begin to investigate the
flowsheet development of the rubidium zone (Rb Head). Samples of
the lithium and rubidium domains were sent to SGS Canada in August
of 2023, to perform phase one mineralogy tests with follow-up
mineral processing testing and literature review. The Li Head and
Rb Head were collected from the Raleigh Lake Deposit and were
received by the SGS Lakefield Canada Advanced Mineralogy Facility
for mineralogy. Mineralogy was conducted to determine liberation,
mineral assemblages which would help to support and guide the
metallurgical test work.
The lithium Li head sample assayed 1.59% Li2O and
0.56% Fe2O3, while the rubidium head sample
graded 6,580 g/t Rb (equivalent to 0.72% Rb2O) with
0.12% Li2O and 0.24% Fe2O3.
The main objective of the phase one scoping level mineral
processing test investigation was to provide a preliminary
indication of the lithium beneficiation of the Li head by heavy
liquid separation (HLS).
The metallurgical target was the preparation of spodumene
concentrate grading >6.0% Li2O while maximizing
lithium recovery.
The pegmatite Li Head sample was initially stage-crushed to 100%
passing 12.7 mm, homogenized, and split into 10 kg test charges.
One of the 10 kg charges was sub-sampled 500 g for head assays and
the remaining was screened at 16 mesh to remove the -1 mm fraction
for mineralogy.
From the 10kg charges, the minus 12.7 mm +1 mm fraction was
further screened at 1/4" (6.3 mm) to generate two fractions of
-12.7 mm +6.3 mm and -6.3 mm +1 mm. The two coarse fractions, -12.7
mm +6.3 mm and -6.3 mm +1 mm, were submitted for Heavy Liquid
Separation (HLS) testing.
The HLS testing results at SG 2.85, 6.0% Li2O
concentrate grade of 14.9 weight % with global lithium recovery of
53.0% was obtained in the fraction of -12.7 mm/+6.3 mm.
The HLS Testing results interpolated to SG 2.83, a 6.0%
Li2O concentrate grade of 8.0 wt% with a global lithium
recovery of 28.5 % was obtained in the -6.3 mm/+1 mm fraction.
Combining the 6% Li2O concentrates from the two
fractions of -12.7 mm/+6.3 mm and 6.3 mm/+1 mm (highlighted in cyan
in Table 8) generated a combined global lithium recovery of
81.5%.
Above a tailings SG-cut point of 2.70, the HLS middling from
each sample contained between 1.27 - 1.69% Li2O with 2.3
- 8.2% of the global lithium distribution. Therefore, the HLS
middling can potentially be stage crushed then mixed with the minus
1 mm fines fraction to produce a flotation feed (or gravity feed)
grading 1.19 % Li2O and 0.59%
Fe2O3.
The combined HLS middling and fines fraction contained 16.2% of
the lithium distribution graded 1.19% Li2O. This is
potential feed for a roll crusher and screening, for flotation
feed, or a ultrafines DMS gravity circuit to increase the lithium
recovery.
The grade of iron in the spodumene concentrate was ~1%
Fe2O3, which is acceptable, however, this
would likely be reduced by treating the concentrate by magnetic
separation.
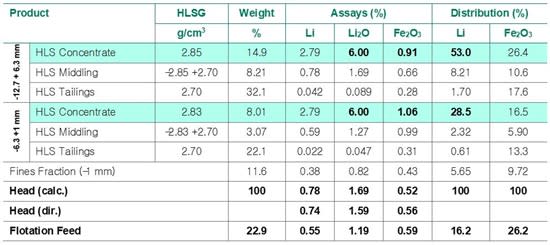
Table 8: Summary of HLS Global Mass Balance (Interpolated @ 6.0%
Li2O).
Recovery Methods
The lithium zone flowsheet development test work showed a viable
flowsheet to crush to minus 12.7 mm and screen at 1 mm, followed by
screening again at 6.3 mm to make two streams (-12.7 mm plus 6.3 mm
and -6.3 mm plus 1mm) for HLS (plant DMS). The minus 1 mm fines and
HLS middlings (DMS plant middlings) would be stored for future
processing and recovery of additional lithium, and other minerals
of interest. HLS floats (DMS floats) may also be considered for
road construction projects. The flowsheets developed for Project
are shown in Figure 3.
The base case process plant is designed to crush 1,500tpd and
process 1,500tpd in a DMS plant to produce a nominal 56,000 tpy of
6% Li2O at 81% recovery.
Engineering and design were developed to a scoping level based
on the results of the SGS laboratory testing. The SGS lab tests
obtained 22.9 weight percentages of 6% Lithium Concentrate and
estimated 81% lithium recovery.
A design factor of 10 % is applied on nominal requirements to
ensure that the process equipment has enough capacity to take care
of the expected feed variation.
Environmental
The preliminary analysis of the Project indicates it will be
subject to multiple Class Environmental Assessments under the
Ontario provincial Environmental Assessment Act. The Project is not
anticipated to trigger a federal impact assessment under the Impact
Assessment Act. Several other permits, approvals or authorizations
will be required to continue Project development beyond early
exploration, including advanced exploration through closure.
At the time of filing, environmental and socio-economic studies
have not been initiated for the Project though will be necessary to
support and inform environmental assessment(s) and permitting
applications. These studies are required to characterize the
existing environmental setting of the Project and to inform design
and/or process considerations.

Figure 3: Crushing area flowsheet (A) and DMS area flowsheet (B)
for the Raleigh Lake project.
Once Project approvals are secured, ILC will be required to
comply with any terms and conditions associated with
Project-specific authorizations issued by provincial or federal
authorities, as well as relevant environmental law and
regulation.
First Nation's and Metis communities are situated near the
Raleigh Lake property and consider the area part of their
traditional territory. ILC has identified Indigenous groups that
may have an interest in the Project and has initiated engagement.
The lands and community of the Wabigoon Lake Ojibway Nation (WLON)
are the closest to the Project, WLON has been the foremost
community for communication and involvement by Company
representatives.
Capital Costs
The Raleigh Lake Preliminary Economic Analysis Study (PEA)
involves the development of an open pit mine, the construction of
on-site processing facilities and all infrastructure required to
support those activities.
The capital cost estimate for the Raleigh Lake has been prepared
to an accuracy of + 30% / - 20% based on a 10% to 40% engineering
completion ratio to conform with the requirements for an American
Association of Cost Engineers (AACE) Class 3 Estimate.
All capital cost estimates are based on Q4 2023 Canadian Dollars
(CAD$) and an assumed US to Canadian Dollar ratio of $1 USD = $1.35
CAD.
Total pre-production capital costs will be CAD $111.9 million as
shown in Table 9, which include capitalized operating costs
incurred before the open pit mine moves into the production
phase.
Table 9: Pre-production Capital Costs.
|
Cost Centre
|
Description
|
Cost
|
|
(CAD$ million)
|
|
Direct CAPEX Costs
|
|
1000
|
Open Pit Mining
|
18.2
|
|
3000
|
Mineral Processing
|
38.5
|
|
4000
|
Power, Electrical and Instrumentation
|
3.8
|
|
5000
|
Site Infrastructure and Support Services
|
11.5
|
|
6000
|
Water Management Systems
|
2.0
|
|
7000
|
Tailings and Mine Waste Management Facilities
|
1.8
|
|
Total Direct CAPEX Costs
|
75.8
|
|
Owner and Indirect CAPEX Cost Summary
|
|
8000
|
Reclamation and Closure
|
10.0
|
|
9000
|
Indirect and Owner Costs
|
18.6
|
|
Total Indirect CAPEX Costs
|
28.6
|
|
9600
|
Contingency
|
7.6
|
|
Total Pre-Production CAPEX Costs
|
111.9
|
Total sustaining capital costs over the mine production phase
will be CAD$17.5 million (Table 10).
Table 10: Total Sustaining Capital Costs (SUSEX).
|
Cost Centre
|
Description
|
Cost
|
|
(CAD$ million)
|
|
Direct SUSEX Costs
|
|
1000
|
Open Pit Mining
|
9.1
|
|
6000
|
Water Management Systems
|
0.2
|
|
7000
|
Tailings and Mine Waste Management Facilities
|
3.8
|
|
Total Direct SUSEX Costs
|
13.0
|
|
Owner and Indirect SUSEX Cost Summary
|
|
9000
|
Indirect and Owner Costs
|
3.2
|
|
Total Indirect Costs
|
3.2
|
|
9600
|
Contingency
|
1.3
|
|
Total SUSEX
|
17.5
|
Operating Costs
The operating cost estimate (Table 11) is based on the total
amount of labour, materials and consumables that will be required
to fully execute the mining and processing plans as described
above.
The total operating costs incurred over the life of the project
are based on sufficient mill feed material being available to begin
processing plant operations in Year 1 of the overall project
schedule, which will include the processing of 54,037 tonnes of
mill feed stockpiled in Year -1 of the pre-production schedule.
Total operating costs for the operation will primarily be those
for mining and processing.
The total LoM operating cost is estimated to be CAD $412.1
million.
The total LoM operating cost of mining is estimated to be CAD
$179 million.
The total LoM operating cost of processing is estimated to be
CAD $124.6 million.
The total LoM operating cost of G&A is estimated to be CAD
$77.5 million.
The total LoM operating cost of concentrate transport is
estimated to be CAD $31 million.
Road Transportation Costs
Road transportation costs incurred over the production life of
the project assume that the final technical grade concentrate would
be transported by truck to a conversion plant located in Winnipeg
or Thunder Bay.
A total cost of CAD$75 per tonne of concentrate was assumed
based on a conservative truck haulage cost of CAD$60 per tonne and
total loading/unloading costs of CAD$15 per tonne of concentrate
produced, or CAD$7.13 per tonne of mill feed for a total LoM cost
of CAD$31.1 million.
Table 11: Unit Operating and Overall Project Costs.
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
Unit
|
|
Unit Operating Costs - Production Phase
|
|
Mining
|
CAD$3.55
|
/t mined
|
|
Mining including Waste (Strip Ratio = 13.2:1)
|
CAD$40.98
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Milling
|
CAD$28.53
|
/t mill feed
|
|
G & A
|
CAD$17.74
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Concentrate transportation
|
CAD$7.13
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Total
|
CAD$94.38
|
/t mill feed
|
|
Overall Project Costs
|
|
Total Mining Cost*
|
CAD$179 million
|
|
|
Total Milling Costs
|
CAD$124.6 million
|
|
|
Total G&A Costs
|
CAD$77.5 million
|
|
|
Total Concentrate Transport Costs
|
CAD$31 million
|
|
|
Total Operating Costs
|
CAD$412.1 million
|
|
* Does not include capitalized waste mining pre-production
Project Economics
The economic analysis of the Raleigh Lake project is based on
cost models prepared for each major component of the overall
project, which includes an open pit mine, crushing and processing
plants, supporting surface infrastructure and a waste rock /
tailings co-disposal facility.
The assumed technical grade 6% spodumene concentrate product and
cost calculations are all expressed in Canadian dollars unless
otherwise noted, with an exchange rate of 1.35 CAD/USD being used
for currency conversions.
The calculated internal rate of return (IRR) of the project does
not include potential external financing costs and assumes that all
required funding will be equity based. The net present value (NPV)
calculations assumed a discounting rate of 8% p.a.
The discounted cash flow model includes revenues, costs, taxes,
and other known factors directly related to the project but
excludes indirect factors such as financing costs, sunk costs, and
corporate obligations.
The results of the economic analysis yielded a post-tax NPV of
CAD$342.9 million, an IRR of 44.3% p.a. and a payback period of 4
years after construction begins or 2 years after the start of the
production phase of the project.
About International Lithium Corp.
International Lithium Corp. believes that the world faces a
significant turning point in the energy market's dependence on oil
and gas and in the governmental and public view of climate change.
In addition, we have seen the clear and increasingly urgent wish by
the USA and Canada to safeguard their supplies of critical battery
metals and to become more self-sufficient. Our Canadian projects
are strategic in that respect.
Our key mission in the next decade is to make money for our
shareholders from lithium and rare metals while at the same time
helping to create a greener, cleaner planet and less polluted
cities. This includes optimizing the value of our existing projects
in Canada and Ireland as well as finding, exploring and developing
projects that have the potential to become world class lithium and
rare metal deposits. We have announced separately that we regard
Zimbabwe as an important strategic target market for ILC, and we
hope to be able to make announcements over the next few weeks and
months.
A key goal has been to become a well-funded company to turn our
aspirations into reality, and following the disposal of the Mariana
project in Argentina in 2021 and the Mavis Lake project in Canada
in January 2022, the Board of the Company considers that ILC is now
well placed in that respect with a strong net cash position.
The Company's interests in various projects now consists of the
following, and in addition the Company continues to seek other
opportunities:
|
Name
|
Location
|
Area (Hectares)
|
Current Ownership Percentage
|
Future Ownership percentage if options exercised or work
carried out
|
Operator or JV Partner
|
|
Raleigh Lake
|
Ontario
|
48,500
|
100%
|
100%
|
ILC
|
|
Wolf Ridge
|
Ontario
|
5,700
|
0%
|
100%
|
ILC
|
|
Avalonia
|
Ireland
|
29,200
|
45%
|
21%
|
Ganfeng Lithium
|
|
Mavis Lake
|
Ontario
|
2,600
|
0%
|
0%
(carries an extra earn-in payment of CAD $0.7 million if resource
targets met)
|
Critical Resources Ltd (ASX:CRR)
|
|
Forgan Lake & Lucky Lake
|
Ontario
|
< 500
|
0%
|
1.5% Net Smelter Royalty
|
Ultra Lithium Inc. (TSX.V:ULT)
|
The Company's primary strategic focus at this point is on the
Raleigh Lake Project's lithium and rubidium project in Canada and
on identifying additional properties in Canada and Zimbabwe.
The Raleigh Lake Project consists of 48,500 hectares (485 square
kilometres) of mineral claims in Ontario and is ILC's most
significant project in Canada. Drilling has so far been on less
than 1,000 hectares of our claims. The exploration results there so
far, which are on only about 8% of ILC's current claims, have shown
significant quantities of rubidium and caesium in the pegmatite as
well as lithium. Raleigh Lake is 100% owned by ILC, is not subject
to any encumbrances, and is royalty free.
With the increasing demand for high tech rechargeable batteries
used in electric vehicles and electrical storage as well as
portable electronics, lithium has been designated "the new oil",
and is a key part of a green energy sustainable economy. By
positioning itself with projects with significant resource
potential and with solid strategic partners, ILC aims to be one of
the lithium and rare metals resource developers of choice for
investors and to continue to build value for its shareholders in
the '20s, the decade of battery metals.
Patrick McLaughlin, P. Geo., and Garth Liukko P.Eng., are
Qualified Persons as defined by NI 43-101 and have verified the
disclosed technical information and have reviewed and approved the
contents of this news release.
On behalf of the Company,
John Wisbey
Chairman and CEO
www.internationallithium.ca
For further information concerning this news release please
contact +1 604-449-6520.
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation
Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the
TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or
accuracy of this release.
Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking
Information
Except for statements of historical fact, this news release
or other releases contain certain "forward-looking information"
within the meaning of applicable securities law. Forward-looking
information or forward-looking statements in this or other news
releases may include: the effect of results of anticipated
production rates, the timing and/or anticipated results of drilling
on the Raleigh Lake or Wolf Ridge or Avalonia projects, the
expectation of resource estimates, preliminary economic
assessments, feasibility studies, lithium or rubidium or caesium
recoveries, modeling of capital and operating costs, results of
studies utilizing various technologies at the company's projects,
budgeted expenditures and planned exploration work on the Company's
projects, increased value of shareholder investments, and
assumptions about ethical behaviour by our joint venture partners
or third party operators of projects. Such forward-looking
information is based on assumptions and subject to a variety of
risks and uncertainties, including but not limited to those
discussed in the sections entitled "Risks" and "Forward-Looking
Statements" in the interim and annual Management's Discussion and
Analysis which are available at www.sedar.com. While
management believes that the assumptions made are reasonable, there
can be no assurance that forward-looking statements will prove to
be accurate. Should one or more of the risks, uncertainties or
other factors materialize, or should underlying assumptions prove
incorrect, actual results may vary materially from those described
in forward-looking information. Forward-looking information herein,
and all subsequent written and oral forward-looking information are
based on expectations, estimates and opinions of management on the
dates they are made that, while considered reasonable by the
Company as of the time of such statements, are subject to
significant business, economic, legislative, and competitive
uncertainties and contingencies. These estimates and assumptions
may prove to be incorrect and are expressly qualified in their
entirety by this cautionary statement. Except as required by law,
the Company assumes no obligation to update forward-looking
information should circumstances or management's estimates or
opinions change.
International Lithium (QB) (USOTC:ILHMF)
Historical Stock Chart
From Nov 2024 to Dec 2024

International Lithium (QB) (USOTC:ILHMF)
Historical Stock Chart
From Dec 2023 to Dec 2024
